AI Decision Intelligence 2026: How Predictive Operations Redefine Industrial Strategy
From Search to Synthesis: How AI is Reshaping Industrial Decision-Making at Scale
The application of Artificial Intelligence in industrial sectors has evolved from automating isolated operational tasks to embedding a predictive intelligence layer across the entire value chain. This fundamental shift moves organizations beyond using AI for simple information retrieval and toward a model where AI acts as a core system for strategic decision-making, directly influencing efficiency, innovation, and competitive positioning.
- Between 2021 and 2024, industrial AI adoption focused on discrete problems like AI-powered computer vision for quality control or basic logistics routing. The goal was task-specific efficiency.
- From 2025 to today, the strategy has matured toward creating an integrated “decision intelligence” capability. Companies are now using AI to synthesize complex, unstructured datasets to forecast future trends, anticipate machine failures, and dynamically optimize supply chains against disruption.
- This progression is validated by a 2025 Mc Kinsey Global Survey, which found that 88% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, demonstrating its mainstream integration beyond siloed experiments.
- The focus is no longer just on historical data analysis. AI models are now used for proactive decision-making, such as scheduling predictive maintenance to reduce downtime or modeling “what-if” scenarios for strategic planning, saving finance teams up to 200 hours annually.
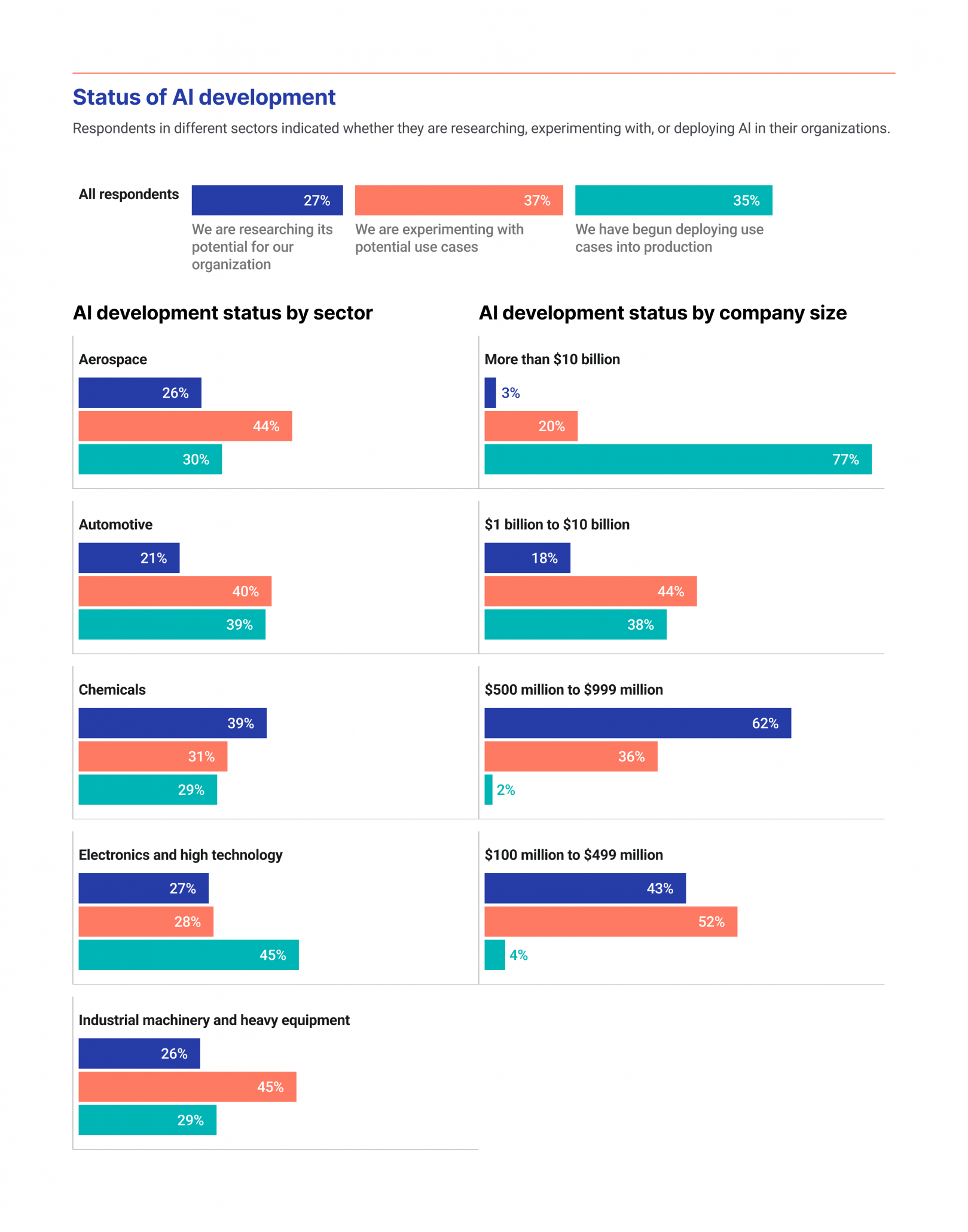
Large Firms Lead AI Production Shift
This chart shows large firms moving AI from experimentation to production, directly illustrating the section’s theme of AI reshaping decision-making at scale.
(Source: Coherent Solutions)
Investment Surges as AI’s Strategic Value Exceeds Experimental ROI
Enterprise investment has decisively pivoted from funding experimental AI pilots to executing strategic, large-scale deployments of decision intelligence platforms. This acceleration is fueled by mounting evidence of tangible returns and near-universal executive confidence in AI’s capacity to transform core business models and industrial operations.

CEO Belief in AI’s Strategic Impact Surges
This chart quantifies the massive shift in executive confidence, which the section identifies as the primary driver for increased strategic investment in AI.
(Source: PCMag)
- Global investments in AI are projected to yield a cumulative economic impact of $22.3 trillion by 2030, according to IDC, establishing the technology as a primary driver of productivity and economic growth.
- Executive conviction is a key enabler. An Accenture report reveals that 97% of executives believe generative AI will be transformational for their company and industry, with 93% reporting that their AI investments are already outperforming other strategic initiatives.
- The industrial AI market itself is expanding rapidly, with a projected size of $154 B by 2030 and a compound annual growth rate of 23%. This growth signals a sustained, long-term commitment to embedding AI into physical operations.
Table: Global AI Market and Investment Forecasts
| Forecast Provider / Market Segment | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IDC / Overall AI Market | 2030 Forecast | Projects a $22.3 Trillion cumulative global economic impact from AI solutions, underscoring its role as a foundational technology for future growth. | AI-powered success—with more than 1000 stories of … |
| Mc Kinsey / Enterprise AI Adoption | 2025 | Finds that 88% of organizations are using AI in at least one business function, confirming its transition to a mainstream enterprise technology. | The State of AI: Global Survey 2025 |
| Accenture / Generative AI | 2025 | Reports that 97% of executives believe Generative AI will transform their industry, signaling strong top-down strategic alignment on AI investment. | Reinventing Enterprise Models in the Age of Generative AI |
| Io T Analytics / Industrial AI Market | 2030 Forecast | The industrial AI market size is projected to reach $154 B, with a 23% CAGR, driven by use cases in quality, inspection, and operations. | Industrial AI market: 10 insights on how AI is transforming … |
Geographic Spotlight: How Regulatory Frameworks Shape AI Deployment
While AI development remains globally distributed, distinct regional strategies for governance are emerging, creating divergent environments for the deployment of high-impact AI decision-making systems in regulated industries. Proactive regulatory frameworks are becoming as important as technological infrastructure in determining where AI scales most effectively.

Productivity Drives Global AI Adoption
This chart’s regional breakdown of AI drivers is a perfect match for the ‘Geographic Spotlight’ theme, showing how motivations for adoption differ across the globe.
(Source: Coherent Solutions)

AI Market Forecast to Hit $3.5T
This chart’s long-term, multi-trillion-dollar market forecast directly complements the section’s table by adding another significant data point on AI’s massive economic scale.
(Source: Grand View Research)
- Between 2021 and 2024, the geographic narrative was dominated by technology development concentrated in the United States and China. The focus was on building foundational models and hardware.
- Starting in 2025, the strategic landscape has shifted to include regulatory leadership as a key differentiator. Canada is advancing its Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) to establish rules for “high-impact” AI systems, creating a predictable environment for deployment.
- Similarly, the European Union’s AI Act implements a risk-based framework that imposes strict requirements on AI used in critical sectors, forcing companies to build governance directly into their technology stacks.
- Investment is following regulatory clarity. In 2025, the growth of Canada’s venture financing market was significantly driven by AI megadeals, indicating that a clear governance structure can attract capital for AI-powered industrial solutions.
Technology Maturity: AI Evolves from Task Automation to an Integrated Decision Layer
The technology underpinning industrial AI has matured from specialized models designed for narrow tasks to integrated, generative systems that function as an enterprise-wide “decision intelligence” layer. However, this advancement has also revealed a persistent gap between technological capability and an organization’s ability to realize clear, measurable returns on investment.

AI Error Rate Plummets Below Human
This chart perfectly visualizes ‘Technology Maturity’ by showing AI performance improving dramatically over time, supporting the section’s narrative of AI evolving from simple tools to advanced systems.
(Source: Frontiers)
- The 2021-2024 period was characterized by the deployment of AI for specific, well-defined tasks like predictive maintenance alerts or image recognition for quality control. These were valuable but functionally siloed.
- From 2025 onward, the frontier has moved to “agentic AI, ” a class of systems identified by Forrester as a top emerging technology that can manage complex workflows, make decisions, and act autonomously to achieve goals in areas like supply chain logistics.
- This maturity has exposed new challenges. A Deloitte survey from early 2026 found that despite broad adoption, fewer than one-quarter of finance leaders report clear, measurable benefits from AI, indicating a critical gap between investment and realized value.
- This suggests success is now less about having the best technology and more about mastering strategic implementation. Organizations that successfully redesign processes to leverage AI as a collaborative partner are the ones reporting strong ROI.
SWOT Analysis: Strategic Outlook for AI-Driven Decision-Making
The strategic positioning of AI in the enterprise has evolved significantly, with its core strengths shifting from task efficiency to systemic intelligence. This transition presents new opportunities for value creation but also introduces organizational weaknesses and external threats related to implementation, governance, and competitive alignment.

Talent and Tech Issues Top AI Hurdles
This chart quantifies key adoption challenges, which directly correspond to the ‘Weaknesses’ and ‘Threats’ components of the SWOT analysis described in the section.
(Source: Coherent Solutions)
- Strengths have transitioned from narrow task automation to broad, predictive intelligence capabilities that can optimize entire systems.
- Weaknesses have moved from purely technical limitations to organizational hurdles, such as the difficulty in measuring ROI and the need for significant process redesign.
- Opportunities are expanding from operational optimization to the creation of entirely new, human-AI collaborative business models.
- Threats now include not just technical risks but also regulatory fragmentation and the competitive risk of being outmaneuvered by more agile, AI-native organizations.
Table: SWOT Analysis for AI in Corporate Decision-Making
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Efficiency in narrow tasks (e.g., fraud detection, credit scoring). Automation of repetitive data analysis. | System-wide predictive intelligence. High enterprise adoption (88%). Proven ROI in early-adopter functions. | AI’s value was validated, shifting its strength from isolated efficiency to strategic, predictive capability across the enterprise. |
| Weaknesses | High cost of model development. Required specialized and scarce talent. Models were often “black boxes.” | Persistent gap between investment and measurable ROI (Deloitte). Risk of reduced productivity from poorly implemented AI. | The challenge is no longer technology access but organizational change management and strategic implementation to unlock value. |
| Opportunities | Predictive maintenance in manufacturing. Supply chain and logistics optimization. Personalized marketing. | Creation of a “decision intelligence” layer. Emergence of “agentic AI” for autonomous workflows. Human-AI collaborative models. Massive economic upside ($22.3 T by 2030). | The opportunity expanded from optimizing existing processes to fundamentally redesigning how strategic decisions are made. |
| Threats | Job displacement concerns. Data privacy and security vulnerabilities. Algorithmic bias. | Regulatory fragmentation (EU AI Act, Canada AIDA). Increased market volatility from AI-driven trading (IMF). Widening competitive gap between leaders and laggards. | External threats matured from internal risks to systemic market and regulatory challenges that require strategic navigation. |
Scenario Modeling: Human-AI Collaboration is the Critical Factor for 2026
The primary determinant of competitive advantage in 2026 will not be the adoption of AI technology but an organization’s ability to master the human-AI collaborative model. Successfully integrating AI as a strategic partner, rather than a mere automation tool, is the most critical action for unlocking its transformative potential.

AI Boosts Productivity and Decision-Making
This chart identifies enhanced decision-making and productivity as top AI benefits, which are the exact outcomes the section attributes to successful human-AI collaboration.
(Source: AIPRM)
- If organizations successfully redesign workflows to leverage AI as a core partner, watch for accelerated innovation cycles and significant efficiency improvements. A key signal is the 97% of executives who, according to Accenture, already see AI as transformational.
- If companies fail to move beyond using AI for simple task automation, watch for stalled ROI and a widening competitive gap. This risk is highlighted by the Deloitte finding that few leaders can point to clear, measurable benefits, indicating a widespread implementation problem.
- A leading indicator of success is the evolution of leadership roles from tactical decision-makers to strategic interrogators of AI systems. The future belongs to leaders who can set objectives for AI agents, interpret their outputs, and make final judgments on complex, high-stakes decisions.
- These could be happening now: Companies investing heavily in upskilling their workforce and redesigning core processes around AI will capture disproportionate value, while others will struggle to justify their technology spend and risk being outmaneuvered.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main change in how industries are using AI now compared to a few years ago?
The primary change is the shift from using AI for isolated, specific tasks (like quality control checks between 2021-2024) to creating an integrated “decision intelligence” layer. Since 2025, companies are using AI to synthesize complex data for strategic purposes, such as forecasting future trends, anticipating machine failures, and dynamically optimizing entire supply chains.
Why are companies increasing their investment in AI, and is it paying off?
Investment is surging because of strong evidence of tangible returns and high executive confidence. An Accenture report found 93% of executives say their AI investments are already outperforming other strategic initiatives. Furthermore, IDC projects a massive $22.3 trillion cumulative economic impact from AI by 2030, establishing it as a primary driver of future productivity and growth.
If AI adoption is so high, why are many companies not seeing clear, measurable benefits?
The issue is less about the technology and more about strategic implementation. A 2026 Deloitte survey revealed that fewer than a quarter of finance leaders report clear, measurable benefits from their AI investments. This indicates a critical gap where companies have adopted the technology but have failed to redesign their processes and workflows to leverage AI as a collaborative partner, thus not unlocking its full value.
How are government regulations in places like Europe and Canada impacting AI development?
Proactive regulatory frameworks are shaping where AI can be deployed most effectively. The European Union’s AI Act and Canada’s Artificial Intelligence and Data Act (AIDA) are creating clear, risk-based rules for high-impact AI systems. This regulatory clarity provides a predictable environment that attracts investment, as demonstrated by the growth of Canada’s venture financing market in 2025.
What is the single most critical factor for succeeding with AI in 2026?
According to the analysis, the most critical factor is an organization’s ability to master the human-AI collaborative model. Success is no longer just about adopting AI technology but about fundamentally redesigning workflows to integrate AI as a strategic partner. Leaders who can set objectives for AI, interpret its outputs, and make final judgments on complex decisions will be the ones to unlock its transformative potential and achieve a strong ROI.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

