AI Infrastructure 2025: Why the $7 Trillion Boom is Hitting a Hard Supply Chain Wall
Industry Risks in 2025: Physical Constraints Now Dictate AI Infrastructure Projects
The primary risk to AI infrastructure growth has shifted from early software and chip adoption challenges between 2021-2024 to a systemic crisis of physical constraints in 2025, where the availability of power, grid components, and specialized packaging now dictates the pace of deployment.
- From 2021 to 2024, industry concerns centered on GPU availability and initial data center capacity, as evidenced by a 34% year-over-year supply increase in North American markets. In 2025, this evolved into an “unprecedented” memory chip shortage expected to last beyond 2026 and a critical bottleneck in TSMC’s Co Wo S advanced packaging capacity.
- The period before 2025 saw a focus on software supply chain security, with disclosures of vulnerabilities in open-source AI/ML libraries. After January 2025, the risk became tangible and physical, with billions of dollars in AI chips reported to be sitting idle due to a global shortage of power transformers and grid equipment.
- While data center power demand was a known factor prior to 2025, it became a primary constraint afterwards. Goldman Sachs’ forecast of a 165% increase in data center power demand by 2030 highlights how energy availability has surpassed capital as the main limiting factor for hyperscalers like Microsoft and Amazon.
Investment Analysis: Capital Commitments Expose AI Supply Chain Chokepoints
Capital allocation in the AI sector has massively escalated since January 2025, shifting from broad market growth to targeted, multi-billion-dollar investments aimed at securing control over chokepoints in the physical supply chain, particularly in hardware and advanced packaging.
- Prior to 2025, investments were focused on market expansion, with the AI infrastructure market growing at a CAGR of 19.5%. The period since 2025 is defined by colossal strategic deals, such as Nvidia’s $100 billion hardware supply agreement with Open AI, designed to lock in long-term access to essential AI accelerators.
- The scale of investment demonstrates a recognition of supply-side scarcity. SK Hynix’s $13 billion investment in a new advanced chip packaging plant in January 2026 is a direct response to the HBM memory bottleneck that intensified throughout 2025.
- Corporate commitments now reflect the full-stack nature of the problem, extending beyond chips to the data centers themselves. Microsoft’s $7 billion plan for two new hyperscale data centers in Wisconsin, announced in September 2025, underscores the immense capital required to house and power the new generation of AI hardware.
AI Infrastructure Market Sees Explosive Investment
This chart illustrates the massive market growth discussed in the section, setting the stage for the escalating capital commitments into the AI supply chain post-2025.
(Source: Research Nester)
Table: Major Corporate Investments in AI Infrastructure (Post-2025)
| Company | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| SK Hynix | Jan 21, 2026 | Announced a $13 Billion investment for a new advanced chip packaging plant to increase capacity for HBM and other memory products amid a global shortage. | Why SK Hynix Is Spending $13 B to Stay Ahead in the AI Era |
| Nvidia / Groq | Dec 29, 2025 | Signed a $20 Billion licensing deal with Groq to accelerate AI inference capabilities, securing a position in a critical part of the AI compute stack. | After a Year of Blistering Growth, AI Chip Makers Get … |
| Microsoft | Sep 23, 2025 | Announced a $7 Billion investment to build two hyperscale AI data centers in Wisconsin to expand capacity for its cloud and AI services. | Microsoft: A US$7 bn Investment into Supply … |
| Nvidia / Open AI | Sep 22, 2025 | Secured a $100 Billion hardware supply deal with Open AI to provide advanced AI hardware for next-generation models, locking in a key customer and future revenue. | NVIDIA Stock Surges on $100 B Open AI and $5 B Intel Deals |
| Nvidia | Mar 20, 2025 | Stated intent to spend “hundreds of billions” to remodel its supply chain away from Asia and towards the US, a strategic response to geopolitical risk and potential tariffs. | Nvidia will spend hundreds of billions on US manufacturing … |
Partnership Analysis: Strategic Alliances Target AI Supply Chain Control
Strategic partnerships formed since 2025 are no longer about market access but about securing fundamental manufacturing capacity and technological capabilities, reflecting a shift from collaborative growth to a defensive consolidation of scarce supply chain resources.

Strategic Alliances Mitigate Critical Supply Chain Risks
This chart defines the key supply and process risks that are driving the formation of strategic partnerships to control the AI supply chain, as detailed in the section.
(Source: ScienceDirect.com)
- While partnerships existed before 2025, the agreements struck since then are of a different magnitude and strategic importance. The $100 billion deal between Nvidia and Open AI, reported in September 2025, functions as a strategic dependency, securing a massive portion of future chip supply for a single player.
- In December 2025, Nvidia’s $20 billion licensing deal with Groq to accelerate AI inference shows a strategic move to address different parts of the AI workload stack, indicating an attempt to control both training and inference hardware ecosystems.
- The $5 billion deal between Nvidia and Intel, also from September 2025, signals a potential realignment in the semiconductor world, where even competitors are forced to collaborate to navigate the complex supply chain and meet overwhelming demand.
Table: Key Strategic Partnerships in the AI Infrastructure Sector
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nvidia / Groq | Dec 29, 2025 | Nvidia’s $20 billion licensing agreement with Groq is designed to bolster its capabilities in AI inference, a high-growth segment of the market separate from AI training. | After a Year of Blistering Growth, AI Chip Makers Get … |
| Nvidia / Open AI | Sep 22, 2025 | A landmark $100 billion deal to supply Open AI with advanced AI hardware, securing a major revenue stream for Nvidia and a critical supply line for Open AI. | NVIDIA Stock Surges on $100 B Open AI and $5 B Intel Deals |
| Nvidia / Intel | Sep 22, 2025 | A $5 billion deal with Intel, indicating a potential collaboration or supply agreement between the two chip giants to navigate manufacturing constraints. | NVIDIA Stock Surges on $100 B Open AI and $5 B Intel Deals |
Geographic Shifts: Geopolitics and Energy Reshape the AI Infrastructure Map
The geographic landscape for AI infrastructure has become a primary source of risk, with the extreme concentration of advanced semiconductor manufacturing in Taiwan, a reality recognized before 2025, now forcing governments and corporations into expensive, multi-billion-dollar diversification efforts to mitigate geopolitical exposure.

North America Leads AI Infrastructure Spending
This chart provides the regional breakdown of the AI infrastructure market, supporting the section’s analysis of geographic spending dominance and diversification efforts.
(Source: Data Bridge Market Research)
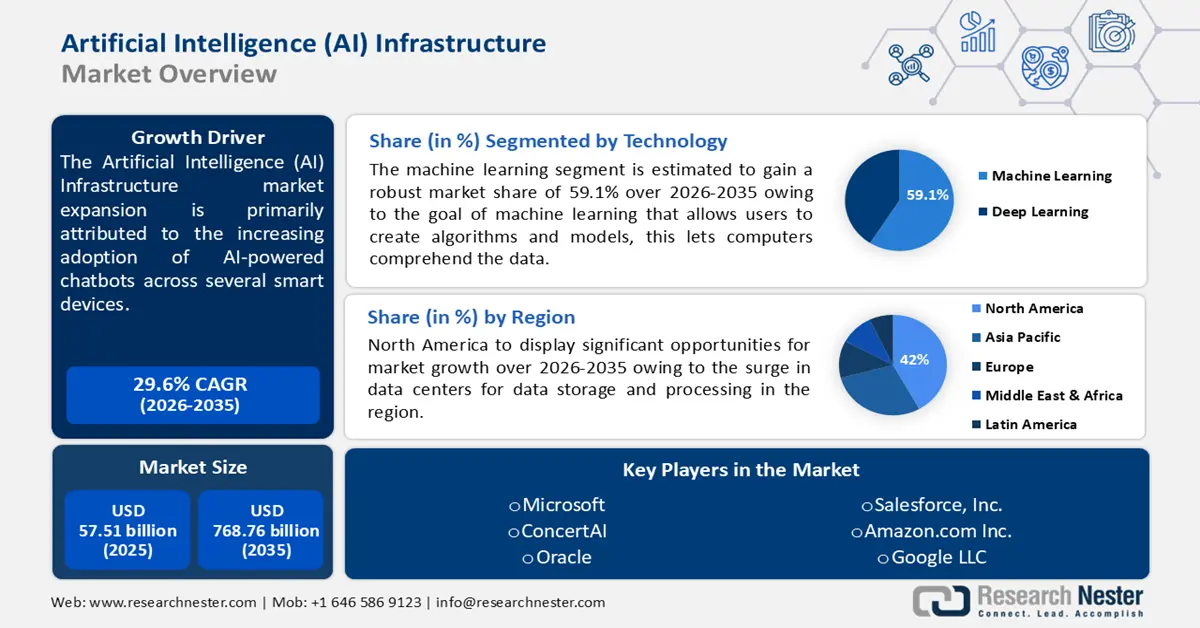
- Between 2021 and 2024, North America dominated AI infrastructure spending and held a significant market share. However, the underlying supply chain remained hyper-concentrated, with TSMC in Taiwan controlling over 90% of advanced chip manufacturing.
- Since January 2025, this concentration has become an active crisis point. Geopolitical tensions, including US export rules targeting China, have directly impacted revenue forecasts, with Nvidia facing a potential $5.5 billion hit.
- In response, policy and corporate strategy are now forcibly reshaping geography. The U.S. CHIPS Act, whose effects are materializing post-2025, aims to re-shore manufacturing, while Nvidia’s CEO stated in March 2025 a plan to spend “hundreds of billions” to move its supply chain toward the US.
- The search for power is also creating new geographic priorities. The stalling of $64 billion in data center projects in the US due to local opposition over power and water consumption shows that future growth will be dictated by regions with favorable energy and regulatory environments, not just proximity to tech hubs.
Technology Maturity: AI Software Ambition Outpaces Physical Infrastructure Reality
While AI models and software reached a high level of maturity before 2025, the technology’s physical foundation, from advanced chip packaging to power grid transformers, remains critically immature at scale, creating a stark imbalance where digital ambition is throttled by analog-world limitations.

Supply Chain Complexity Creates Physical Bottlenecks
This infographic quantifies the complexity and risk within the physical supply chain, illustrating the ‘analog-world limitations’ that the section identifies as throttling AI’s digital ambition.
(Source: Interos)
- From 2021-2024, the narrative was about the rapid maturation of Large Language Models and AI software. Since 2025, the focus has shifted to the immaturity of the supporting hardware ecosystem. Shortages in Co Wo S packaging and High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM) are now the primary technical hurdles preventing chip designers like Nvidia from meeting demand.
- The technology for generating electricity is mature, but the infrastructure to deliver it to data centers is not. The post-2025 period is defined by a global shortage of power transformers and grid equipment, a low-tech but critical component with long lead times, which is stranding high-tech AI hardware.
- Advanced cooling technologies, once a niche consideration, have become a mandatory and maturing field. The move towards liquid cooling, driven by increasing chip density and power consumption, is a direct technical response to the physical limits of air cooling that became apparent as AI data centers scaled post-2024.
SWOT Analysis: AI Infrastructure Supply Chain Constraints in 2025
The AI infrastructure market’s primary strength, its unprecedented demand, is directly creating its greatest weakness: a series of crippling supply chain bottlenecks. The opportunity to solve these physical constraints is now threatened by escalating geopolitical tensions.
- The analysis reveals that the market’s trajectory is determined by a conflict between financial capital and physical realities.
- Strengths in demand and investment are counteracted by weaknesses in manufacturing capacity and energy infrastructure.
- Opportunities lie in creating new supply chains and energy solutions, but these are directly threatened by policy risks and geographic concentration.
Table: SWOT Analysis for AI Infrastructure Growth and Supply Chain Risk
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Strong market growth (19.5% CAGR); high enterprise adoption of AI analytics (50% of supply chain orgs). | Unprecedented capital commitments ($392 B+); massive strategic deals (Nvidia/Open AI’s $100 B deal). | The market validated that financial capital is abundant and demand is exponential, shifting the focus entirely to supply-side execution. |
| Weaknesses | Initial chip shortages; delays in data center components and cooling infrastructure. | “Unprecedented” memory (HBM) shortage; critical Co Wo S packaging bottleneck at TSMC; global shortage of power transformers. | The weakness shifted from a general chip shortage to highly specific and more intractable bottlenecks in advanced packaging and basic grid equipment. |
| Opportunities | Using AI to improve supply chain visibility and efficiency (e.g., ASML pilot). | Massive adjacent markets in energy infrastructure, grid modernization, and advanced cooling; viability of alternative foundries (Intel). | The constraints themselves created new, multi-trillion-dollar market opportunities in energy, construction, and non-TSMC semiconductor manufacturing. |
| Threats | Geopolitical tensions and distributed IC manufacturing risks; software supply chain vulnerabilities. | Direct financial impact from US-China export controls (Nvidia’s $5.5 B risk); extreme geographic concentration (TSMC’s 90%); power/water activism stalling projects ($64 B in US). | Threats became acute and financially quantifiable. Geopolitical risk is no longer a hypothetical but a direct driver of corporate strategy and cost. |
Scenario Modeling: Power Grid Availability is the Critical Signal for 2025 and Beyond
Looking ahead, the most critical determinant of AI infrastructure growth will not be the size of investment or the sophistication of AI models, but the rate at which the industry can solve the power generation and grid connectivity bottleneck.

AI Data Center Power Demand Forecasted to Surge
This chart directly visualizes the core argument of the section: that surging power demand from AI is the most critical bottleneck for future growth.
(Source: Deloitte)
- If power grid investments and transformer manufacturing output accelerate, watch for hyperscalers to rapidly deploy their idle chip inventory. This would lead to a surge in compute capacity and could be signaled by utility companies announcing large-scale data center connection projects.
- If TSMC’s capacity expansion for advanced packaging and 2 nm chips faces delays, watch for Nvidia’s growth to slow and for competitors with alternate supply arrangements, like Intel Foundry Services, to gain market share. This would be confirmed by quarterly earnings reports showing constrained guidance.
- If US-China trade policies escalate, watch for further supply chain fragmentation and increased costs. A key signal would be companies like Nvidia accelerating plans to spend “hundreds of billions” to remodel supply chains away from Asia, validating a long-term, high-cost scenario.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the biggest challenge for the AI industry in 2025, according to the analysis?
The primary challenge has shifted from software adoption to a crisis of physical constraints. The pace of AI infrastructure growth is now dictated by the availability of power, grid components like transformers, and specialized manufacturing elements such as TSMC’s CoWoS advanced packaging and HBM memory chips.
Why are companies making multi-billion dollar investments in the AI supply chain?
These massive investments are no longer for general market growth but are targeted, strategic moves to secure control over critical supply chain chokepoints. For example, Nvidia’s $100 billion deal with OpenAI is designed to lock in a long-term supply of essential AI accelerators, while SK Hynix’s $13 billion plant investment directly addresses the HBM memory bottleneck.
I thought the main problem was a shortage of GPUs. What’s different now?
While demand for GPUs is high, the bottleneck has become more specific. The issue now includes the physical components needed to *produce* and *power* the GPUs at scale. This involves shortages in advanced packaging (CoWoS) and HBM memory needed to build the chips, and a critical lack of power transformers and grid infrastructure, which has left billions of dollars in AI chips sitting idle because they cannot be powered on.
What are the most critical supply chain bottlenecks currently hitting AI infrastructure?
Based on the analysis, the three most critical bottlenecks are: 1. Power & Grid Infrastructure: A global shortage of power transformers and grid equipment, unable to meet the projected 165% increase in data center demand. 2. Advanced Chip Packaging: A specific bottleneck in TSMC’s CoWoS capacity, which is essential for assembling high-performance AI processors. 3. High-Bandwidth Memory (HBM): An “unprecedented” shortage of HBM, a type of memory crucial for AI accelerators.
Besides computer chips, what other physical infrastructure is stalling AI development?
The most significant non-chip bottleneck is the electrical grid. A global shortage of basic but essential components like power transformers is preventing data centers from connecting to the power supply. Additionally, advanced cooling systems are now a critical requirement, as traditional air cooling is insufficient for the power density of new AI hardware. Finally, the physical data center buildings themselves require immense capital and time to construct and are facing opposition over power and water use.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

