Fuel Cell Energy Partnerships 2025: Strategic Pivot from R&D to Data Center Commercialization
Fuel Cell Energy Commercial Projects: Shifting from Pilots to Large-Scale Data Center Power 2025
Fuel Cell Energy’s commercial strategy has pivoted from technology validation projects between 2021 and 2024 to aggressive, large-scale commercial deployments in 2025, primarily targeting the power-intensive data center sector.
- The period from 2021-2024 focused on foundational, proof-of-concept projects like the Tri-gen system with Toyota, which demonstrated the ability to produce electricity, hydrogen, and water from a single platform. This period also saw the extension of the Exxon Mobil joint development agreement, validating the technology for industrial carbon capture.
- In 2025, the focus has decisively shifted to commercial scale, highlighted by a collaboration with Diversified Energy Co. (DEC) and TESIAC to develop 360 MW of off-grid power for AI data centers. A Memorandum of Understanding with Inuverse signed in July 2025 aims to deploy fuel cells for the AI Daegu Data Center in South Korea.
- The company is now monetizing earlier relationships, securing $25 million in EXIM debt financing in December 2025 to supply modules for the 58.8 MW Gyeonggi Green Energy power plant. This builds upon a relationship and market access established in the prior period.
- This evolution from single-site demonstrations to multi-hundred-megawatt agreements signifies a critical shift in the adoption of fuel cells from niche applications to solutions for industrial power challenges. The variety of applications, from baseload power to carbon capture and hydrogen production, shows the technology’s flexibility is now being commercially leveraged.
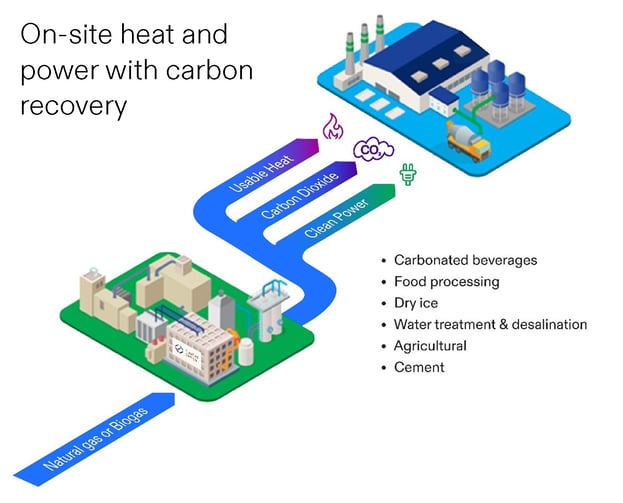
How FuelCell Energy’s Tri-Gen System Works
This infographic details the Tri-gen process, a foundational technology mentioned in the section as a key pilot project before the company’s large-scale commercial pivot.
(Source: FuelCell Energy)
Fuel Cell Energy Investment Analysis: Securing Non-Dilutive Capital for Global Growth 2025
Fuel Cell Energy is increasingly leveraging project-specific debt and financing from export-credit agencies to fund its international expansion and manufacturing scale-up, marking a strategic move to reduce its historical reliance on dilutive equity financing.
- In December 2025, the company secured $25 million in debt financing from the Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM). This funding is specifically designated for producing modules for the Gyeonggi Green Energy (GGE) power plant upgrade in South Korea.
- This follows a similar transaction from November 2024, when Fuel Cell Energy secured $9.4 million in project debt financing from EXIM, also for projects with GGE, demonstrating a repeatable financing model for international sales.
- These non-dilutive financing agreements are crucial for a company that historically funded operations through share dilution, as evidenced by a 45.7% increase in share count noted in analyses from early 2026.
- The strategy of using government-backed financing for specific, revenue-generating international projects de-risks expansion and preserves shareholder equity while validating the commercial viability of its order book.
Table: Fuel Cell Energy Key Financing Deals (2024-2025)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gyeonggi Green Energy (GGE) / EXIM Bank | December 2025 | Secured $25 million in debt financing to fund the production of modules for the 58.8 MW power plant upgrade in Hwaseong, Korea. This non-dilutive capital supports manufacturing for a key international order. | Fuel Cell Energy Secures $25 M in Repeat EXIM Financing |
| Gyeonggi Green Energy (GGE) / EXIM Bank | November 2024 | Secured $9.4 million in project debt financing from EXIM to support fuel cell projects in South Korea. This established a critical financing relationship for international sales. | Fuel Cell Energy Secures Project Financing from EXIM Bank |
| Group 1001 and Franklin Park | December 2023 | Closed $6.3 million in tax equity financing for the Tri-gen Project with Toyota and the Derby, Connecticut fuel cell park. This leveraged tax incentives to support domestic project deployment. | Fuel Cell Energy Closes Tax Equity Financings |
Fuel Cell Energy Strategic Alliances Drive Data Center and Hydrogen Market Entry 2025
Fuel Cell Energy’s partnerships have strategically evolved from technology development with industrial majors to market-entry collaborations in 2025 focused on the high-growth data center and hydrogen production sectors.
- Between 2021-2024, foundational partnerships like the extended Joint Development Agreement with Exxon Mobil for carbon capture and the Tri-gen project with Toyota served to validate the core technology platforms for industrial use.
- The year 2025 marks a pivot to commercial deployment through new alliances, including an MOU with Inuverse in July 2025 to target the South Korean AI data center market and a collaboration with Diversified Energy and TESIAC to develop 360 MW of power for off-grid data centers.
- The company is also expanding its hydrogen ecosystem, entering a joint development agreement in March 2025 with Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering (MHB). The partnership aims to develop a low-carbon fuel production facility in Asia using its SOEC technology, with a feasibility study for a 160 MW project already submitted.
- These recent partnerships demonstrate a clear shift from proving technological capability to securing large-scale, revenue-generating projects in targeted high-demand markets, directly addressing the energy needs of the digital economy and clean fuel transition.
Table: Fuel Cell Energy Strategic Partnerships (2025)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exxon Mobil | August 2025 | Began construction of a pilot plant in Rotterdam to demonstrate carbonate fuel cell technology for capturing industrial CO₂ while producing power. This moves a long-term R&D partnership into a critical physical demonstration phase. | Exxon Mobil Begins Building Rotterdam Carbonate Fuel … |
| Inuverse | July 2025 | Signed an MOU to deploy fuel cell power solutions for the AI Daegu Data Center in South Korea. This agreement directly targets the hyperscale and AI markets, aligning with the company’s new strategic focus. | Fuel Cell Energy and Inuverse Partner for Data Center … |
| Diversified Energy, TESIAC | March 2025 | Formed a collaboration to leverage coal mine methane and natural gas for off-grid data center power projects, targeting 360 MW of capacity. This creates a vertically integrated approach to a key growth market. | Maximizing the Value of Your Molecule: A Game-Changing … |
| Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering (MHB) | March 2025 | Signed a joint development agreement for a feasibility study of a low-carbon fuel production facility using SOEC technology. This partnership opens a pathway into the Asian hydrogen economy. | Fuel Cell Energy and Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering … |
Fuel Cell Energy Global Footprint: Expanding from North America to Asian Energy Hubs 2025
While maintaining a North American base for R&D and key projects, Fuel Cell Energy’s commercial focus has intensely shifted towards Asia, with South Korea emerging as the primary destination for its large-scale power generation deployments.
- Between 2021-2024, activities were geographically diverse, including the Toyota Tri-gen project in California, the Exxon Mobil R&D collaboration with a pilot plant planned for Rotterdam, and foundational agreements targeting Africa with Oando and broader Asia with MHB.
- The year 2025 solidified South Korea as the central hub for commercial activity. Key events include the $25 million in EXIM financing for the Gyeonggi Green Energy plant, a 10 MW repowering agreement with CGN, and the MOU with Inuverse for a data center in Daegu.
- This Asian expansion was strategically enabled by the 2021 settlement with POSCO Energy, which formally resolved market access disputes and paved the way for the current deal flow in the region.
- The strategy shows a clear pattern of leveraging US-based technology development and government-backed financing, like the EXIM facility, to penetrate and scale within the high-demand, policy-supported energy markets of Asia.
Fuel Cell Energy Technology Status 2025: Carbonate Fuel Cells at Commercial Scale, SOEC Targets Hydrogen Market
Fuel Cell Energy’s molten carbonate platform has achieved commercial scale for power generation and carbon capture, while its solid oxide technology is now being commercially targeted for high-efficiency hydrogen production.
- From 2021-2024, the primary focus was on demonstrating the multi-faceted capabilities of its technologies. The Tri-gen project with Toyota validated the carbonate fuel cell’s ability to produce power, hydrogen, and water simultaneously, while the Exxon Mobil partnership advanced its use for industrial carbon capture.
- By 2025, the carbonate platform is being deployed at commercial scale, evidenced by large module supply agreements with Gyeonggi Green Energy and the strategic pivot to provide baseload power for data centers with partners like Inuverse.
- The Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cell (SOEC) platform has moved from development to targeted commercial application in 2025. The collaboration with Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering for a potential 160 MW low-carbon fuel facility marks its first major push into the green hydrogen production market.
- This progression shows the company is successfully moving its technologies from pilot and demonstration phases into distinct, revenue-generating commercial applications for power, carbon capture, and hydrogen.
Fuel Cell Energy SWOT Analysis 2025: From Financial Strain to Commercial Traction
Fuel Cell Energy’s strategic pivot in 2025 is leveraging its technological strengths to capitalize on the data center market opportunity, but it must overcome historical unprofitability and intense competition to achieve sustainable growth.

Financial Strain Persists Despite Revenue Growth
This chart directly illustrates the ‘Weaknesses’ described in the SWOT analysis, showing the company’s persistent net losses and financial strain through 2023.
(Source: Medium)
- Strengths in differentiated technology, particularly for carbon capture, are now being validated through major commercial agreements that have moved beyond the pilot stage.
- Weaknesses related to persistent net losses and a history of shareholder dilution remain a primary concern, though improving margins and new non-dilutive financing arrangements show progress.
- Opportunities in the power-starved AI data center market and the growing hydrogen economy are the central drivers of the company’s current strategy and recent partnerships.
- Threats from better-capitalized competitors like Bloom Energy, who are aggressively targeting the same data center customers in key markets, represent the most significant external risk to market share.
Table: SWOT Analysis for Fuel Cell Energy
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2024 – 2025 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Differentiated carbonate technology with inherent CO₂ capture. High-efficiency solid oxide platform. Technology validated in pilot projects (Toyota Tri-gen, Exxon Mobil R&D). | Technology deployed at commercial scale (GGE project). Strong cash position ($341.8 M). New 1.25 MW power block product introduced. | The company’s core technology moved from validated potential in pilots to a commercial product securing large-scale, revenue-generating contracts. |
| Weaknesses | Persistent net losses (-$107.1 M in FY 23). History of shareholder dilution to fund operations. Volatile, project-based revenue. | Continued unprofitability (-$191.4 M net loss in FY 25) despite revenue growth. A 1-for-30 reverse stock split was executed in November 2024 to address low stock price. | Unprofitability persists as a major challenge, but improving gross margins (from -39.8% to -19.2%) and access to non-dilutive financing (EXIM) signal a potential path to financial stability. |
| Opportunities | Nascent hydrogen economy. Decarbonization policies. General interest in clean power for data centers. | Explicit strategic pivot to the AI data center power crisis. 45 Q tax credit provides tailwind for carbon capture projects. Rapidly growing fuel cell market projected at 26.3% CAGR. | The market opportunity became concrete and urgent. The company’s strategy is now fully aligned with the massive power needs of AI, a specific and high-value target market. |
| Threats | Competition from established players like Bloom Energy. Capital-intensive nature of the business. | Direct and intense competition from Bloom Energy in the data center market, particularly in Korea. Risk of execution failure on newly signed large-scale contracts. | Competition is no longer general but has become direct and acute within the company’s primary target market, raising the stakes on execution and speed to market. |
Fuel Cell Energy Outlook: Execution on Data Center and Hydrogen Projects is Key for 2026
Fuel Cell Energy’s success in the next 12-24 months depends entirely on its ability to convert its strategic data center and hydrogen partnerships into profitable, large-scale deployments.
- The immediate focus will be on executing the agreements with Diversified Energy/TESIAC and Inuverse. These partnerships represent the cornerstone of the new data center strategy and are critical to achieving the stated goal of 100 MW of annualized production needed to reach positive adjusted EBITDA.
- Progress on the Exxon Mobil pilot plant in Rotterdam and the Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering feasibility study will be crucial validation points. Success in these projects would confirm the commercial viability of the company’s carbon capture and hydrogen technologies, opening up significant long-term markets.
- Financial performance, specifically the ability to continue improving gross margins and securing further non-dilutive financing like the EXIM deals, will determine if the company can scale operations without reverting to its historical pattern of shareholder dilution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main change in Fuel Cell Energy’s strategy in 2025?
In 2025, Fuel Cell Energy pivoted from smaller, technology-validation pilot projects (2021-2024) to pursuing large-scale commercial deployments. The new strategy aggressively targets the power-intensive data center sector, marking a shift from R&D to commercialization.
How is the company funding its expansion and avoiding shareholder dilution?
Fuel Cell Energy is increasingly using non-dilutive capital, such as project-specific debt from export-credit agencies. The text highlights securing two separate financing deals from the Export-Import Bank of the United States (EXIM) for $25 million (Dec 2025) and $9.4 million (Nov 2024) to fund projects in South Korea, reducing its historical reliance on issuing new shares.
Which specific market is Fuel Cell Energy targeting for growth, and with which partners?
The company is primarily targeting the AI data center market. Key partnerships in 2025 include a collaboration with Diversified Energy and TESIAC to develop 360 MW of power for off-grid data centers, and a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Inuverse to deploy fuel cells for the AI Daegu Data Center in South Korea.
Which geographical region is central to Fuel Cell Energy’s current commercial deals?
Asia, and specifically South Korea, has become the central hub for Fuel Cell Energy’s commercial activity in 2025. This is demonstrated by the large module supply and financing agreements for the Gyeonggi Green Energy power plant and the new data center MOU with Inuverse in Daegu.
What are the two main technologies Fuel Cell Energy is deploying and for what purpose?
The company is deploying its molten carbonate platform at a commercial scale for baseload power generation and carbon capture, as seen in its data center strategy and ExxonMobil pilot. Simultaneously, it is commercializing its Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cell (SOEC) platform for high-efficiency hydrogen production, highlighted by its partnership with Malaysia Marine and Heavy Engineering.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Bloom Energy SOFC 2025: Analysis of AI & Partnerships
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

