Amogy Ammonia-to-Power Analysis: Commercial Scale and Strategic Partnerships in 2025
Amogy’s Commercial Projects Accelerate Ammonia-to-Power Adoption in 2025
In 2025, Amogy transitioned from technology demonstration to commercial execution, securing manufacturing and deployment agreements that shift its focus from proving viability to enabling industrial-scale production and market entry.
- Between 2021 and 2024, Amogy focused on progressively scaling its technology through world-first demonstrations, advancing from a 100 k W tractor (May 2022) and a 300 k W semi-truck (January 2023) to a 1 MW system on the NH 3 Kraken tugboat (September 2024). These projects successfully validated the technical feasibility of its integrated ammonia cracker and fuel cell system across different power outputs.
- The strategy shifted in 2025 with the establishment of concrete commercial pathways, highlighted by a multi-year manufacturing partnership with Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) in November 2025. This agreement outsources production of Amogy’s ammonia-to-power systems to a dedicated facility in South Korea, providing scalable manufacturing capacity without major capital expenditure.
- The company’s commercial focus is anchored by the Pohang distributed power project, announced in April 2025. This collaboration with GS E&C and HD Hyundai Infracore will deploy a 1 MW pilot system by 2026, with a clear roadmap to scale to 40 MW, marking Amogy’s entry into the stationary power market.
- Further diversification in 2025 includes partnerships to pilot solutions for floating power and data centers (Kinetics), large-scale hydrogen production (JGC Holdings), and industrial facilities in Taiwan (Green Harvest). This broad application scope demonstrates the technology’s adaptability beyond its initial maritime focus.
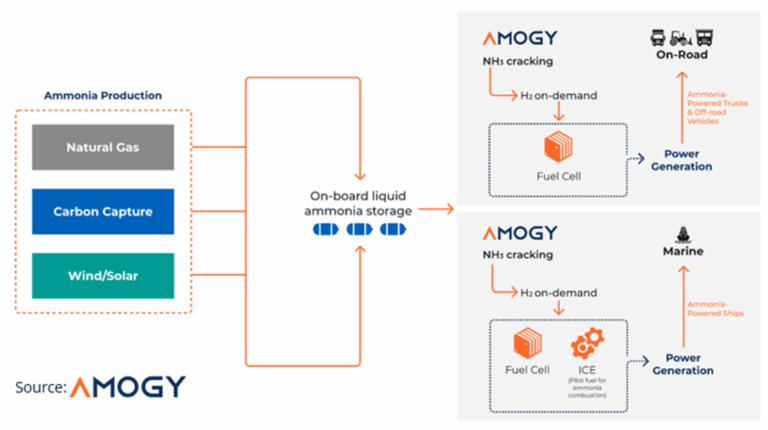
Amogy’s Ammonia-to-Power Process Visualized
This diagram illustrates the core ammonia-to-power technology that Amogy is deploying in its commercial projects, providing essential context for the systems being adopted.
(Source: Cleantech Group)
Investment Analysis: Strategic Funding De-Risks Amogy’s Commercialization Path
Amogy’s 2025 funding activities reflect a strategic shift toward securing capital from key commercial partners, which validates its technology and de-risks market entry by aligning investments with deployment goals.

Amogy’s Dominance in Pre-2025 Venture Investment
This chart provides historical context, showing Amogy’s strong venture capital backing before its 2025 strategic shift toward funding from commercial partners.
(Source: Cleantech Group)
- In November 2025, Amogy secured a $15 million strategic investment from GS E&C, a key partner in the Pohang distributed power project. This funding directly supports a flagship commercial deployment, linking capital to a specific market-entry vehicle rather than general R&D.
- The company raised $56 million in a January 2025 venture round co-led by existing investor Aramco Ventures and new investor SV Investment. This round brought total funding to over $270 million, providing the necessary capital to finance pilot projects and its operational expansion into Asia.
- An additional $23 million extension in July 2025 brought a recent funding round’s total to $80 million, with the explicit goal of accelerating growth in Asian markets. This capital is directly tied to its geographic focus on South Korea and its network of industrial partners in the region.
- Compared to competitors like H 2 SITE, which secured $38.5 million for ammonia cracking in July 2025, Amogy’s ability to attract significant, recurring investments from strategic end-users like GS E&C and manufacturers provides a distinct commercial advantage.
Table: Amogy Corporate Funding Rounds
| Date | Funding Type | Funding Amount ($M) | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-11-17 | Strategic Investment | $15 M | Funding from partner GS E&C to directly support the deployment of ammonia-based distributed energy systems, starting with the Pohang pilot. | Amogy Raises $15 M from GS E&C |
| 2025-07-15 | Equity Financing (Extension) | $23 M | Extended a funding round to a total of $80 million. Capital is designated for accelerating global growth and market entry in Asia. | Amogy Increases Latest Funding to $80 M |
| 2025-01-15 | Venture Financing | $56 M | Round co-led by Aramco Ventures and SV Investment to bolster commercialization efforts and expand operations. | Amogy Raises $56 Million to Bolster Commercialization |
| 2023-03-22 | Series B-1 | $139 M | Led by SK Innovation, this round provided foundational capital to scale technology from prototypes toward commercial manufacturing. | Amogy Secures $139 Million Series B-1 |
Amogy’s Partnership Strategy Cements Its Position in Global Supply Chains
Amogy’s business model relies on a network of strategic partnerships with industrial incumbents to outsource manufacturing, de-risk market entry, and secure commercial off-takers for its ammonia-to-power systems.

The Green Ammonia Value Chain Explained
This diagram visualizes the global supply chain mentioned in the heading, showing the end-to-end process where Amogy’s partnerships for manufacturing and deployment fit.
(Source: Clean Economy Chronicles)
- The cornerstone of Amogy’s 2025 commercialization strategy is its manufacturing agreement with Samsung Heavy Industries. This partnership provides immediate, scalable production capacity in South Korea, positioning Amogy as a technology provider and systems integrator rather than a capital-intensive manufacturer.
- Prior to 2025, partnerships focused on technology validation and supply chain, such as the December 2022 agreement with Ballard Power Systems to procure fuel cells. In contrast, 2025 partnerships with GS E&C, HD Hyundai Infracore, and Kinetics are centered on deploying the integrated system in specific commercial applications like stationary power and data centers.
- Collaborations with engineering firms like KBR and JGC Holdings, announced in September and April 2025, aim to advance the core ammonia cracking technology for large-scale hydrogen production. These partnerships target the front-end of the system, reinforcing Amogy’s core intellectual property.
- The company is building a geographically diverse customer base through deployment agreements with partners like Green Harvest in Taiwan (July 2025) and A*STAR in Singapore (September 2025), establishing a foothold in key Asian energy markets.
Table: Amogy Strategic Partnerships
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Samsung Heavy Industries | Nov 2025 | Multi-year manufacturing partnership for SHI to produce and test Amogy’s ammonia-to-power systems in a dedicated South Korean facility. | Samsung Heavy to build Amogy ammonia power systems |
| GS E&C, HD Hyundai Infracore, City of Pohang | Apr 2025 | Collaborative deployment of a 1 MW pilot power generation system in Pohang, South Korea, by 2026, with plans to scale to 40 MW. | GS E&C, Amogy, and HD Hyundai Infracore Partner with Pohang |
| Kinetics | Dec 2025 | Strategic partnership and investment to pilot Amogy’s solutions for floating power and data center infrastructure. | Kinetics Invests in and Partners with Amogy |
| JGC Holdings | Apr 2025 | Collaboration to develop large-scale ammonia cracking technology for low-carbon hydrogen production, targeting completion by 2030. | Amogy and JGC to develop large-scale ammonia cracking |
Amogy’s Geographic Focus Shifts to Asia to Capture Key Industrial Markets
While founded in the U.S., Amogy’s commercial activities in 2025 demonstrate a decisive strategic pivot to Asia, specifically targeting South Korea as a primary market for manufacturing, deployment, and investment.

Amogy Targets Key Decarbonization Markets
This chart identifies the large emissions markets Amogy is targeting, explaining the strategic rationale for its geographic pivot to industrial and shipping hubs in Asia.
(Source: Business Insider)
- From 2021 to 2024, Amogy’s operations were predominantly US-based, with R&D in Brooklyn, New York, and vehicle demonstrations taking place in the U.S. A Houston research and manufacturing facility was also established to support catalyst development.
- In February 2025, Amogy formally expanded its operations into South Korea to be closer to key investors and partners like SK Innovation, Samsung Heavy Industries, and Hanwha. This move aligns the company with South Korea’s national goal to commercialize ammonia-fueled power generation by 2030.
- Nearly all major partnerships and projects announced in 2025 are anchored in South Korea. This includes the Samsung Heavy Industries manufacturing deal, the 1 MW to 40 MW Pohang power project with GS E&C and HD Hyundai Infracore, and strategic investments from Korean firms.
- Beyond South Korea, Amogy is establishing a presence in other strategic Asian markets. A July 2025 partnership with Green Harvest targets industrial decarbonization in Taiwan, while a September 2025 agreement with A*STAR aims to develop ammonia-powered solutions for Singapore’s green economy.
Amogy Technology Maturity Advances from Prototype to Commercially Viable System
Amogy’s technology has progressed from scaled demonstrations to a commercially validated system, with 2025 marking the transition to third-party manufacturing and deployment in utility-scale pilot projects.

Amogy’s Technology Shows Superior Energy Density
This chart quantifies the technology’s maturity by showing its superior energy density, which validates its commercial viability for heavy-duty applications.
(Source: All About Circuits)
- In the 2021-2024 period, technology maturity was proven through a rapid succession of increasingly powerful prototypes. The successful scaling from a 5 k W drone to a 1 MW tugboat demonstrated the system’s modularity and technical feasibility for heavy-duty applications.
- In 2025, the focus shifted to commercial and industrial validation. The agreement for Samsung Heavy Industries to manufacture the ammonia-to-power systems confirms that the technology is mature enough for production by a major industrial firm.
- The planned 1 MW pilot project in Pohang, South Korea, moves the technology from a controlled demonstration to a real-world, grid-connected application. This project will provide critical data on long-term durability, reliability, and operational costs, which are the final steps toward full commercial maturity.
- Amogy’s core innovation remains its proprietary cracking catalyst, which it claims is up to 70% more efficient than alternatives. Partnerships in 2025 with firms like KBR are focused on integrating this mature catalyst technology into large-scale hydrogen production platforms, further validating its readiness.
SWOT Analysis: Amogy’s Strategic Position in the Ammonia-to-Power Market
Amogy’s key strength is its capital-light, technology-focused business model, but its success now hinges on the performance of its initial commercial pilots and the long-term durability of its core catalyst technology.

Ammonia’s Competitive Edge as a Fuel
This chart supports the SWOT analysis by highlighting the fundamental strengths of ammonia as a fuel, which underpins Amogy’s strategic position and market opportunity.
(Source: Amogy)
- Strengths: A proprietary, high-efficiency ammonia cracking technology combined with a partnership-heavy model that outsources capital-intensive fuel cell and system manufacturing.
- Weaknesses: A reliance on partners for manufacturing and market access, and unproven long-term performance of its catalysts in harsh, real-world operating environments like maritime shipping.
- Opportunities: Access to large, hard-to-abate sectors like shipping and stationary power, with a clear geographic entry point in the supportive South Korean market.
- Threats: The performance and cost-effectiveness of its pilot projects, competition from other ammonia cracking technologies, and dependence on the future availability of affordable green ammonia.
Table: SWOT Analysis for Amogy
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Proprietary cracking technology and strong R&D team from MIT. Early-stage investor backing from venture funds. | Validated, capital-light business model using partners (SHI) for manufacturing. Strategic backing from industrial end-users (GS E&C, SK Innovation). | The business model shifted from theoretical to validated through the Samsung manufacturing deal. Investor base evolved from VCs to strategic partners. |
| Weaknesses | Unproven scalability of the powerpack system. Technology confined to controlled, short-term demonstrations. | Limited direct manufacturing control. Long-term catalyst durability and reliability under continuous commercial operation remain unproven. | Scalability was proven by advancing from a 100 k W tractor to a 1 MW tugboat. The weakness shifted from “can it scale?” to “can it last?” which the 2026 Pohang pilot will test. |
| Opportunities | Address decarbonization in heavy transport (shipping, trucking). Leverage existing global ammonia infrastructure. | Enter the stationary power market via the 40 MW Pohang project. Become a dominant technology licensor in the South Korean and broader Asian markets. | The stationary power opportunity became concrete with the Pohang project. The path to market entry in Asia was clarified through partnerships with SHI, GS E&C, and Green Harvest. |
| Threats | Technical failure during scale-up demonstrations. Inability to secure follow-on funding for larger projects. | Pilot project failure (e.g., Pohang) impacting commercial viability. Competition from other cracking technologies (e.g., H 2 SITE). Reliance on volatile green ammonia pricing. | The primary threat is now commercial, not technical. Success or failure hinges on the real-world performance and economics of its first commercial-scale deployments. |
Forward-Looking Insights: Amogy’s Future Hinges on Pohang Pilot Success
The successful deployment and operation of the 1 MW pilot project in Pohang, South Korea, by 2026 is the single most critical milestone for Amogy, as it will serve as the commercial proof point for its technology’s reliability, efficiency, and economic viability.
- All of Amogy’s strategic moves in 2025 converge on the Pohang project. The $15 million investment from GS E&C directly funds it, and the manufacturing agreement with Samsung Heavy Industries is set to produce the systems needed for it.
- The success of this pilot is the gateway to the planned 40 MW commercial scale-up. A positive outcome would validate Amogy’s system for the stationary power market and provide a powerful case study for its maritime and industrial applications.
- Failure or underperformance at Pohang would present a significant setback, potentially jeopardizing partner confidence and the company’s ability to secure financing for subsequent large-scale deployments.
- Therefore, key indicators to monitor are the on-time deployment of the 1 MW system in 2026 and the initial performance data related to system efficiency, uptime, and operational costs. These results will determine Amogy’s trajectory for the remainder of the decade.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the major change in Amogy’s strategy in 2025?
In 2025, Amogy shifted its strategy from technology demonstration to commercial execution. After proving its ammonia-to-power system was technically feasible with projects like a 1 MW tugboat, the company’s focus moved to securing manufacturing agreements and deploying its technology in commercial-scale pilot projects.
Why is Amogy focusing so heavily on South Korea?
Amogy’s focus on South Korea is a strategic move to be closer to key industrial partners and investors like Samsung Heavy Industries, GS E&C, and SK Innovation. The country serves as the hub for its manufacturing (via SHI) and its first major commercial project (the Pohang power plant). This aligns with South Korea’s national goal to commercialize ammonia-fueled power by 2030.
What is the Pohang project and why is it so important for Amogy?
The Pohang project is a collaboration with partners GS E&C and HD Hyundai Infracore to deploy a 1 MW ammonia-to-power pilot system in South Korea by 2026, with a roadmap to scale to 40 MW. It is critically important as it marks Amogy’s entry into the stationary power market and will serve as the first commercial-scale test of the technology’s long-term reliability, efficiency, and economic viability.
Does Amogy manufacture its own ammonia-to-power systems?
No, Amogy employs a capital-light business model. Instead of manufacturing the systems itself, it has entered into a multi-year partnership with Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) in South Korea. SHI will produce and test the ammonia-to-power systems, allowing Amogy to focus on its role as a technology provider and systems integrator.
How is Amogy funding its commercialization efforts?
In 2025, Amogy’s funding strategy shifted to securing strategic investments from its commercial partners. For example, it received a $15 million investment from GS E&C, a partner in the Pohang project, directly linking the capital to a specific deployment. This is in addition to larger venture rounds raised in 2025, bringing its total funding to over $270 million to support its expansion into Asia.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

