AI’s Energy Demand: How Corporate AI Spending Will Strain Infrastructure in 2026
Corporate AI Adoption Accelerates Energy Spending and Infrastructure Risk
Corporate AI adoption has shifted from experimental pilots to a strategic necessity, creating unprecedented demand for energy and computing infrastructure that now represents a primary risk and cost center. While the potential for competitive advantage drives investment, the escalating operational costs, particularly for energy, are a critical constraint that leaders must address before scaling.
- Between 2021 and 2024, enterprises primarily engaged in isolated AI pilots, focusing on proving technological feasibility. The main question was whether AI could solve a specific problem. By 2025, the focus has pivoted to the economic viability of scaling, with a 14 x increase in concern over implementation costs, which include the significant energy and infrastructure expenditures required for enterprise-wide deployment.
- The financial commitment is growing rapidly, with companies projected to double their AI spending to approximately 1.7% of revenues by 2026. This surge in spending directly correlates with increased demand for power-intensive data centers and cloud computing resources, making energy consumption a central component of AI’s total cost of ownership.
- Despite heavy investment, the path to value is uncertain, with recent reports indicating 95% of organizations investing in Generative AI are realizing zero return. This disparity highlights the risk of scaling infrastructure and energy consumption without a clear, quantifiable business case and a robust framework for managing costs.
- The increasing concern over data security, which tripled between 2023 and 2024, further complicates infrastructure decisions. Securing vast datasets for AI requires not only robust software but also secure, and often power-intensive, physical and cloud infrastructure, adding another layer of cost and complexity.
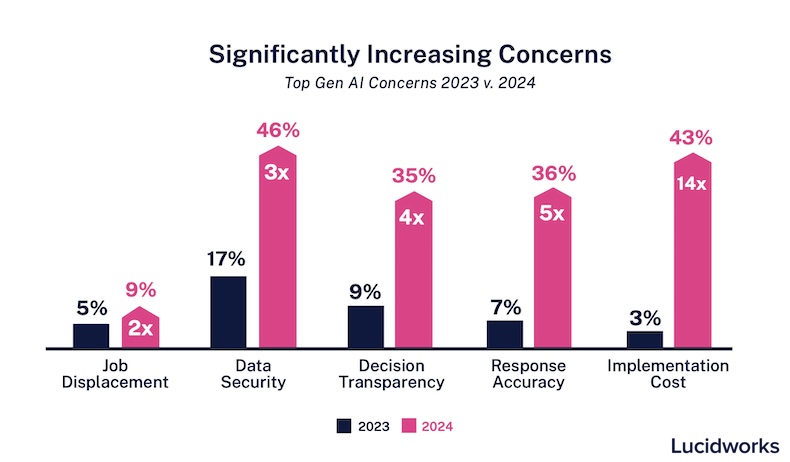
AI Implementation Cost Concerns Explode
This chart shows that concern over AI implementation costs has become a primary issue for businesses, increasing 14-fold between 2023 and 2024. This data validates the section’s premise that escalating costs are a primary risk in scaled AI adoption.
(Source: MarketingProfs)
Strategic Alliances Shape Enterprise AI Deployment and Infrastructure Access
Major technology and consulting firms are forming critical partnerships to provide the integrated solutions and infrastructure necessary for enterprises to scale AI, moving them beyond isolated proofs-of-concept. These alliances are becoming the primary mechanism for accessing the high-end computing power and specialized expertise required for large-scale AI deployment.
- In December 2025, Accenture announced multi-year partnerships with both Anthropic and Open AI. These collaborations are explicitly designed to help enterprise clients move from AI pilots to full-scale integration, leveraging the consulting power of Accenture with the advanced models of its partners, all of which run on power-intensive hyperscale infrastructure.
- The underlying infrastructure is controlled by a few key players who are also major investors. Microsoft has invested $13 billion in Open AI, while Anthropic has secured a $4 billion commitment from AWS and a $2 billion investment from Google. This consolidation concentrates control over the essential computing resources needed to train and run large models.
- These partnerships create an ecosystem where access to cutting-edge AI is intrinsically tied to the infrastructure provided by the major cloud hyperscalers. For enterprises, this means the choice of an AI partner often dictates the choice of a cloud provider, creating dependencies on their infrastructure capacity and pricing models.
Table: Key Enterprise AI Partnerships and Investments
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accenture & Anthropic | December 2025 | Multi-year partnership to co-develop industry-specific AI solutions and help enterprises scale AI. Aims to combine Anthropic’s models with Accenture’s industry expertise. | Accenture and Anthropic Launch Multi-Year Partnership… |
| Accenture & Open AI | December 2025 | Collaboration to help clients reinvent their organizations with generative AI. Focuses on accelerating enterprise reinvention by leveraging Open AI’s platform. | Open AI and Accenture Accelerate Enterprise Reinvention… |
| AWS & Anthropic | 2025 | AWS made a $4 billion investment in Anthropic, making it the primary cloud provider for Anthropic’s model training and deployment. This secures critical infrastructure for Anthropic. | 25 Practical Tips for AI Governance Leaders in 2025 |
| Google & Anthropic | 2025 | Google invested $2 billion in Anthropic, providing access to its advanced AI accelerators (TPUs) and cloud infrastructure. | 25 Practical Tips for AI Governance Leaders in 2025 |
| Microsoft & Open AI | 2025 | Microsoft’s total investment reached $13 billion, making it the exclusive cloud provider for Open AI and deeply integrating Open AI models into its Azure platform. | 25 Practical Tips for AI Governance Leaders in 2025 |
North America Leads Enterprise AI Investment and Infrastructure Strain
While AI adoption is a global imperative, North America currently dominates in strategic investment and scaled deployment, making it the primary region where the associated energy and infrastructure constraints are first emerging. The concentration of hyperscalers, AI labs, and large enterprise adopters in the U.S. establishes it as the key market for understanding the real-world impact of AI on energy systems.
- Between 2021 and 2024, AI experimentation was geographically dispersed, with companies worldwide conducting pilots. However, the strategic thinking and analysis from leading consulting firms like Mc Kinsey, BCG, and Pw C were primarily driven from a North American perspective, shaping the global corporate agenda.
- Starting in 2025, the massive capital injections into AI are heavily concentrated in the United States. Investments from U.S.-based hyperscalers like Microsoft, AWS, and Google into AI leaders like Open AI and Anthropic ensure that the most advanced, energy-intensive model development and deployment occur within their domestic data center footprints.
- Consequently, the most significant strain on energy infrastructure is appearing first in North American data center hubs. This region serves as a bellwether for the challenges other economies will face as they attempt to scale their own AI initiatives, from grid capacity constraints to the competition for renewable energy sources to power AI workloads.
Enterprise AI Moves Beyond Pilots, Exposing Scalability and Infrastructure Gaps
The maturity of enterprise AI is bifurcated; while the underlying AI models are advanced, the ability of most companies to deploy them at scale remains critically low. This gap between technological potential and practical implementation is primarily caused by inadequate infrastructure, poor data readiness, and a lack of scalable governance, which collectively prevent organizations from moving beyond the pilot stage.

Skills, Cost, and Infrastructure Hamper AI
The primary barriers to scaling AI are a lack of internal talent, budget constraints, and inadequate infrastructure limitations. This chart quantifies these challenges, which directly contribute to the scalability and infrastructure gaps described in the section.
(Source: AI Leaders Council)
- From 2021 to 2024, success was often measured by the launch of a functional pilot. In contrast, 2025 data reveals a stark reality: only 10% of companies are applying generative AI at scale, and a mere 1% consider their organizations to be at AI maturity, according to reports from BCG and Mc Kinsey.
- This “scaling gap” is not due to a lack of technology but rather a failure in foundational readiness. A primary challenge is the lack of a modern technology stack and robust data management. Without a clean, accessible data foundation and the infrastructure to process it, even the most powerful AI models will fail to deliver value.
- The high failure rate, with 95% of enterprises reportedly seeing zero return from Gen AI investments, is a direct consequence of this implementation gap. Companies are investing in advanced AI tools without concurrently investing in the data governance, infrastructure upgrades, and organizational change required to support them at an enterprise level.
SWOT Analysis: Navigating AI’s Energy Demands and Infrastructure Challenges
The strategic landscape for scaling AI is defined by the immense potential for competitive advantage, which is directly threatened by rising infrastructure costs, data security risks, and a severe talent shortage. Successfully navigating this environment requires leaders to balance the pursuit of high ROI with a disciplined approach to managing the total cost of ownership, particularly the escalating energy and computing expenditures.

Leadership Knowledge Gap Is Top AI Risk
A significant risk in AI deployment is the lack of internal knowledge and capabilities, followed closely by data privacy concerns. This aligns with the SWOT analysis, highlighting a key internal weakness (talent) and external threat (data risk) that organizations must address.
(Source: Corporate Board Member)
- Strengths are centered on validated financial returns for successful adopters, while Weaknesses highlight the pervasive internal barriers that prevent most firms from achieving those returns.
- Opportunities lie in leveraging external partnerships and new AI-driven business models, but these are constrained by Threats from rising costs and security vulnerabilities.
Table: SWOT Analysis for Scaling Enterprise AI
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Theoretical ROI and productivity gains were the primary drivers. Focus was on competitive potential and innovation. | Demonstrated ROI of $3.50 for every $1 spent for successful adopters. AI leaders show 1.5 x faster revenue growth and 53% higher gross profit. | The financial benefits of successful AI adoption are no longer theoretical but have been validated by leading firms, justifying larger investments for those who can execute. |
| Weaknesses | Concerns centered on the lack of skilled talent and the difficulty of identifying clear use cases for AI. | A 95% failure rate in realizing ROI from Gen AI. Only 1% of companies believe they are at AI maturity. Pervasive challenges with data quality and integrating with legacy systems. | The “pilot purgatory” problem was confirmed and quantified. The primary barriers shifted from ideation to the practical, internal challenges of data readiness and technical integration. |
| Opportunities | Focus on optimizing existing processes and improving internal efficiency. Partnerships were largely experimental. | Creation of new AI-driven business models. Strategic partnerships with hyperscalers (AWS, Google, Microsoft) to access infrastructure and expertise. | The strategic focus broadened from cost-cutting to fundamental business model innovation. The ecosystem consolidated, making partnerships a necessity, not an option. |
| Threats | Risks were perceived as abstract, including job displacement and long-term ethical concerns. | Concrete financial and operational risks dominate. A 14 x increase in concern over implementation costs and a 3 x rise in data security fears. Rising energy costs become a critical TCO factor. | Abstract long-term risks have been replaced by immediate, quantifiable threats to the P&L. Infrastructure and energy costs are now a primary boardroom concern for AI adoption. |
2026 Outlook: Monitoring AI’s Energy Consumption and ROI Realization
If enterprise AI spending continues its trajectory toward 1.7% of revenue by 2026, leaders must watch for early signals of whether this investment translates into measurable ROI or becomes a significant cost center driven by unmanaged energy and infrastructure expenditures. The key is to track whether the immense capital outlay for computing power is generating a commensurate return in productivity and revenue.

How to Measure AI’s Productivity Impact
As enterprises invest in AI, they must monitor its return, and this chart details the key metrics tech giants use to measure AI’s impact. These KPIs provide a concrete framework for tracking the ROI realization discussed in the 2026 outlook.
(Source: The Pragmatic Engineer)
- If enterprise AI adoption scales successfully, then watch for hyperscalers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud to announce accelerated capital expenditure plans for new data center construction in their quarterly earnings calls. This would be a direct signal that AI workload demand is driving a new wave of energy infrastructure build-out.
- These could be happening: Companies that successfully link AI investment to quantifiable business outcomes will begin to report higher margins and faster growth, creating a clear “Gen AI Divide” as predicted. Conversely, laggards will face pressure as their unmanaged AI-related operating expenses, including soaring cloud and energy bills, erode profitability, validating the 95% “zero return” statistic.
- Look for strategic partnerships between AI leaders (e.g., Open AI, Anthropic) and energy companies or independent power producers. Such deals would signal a proactive move to secure long-term, low-cost energy supply, confirming that energy has become a primary strategic constraint for the growth of artificial intelligence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is AI’s energy consumption suddenly a major concern for businesses in 2025-2026?
The concern has grown because corporations are moving from small, experimental AI pilots to large, enterprise-wide deployments. This scaling up requires massive, power-intensive data centers and cloud computing resources, making energy a primary operational cost and a significant risk to infrastructure, a concern that has increased 14-fold since the pilot phase.
The article mentions a 95% failure rate for Gen AI investments. What is the main reason for this?
The high failure rate is not due to the AI technology itself but a ‘scaling gap.’ Most companies (90%) have not applied generative AI at scale because they lack the foundational readiness. The primary causes are inadequate infrastructure, poor data quality and management, and the lack of a modern technology stack needed to support AI across an entire organization.
How do partnerships with companies like Microsoft, AWS, and Google affect a company’s ability to use AI?
These technology giants are the primary investors in leading AI labs like OpenAI and Anthropic, investing billions to become their exclusive or primary cloud providers. This creates an ecosystem where access to cutting-edge AI models is intrinsically tied to using the infrastructure of a specific hyperscaler (e.g., OpenAI on Microsoft Azure). For businesses, the choice of an AI partner now often dictates their choice of cloud provider, creating dependency on their infrastructure and pricing.
How much are companies expected to spend on AI by 2026, and what is driving this cost?
By 2026, companies are projected to double their AI spending to approximately 1.7% of their total revenues. This surge is directly correlated with the increased demand for power-intensive data centers and cloud computing resources, making energy consumption a central and escalating component of AI’s total cost of ownership.
What is one key indicator to watch for in 2026 that will signal AI is severely straining the energy grid?
A key indicator would be strategic partnerships forming between major AI companies (like OpenAI or Anthropic) and energy producers. Such deals would be a proactive move to secure long-term, low-cost power, confirming that energy supply has become a primary strategic constraint on AI’s growth and scalability.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

