AI Data Center Power in 2026: Why Renewables and Gas Form an Unbreakable Hybrid Grid
AI’s Power Demand: How Hybrid Energy Models Became the Industry Standard for Data Centers
The enormous, 24/7 power requirement of artificial intelligence has forced a strategic pivot from purely renewable energy procurement to a hybrid model that combines low-cost renewables with firm power, primarily natural gas. This pragmatic shift is a direct response to the inadequacy of intermittent-only sources to meet the gigawatt-scale, high-reliability needs of AI data centers, a reality that became undeniable between 2025 and today, contrasting sharply with the aspirational clean energy goals of the 2021-2024 period.
- Between 2021 and 2024, the primary strategy for hyperscalers was securing large-scale renewable Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) to meet 100% clean energy targets, exemplified by the landmark 10.5 GW renewable energy deal between Microsoft and Brookfield in May 2024.
- From 2025 onward, the staggering scale of AI’s projected demand, with forecasts suggesting data centers could consume up to 12% of U.S. electricity by 2030, made it clear that renewables alone could not ensure the required 99.999% uptime.
- This realization drove the adoption of a hybrid approach, validated by Chevron’s partnership in January 2025 to power AI data centers with U.S. natural gas, explicitly positioning fossil fuels as a necessary reliability layer.
- Further evidence of this portfolio strategy emerged in August 2025 when Equinix announced collaborations with five different next-generation nuclear and fuel cell providers, demonstrating a deliberate diversification to secure firm, low-carbon power and mitigate reliance on any single source.
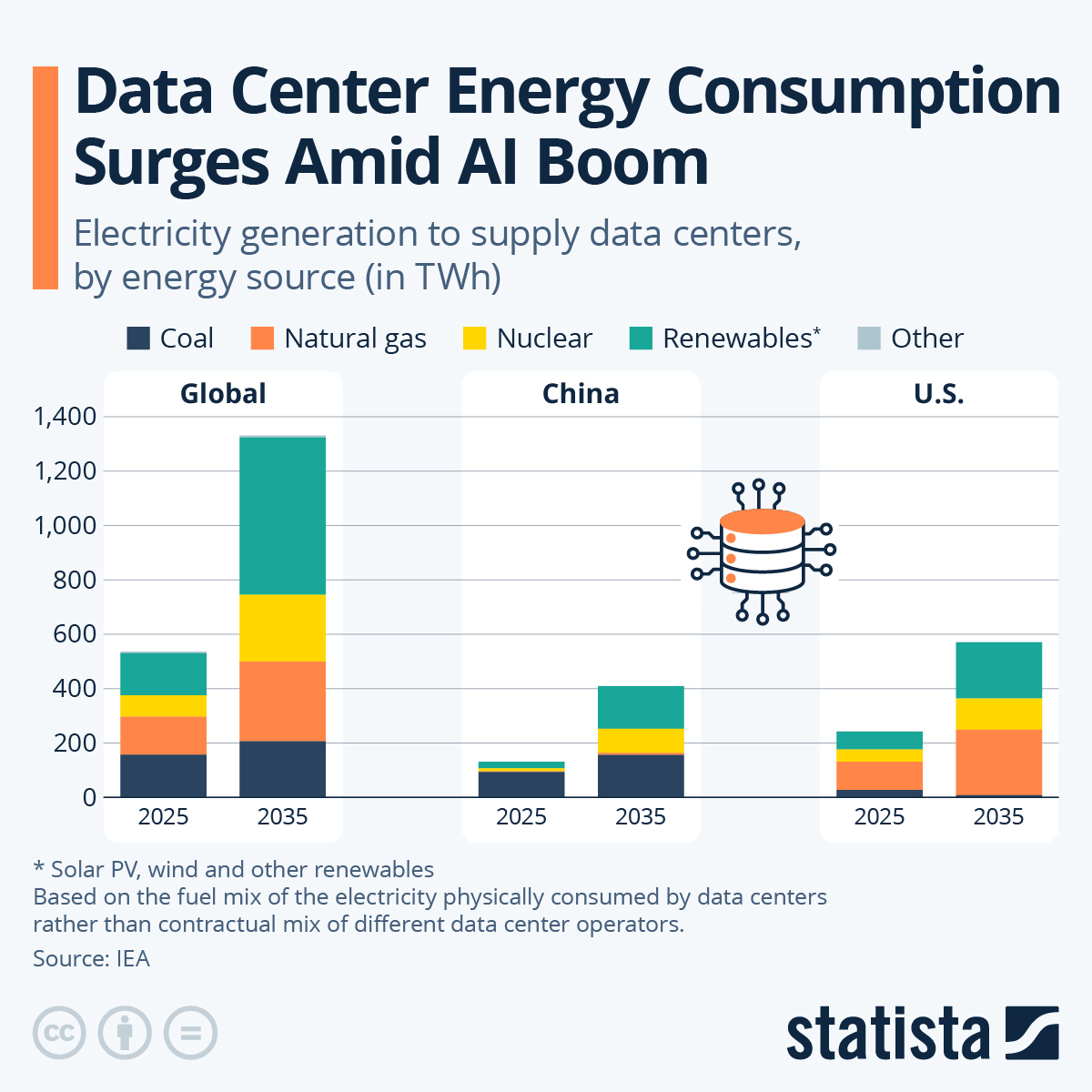
AI Boom to Double Data Center Energy Demand
This chart shows global data center demand more than doubling by 2035, directly illustrating the section’s premise of an “enormous” power requirement. It also projects an increase in firm power like natural gas, supporting the pivot to a hybrid model.
(Source: Statista)
AI Energy Investments: Capital Flows into Hybrid Power Infrastructure
Investment patterns have fundamentally shifted, with capital now targeting integrated, multi-source energy ecosystems rather than just standalone renewable projects. This trend reflects a sophisticated understanding that supporting AI growth requires massive investments in a balanced portfolio of generation assets, including renewables for bulk energy and firm power sources for reliability.
- The market’s direction is confirmed by the October 2024 formation of a $50 billion strategic partnership between KKR and Energy Capital Partners (ECP), specifically designed to fund both data centers and the diverse power generation infrastructure they require.
- In December 2024, Google, Intersect Power, and TPG Rise Climate announced a targeted $20 billion investment to co-locate new data centers with new clean energy generation, signaling a move towards physically integrated power solutions to improve efficiency and bypass grid constraints.
- Vantage Data Centers’ $9.2 billion equity investment in June 2024, explicitly driven by AI demand, necessitates securing vast and varied power contracts to support the expansion of its hyperscale campuses.
- While the hybrid model dominates, large-scale renewable deals continue where resources are abundant, as shown by Microsoft’s $6 billion investment in September 2025 for renewable-powered AI infrastructure in Norway, leveraging the region’s hydro-rich grid.
Table: Key Investments in AI and Energy Infrastructure (2024-2025)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google, Intersect Power, TPG Rise Climate | Dec 2024 | Targeted $20 billion partnership to co-locate gigawatts of new data center capacity with dedicated renewable power generation across the US. The strategy aims to directly link power supply with demand. | Intersect Power |
| Crusoe Energy | Dec 2024 | Raised $600 million in a Series D funding round to expand its infrastructure that powers data centers using stranded energy sources like flared natural gas, reaching a $2.8 billion valuation. | Carbon Credits |
| KKR, Energy Capital Partners (ECP) | Oct 2024 | Formed a $50 billion strategic partnership to support AI growth through large-scale investments in both data centers and the power infrastructure required to support them. | ECP |
| Microsoft | Sep 2025 | Announced a $6 billion investment to develop renewable-powered AI data infrastructure in Norway, leveraging the nation’s abundant clean energy resources. | ESG News |
| Vantage Data Centers | Jun 2024 | Completed a $9.2 billion equity investment led by Digital Bridge and Silver Lake to fund the expansion of its data center campuses, driven by unprecedented cloud and AI demand. | Vantage Data Centers |
Strategic Alliances: Powering AI Data Centers with Hybrid Energy Partnerships
Corporate partnerships have matured from simple renewable energy procurement to complex alliances that build integrated power ecosystems. This evolution sees tech giants, energy producers, and infrastructure investors collaborating to create reliable, multi-source power solutions tailored for AI, moving far beyond the standard PPA model prevalent before 2025.
- The landmark strategic partnership between Google Cloud and Next Era Energy in December 2025 to jointly develop new gigawatt-scale data center campuses with integrated clean power generation marks a new era of deep, systemic collaboration.
- The entry of fossil fuel majors into the AI power ecosystem was solidified by Chevron’s January 2025 partnership to supply natural gas for data centers, confirming its role as a key reliability partner for the tech industry.
- Demonstrating a clear strategy to build a diversified portfolio of firm, low-carbon power, Equinix announced collaborations in August 2025 with five different providers of next-generation nuclear and fuel cell technologies.
- Hyperscalers continue to use large-scale PPAs to secure bulk renewable energy, as seen in Meta’s June 2025 agreement with Invenergy for nearly 800 MW of renewable energy to support its data center operations and clean energy goals.
Table: Key Partnerships for AI Data Center Power (2025)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meta, Google, Next Era | Dec 2025 | Team up for long-term agreements to power data centers and enhance U.S. grid reliability, indicating cross-industry collaboration to address systemic power challenges. | Carbon Credits |
| Google Cloud, Next Era Energy | Dec 2025 | Announced a landmark strategic partnership to jointly develop new data center campuses with integrated clean power generation, a shift from procurement to co-development. | Next Era Energy |
| Equinix, Various Energy Providers | Aug 2025 | Collaborated with five leading alternative energy providers, including nuclear and fuel cell companies, to secure reliable, on-site power for AI-ready data center growth. | Equinix |
| Meta, Invenergy | Jun 2025 | Signed an agreement for nearly 800 MW of renewable energy to provide near-term power for data center growth while supporting corporate clean energy goals. | Invenergy |
| Chevron, Undisclosed Partner | Jan 2025 | Formed a partnership to power AI data centers with U.S. natural gas, explicitly positioning gas as a reliability solution for the tech industry’s power-intensive operations. | World Oil |
Geographic Hotspots: Where Hybrid Power Models for AI are Taking Hold
The global search for abundant, reliable, and cost-effective power is reshaping the geographic map of data center development. While established hubs struggled with grid constraints during the 2021-2024 period, the post-2025 era is defined by a strategic expansion into regions that offer a favorable mix of renewable resources, available natural gas, and supportive regulatory environments, a trend unaffected by political rhetoric favoring one energy source over another.

US Power Pipeline Reveals Geographic Hotspots
This map of planned US power plants directly illustrates the “geographic map of data center development” discussed in the section. It visualizes where new energy projects are being developed to meet demand.
(Source: Bloomberg.com)
- Before 2025, increasing grid saturation in traditional data center markets like Northern Virginia highlighted the urgent need for geographic diversification to support future growth.
- The United States remains the primary theater for this expansion, with major partnerships like the Google/Intersect Power deal targeting a nationwide build-out of co-located data center and clean energy facilities.
- International expansion is highly strategic, exemplified by Microsoft’s $6 billion investment in Norway. This move leverages the country’s high concentration of renewable energy and cool climate to power AI infrastructure efficiently and sustainably.
- Regions with strong resource diversity, like Texas, are becoming key hubs. Google’s February 2026 solar PPA with Total Energies to power its Texas data centers leverages the state’s abundant solar potential and competitive energy market.
Powering AI: How Mature Energy Tech is Meeting 2026’s Unprecedented Demand
The immediate, gigawatt-scale power needs of AI are being met by commercially mature technologies, cementing a pragmatic, multi-source energy strategy. While utility-scale solar and wind were the focus between 2021-2024 due to their low cost, the post-2025 period is characterized by the integration of natural gas for reliability, alongside strategic validation of next-generation technologies like SMRs and advanced fuel cells for long-term, carbon-free baseload power.

New US Power Mix Mirrors Hybrid Strategy
This chart’s breakdown of proposed power capacity, showing renewables alongside a significant 13% for natural gas, perfectly illustrates the “multi-source energy strategy” of combining mature technologies.
(Source: Bloomberg.com)
- In the 2021-2024 timeframe, the primary technology play was scaling mature utility-scale solar and wind projects, whose cost-competitiveness made them the default choice for corporate PPAs.
- From 2025 onward, the technology mix has broadened out of necessity. Natural gas, a fully mature and dispatchable technology, is now widely accepted as a critical reliability layer to bridge power gaps in the near term.
- Next-generation nuclear, particularly Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), is advancing from research to strategic validation. Deals by Meta and Google with providers like Oklo and Terra Power confirm the industry’s intent to use SMRs as a future commercial source of 24/7 carbon-free power.
- On-site generation technologies are also gaining traction. Bloom Energy’s fuel cells are moving from a niche application to a strategic tool for bypassing grid interconnection queues, validated by a $5 billion partnership announced in October 2025 to power AI data centers.
SWOT Analysis: The Hybrid Energy Strategy for AI Data Centers
The hybrid energy model for AI data centers derives its strength from providing unparalleled reliability but exposes operators to fuel price volatility and carbon emissions. The primary opportunity lies in replacing natural gas with next-generation clean firm power, while the greatest threat comes from persistent regulatory and grid interconnection delays that choke the deployment of all energy types.

Cost Analysis Validates Hybrid Energy Model
This chart supports the SWOT analysis by quantifying a key “Strength”: the low cost of solar and wind. It shows the economic rationale for incorporating renewables into the hybrid model.
(Source: Bloomberg.com)
- Strengths: The model ensures the 24/7 reliability that AI requires by combining low-cost renewables with dispatchable firm power.
- Weaknesses: The reliance on natural gas introduces fuel price volatility and conflicts with long-term corporate net-zero commitments.
- Opportunities: Active investment in Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), geothermal, and hydrogen fuel cells creates a clear path to replace the natural gas bridge with carbon-free firm power.
- Threats: Systemic delays in permitting and grid interconnection for all energy projects represent the single largest impediment to meeting AI’s power demand.
Table: SWOT Analysis for the AI Data Center Hybrid Energy Model
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2023 | 2024 – 2025 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Low Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) from solar and wind PPAs. | Ensures 24/7/365 power reliability by pairing intermittent renewables with firm generation (natural gas, nuclear). | The market shifted focus from pure cost optimization to a balanced strategy of cost and absolute reliability to meet AI’s stringent uptime requirements. |
| Weaknesses | Intermittency of renewables created reliability gaps; grid constraints in key hubs like Northern Virginia. | Dependence on natural gas introduces fuel price volatility and carbon emissions, complicating corporate ESG goals. | The sheer scale of AI power demand made the intermittency of a pure-renewable strategy an unacceptable business risk, forcing the inclusion of natural gas. |
| Opportunities | Falling costs of battery energy storage systems (BESS) to help manage intermittency. | Strategic investments and partnerships in next-generation clean firm power like SMRs (Meta, Oklo) and fuel cells (Equinix) to replace gas in the long term. | The market validated the need for a long-term, carbon-free replacement for natural gas, catalyzing partnerships with next-generation nuclear and fuel cell developers. |
| Threats | Supply chain disruptions for solar panels and wind turbines. | Crippling delays in grid interconnection queues and slow permitting for all energy infrastructure, regardless of fuel type. | The primary bottleneck shifted from component manufacturing to the fundamental inability of grid infrastructure and regulatory processes to keep pace with demand growth. |
2026 Outlook: Grid Constraints Will Force Deeper Energy-Tech Integration
If grid interconnection queues and project permitting delays continue to impede the development of new large-scale power generation, the critical signal to watch in 2026 will be an accelerated push toward on-site power and co-located data center and power plant projects. This trend represents a strategic move by tech companies to internalize their energy supply chain and de-risk AI expansion from public infrastructure failures.
- If this happens: Grid development continues to lag behind the exponential growth in AI power demand.
- Watch this: An increase in strategic partnerships that mirror the Google and Intersect Power model, where data centers and dedicated power plants are developed as a single, integrated project to bypass grid availability issues.
- Watch this: A surge in the deployment of on-site power solutions, such as Bloom Energy’s fuel cells, as data center operators seek to secure power generation capabilities independent of strained local grids.
- These could be happening: Technology companies may escalate their role in the energy sector by taking direct equity in power generation assets or acquiring energy development firms, as foreshadowed by the deep integration seen in the Google Cloud and Next Era Energy partnership.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are AI data centers moving away from a 100% renewables strategy?
AI data centers require constant, 24/7 power with extremely high reliability (99.999% uptime). The article explains that from 2025 onward, it became clear that intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind alone could not guarantee this level of reliability for the gigawatt-scale needs of AI. This forced a strategic pivot to a hybrid model that includes firm power for continuous operation.
What is the “hybrid energy model” and what does it consist of?
The hybrid energy model is a strategy that combines low-cost bulk energy from renewable sources (like large-scale solar and wind PPAs) with dispatchable, firm power sources to ensure reliability. According to the article, this firm power layer is currently dominated by natural gas, but companies are actively investing in future carbon-free firm options like next-generation nuclear (SMRs) and advanced fuel cells.
If tech companies have clean energy goals, why are they partnering with natural gas producers like Chevron?
The use of natural gas is a pragmatic response to the immediate, massive, and non-negotiable power reliability demands of AI. The article positions natural gas as a necessary “reliability layer” or “bridge fuel” to cover the gaps left by intermittent renewables. While this creates tension with long-term ESG goals, the business risk of power outages for AI operations is considered too high to rely solely on today’s renewable technology.
What is the biggest challenge preventing the expansion of power for AI?
According to the article’s SWOT analysis and 2026 outlook, the single largest threat is not a lack of energy technology but systemic infrastructure and regulatory bottlenecks. Specifically, “crippling delays in grid interconnection queues and slow permitting for all energy infrastructure” are identified as the primary impediment to building out the power generation needed to meet AI’s demand.
How are investment strategies changing to meet AI’s power demand?
Investment has shifted from funding standalone renewable projects to financing integrated, multi-source energy ecosystems. As highlighted by the KKR and ECP partnership, capital is now flowing into balanced portfolios that include both data centers and the diverse power generation required to support them. This includes co-locating data centers with power plants (like the Google/Intersect Power deal) to bypass grid constraints and ensure a direct, reliable energy supply.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

