AI Data Center Energy Demand: 2025 Grid Constraints and Infrastructure Investment Signals
The transition of Artificial Intelligence (AI) compute to an abundant commodity is creating a new primary business risk: the physical constraint of energy availability and data center capacity. As the cost of AI inference plummets, demand is exploding, shifting the strategic focus from managing software expenses to securing the power and infrastructure required for large-scale deployment. This pivot forces energy executives and investors to assess the systemic risks and opportunities tied to a historic, multi-trillion-dollar infrastructure build-out that is already testing the limits of global energy grids.
AI’s Commercial Scale-Up Creates Unprecedented Energy and Infrastructure Risks in 2025
The rapid commoditization of AI models has shifted the primary business constraint from the cost of intelligence to the physical availability of power and infrastructure. Between 2021 and 2024, the central challenge was managing the high cost of training and running AI models, a software and capital problem. Starting in 2025, the challenge has become a physical one, centered on securing access to the massive-scale data centers and the enormous energy supply required to power them, signaling a fundamental market shift for energy and infrastructure stakeholders.
- The demand for AI-ready data center capacity is now projected to grow at an average rate of 33% per year through 2030, a pace that outstrips traditional energy infrastructure planning cycles and creates significant grid stability risks.
- This demand is fueling a historic capital investment cycle, with forecasts projecting nearly $7 trillion will be spent on global data center infrastructure by 2030 and global AI spending reaching approximately $2 trillion in 2026 alone.
- The scale of individual projects is increasing, with new AI data center campuses requiring hundreds of megawatts of power, exemplified by a 2025 agreement for a 250 MW AI data center in Texas, directly linking AI expansion to large-scale energy development.
- This pivot is validated by the actions of major technology firms like Google, Meta, Microsoft, and Amazon, which are collectively spending an additional $300 billion on data centers, moving the competitive bottleneck from owning the best algorithm to controlling the physical means of computation.
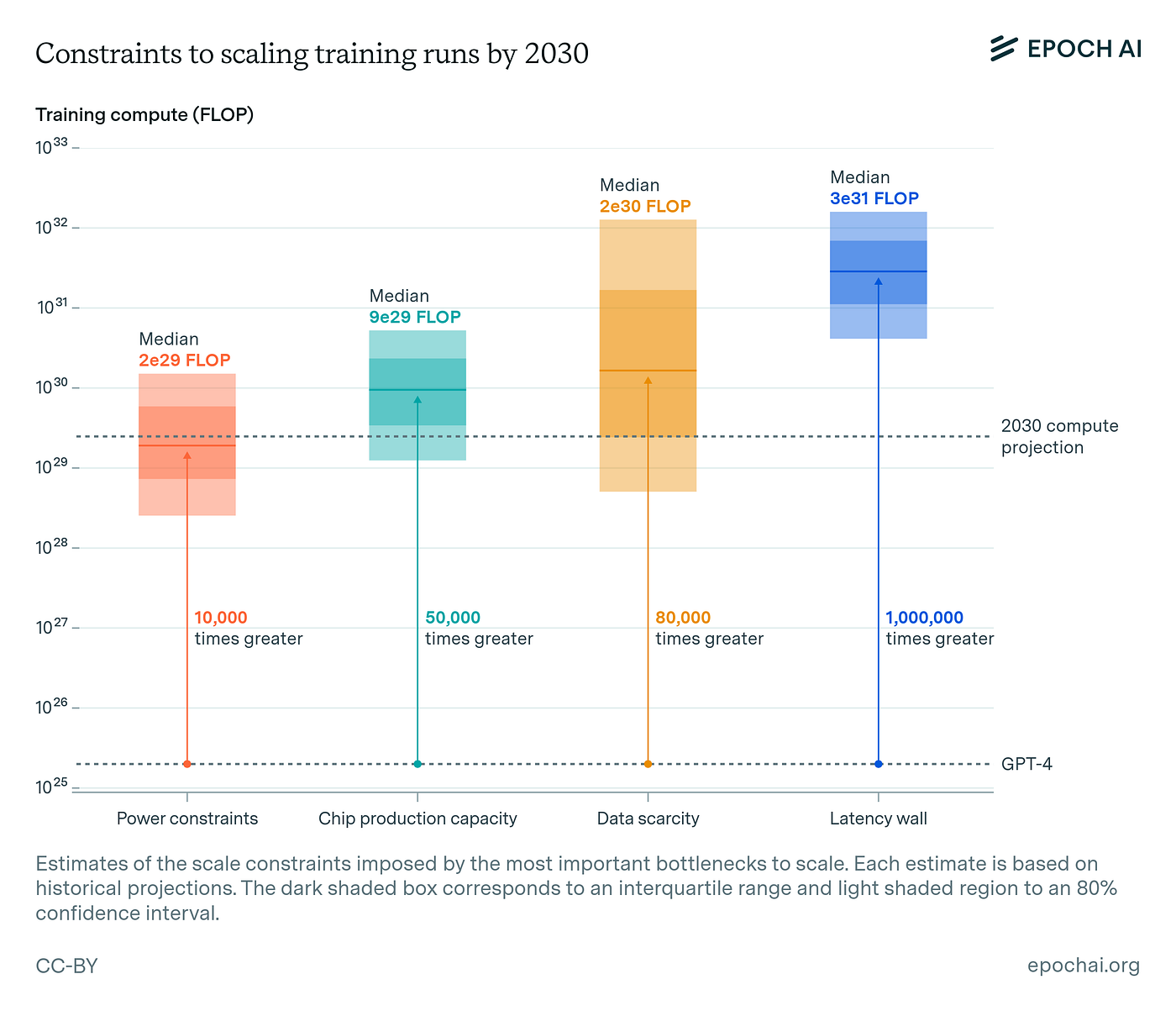
Power Constraints Emerge as Key AI Bottleneck
This chart directly supports the section’s thesis that energy is the primary risk, projecting that by 2030, ‘Power constraints’ will be the most significant bottleneck for AI.
(Source: Medium)
Strategic Partnerships in 2025: Securing AI Compute and Energy Capacity
In 2025, strategic partnerships have become the dominant strategy for mitigating the risks of compute and energy scarcity, as AI leaders form critical alliances with specialized cloud providers and energy firms to secure the physical backbone for growth. While prior years saw collaborations focused on model development, the recent wave of partnerships is centered on long-term access to infrastructure and power, confirming that securing hard assets is now the top priority.
- Open AI demonstrated a strategic diversification of its infrastructure supply chain by expanding its agreement with specialized cloud provider Core Weave to $22.4 billion and signing a separate five-year, $300 billion cloud contract with Oracle in 2025, reducing reliance on single providers.
- The convergence of AI and energy infrastructure became explicit with the September 2025 agreement between New Era Energy & Digital and Thunderhead Energy Solutions to develop a 250 MW AI data center campus, a clear signal that new energy generation is being developed specifically for AI workloads.
- Infrastructure specialization is a growing trend, highlighted by Applied Digital’s 15-year, 250 MW data center lease with Core Weave announced in June 2025 to host high-performance computing, indicating a move toward purpose-built facilities rather than general-purpose cloud instances.
- These deals underscore a broader market realization that the immense capital required for at-scale AI necessitates collaboration, driving a convergence of AI labs, cloud providers, energy companies, and governments to build the next generation of “AI gigafactories.”
Table: Key AI Infrastructure and Energy Partnerships in 2025
| Partners | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open AI / Oracle | September 2025 | Open AI signed a five-year, $300 billion cloud contract with Oracle to secure massive-scale compute capacity, diversifying its infrastructure partners. | The Dream of Abundant Intelligence |
| Open AI / Core Weave | September 2025 | The partnership was expanded to $22.4 billion, providing Open AI with access to specialized AI cloud infrastructure and further diversifying its compute supply chain. | Open AI-Core Weave Partnership Grows to $22.4 Billion |
| New Era Energy & Digital / Thunderhead Energy Solutions | September 2025 | Signed a strategic power agreement for a 250 MW AI data center campus in Texas, directly linking new energy infrastructure development to AI demand. | New Era Energy & Digital, Inc. – News |
| Applied Digital / Core Weave | June 2025 | Announced a 15-year, 250 MW data center lease to host Core Weave‘s high-performance computing workloads, highlighting the need for long-term, specialized infrastructure. | Applied Digital and Core Weave Ink 15-Year Deal |
Global AI Infrastructure Hotspots: US Leads in Data Center and Energy Expansion
The United States has solidified its position as the global epicenter for the AI infrastructure build-out, driven by the heavy concentration of domestic technology giants, massive capital inflows, and the initiation of new, dedicated energy projects. While activity is global, the scale and pace of deployment in the U.S. far exceed that of other regions. For example, some nations show significantly slower adoption, creating a geographic imbalance in the development of the physical layer of the AI economy.

US Leads World in AI Company Growth
This chart illustrates the section’s point about US leadership, showing a dramatic surge in American AI companies that far outpaces growth in Europe and China.
(Source: National Center for Energy Analytics)
- The majority of the announced infrastructure investments, including the additional $300 billion from Google, Meta, Microsoft, and Amazon, are concentrated within the United States, which hosts the bulk of their existing and planned data center campuses.
- The emergence of new energy projects directly tied to AI data centers, such as the 250 MW campus in Texas, underscores how energy-rich regions in the U.S. are becoming strategic locations for AI expansion.
- This contrasts with the situation in other developed nations like Canada, where only 12% of firms had integrated AI into their operations as of June 2025, indicating a significant lag in the underlying demand and infrastructure build-out compared to the U.S.
From Model Scarcity to Infrastructure Scarcity: AI’s Maturity Pivot in 2025
The technological focus of the AI industry has matured from developing better models to deploying the physical infrastructure capable of running them at scale. The period from 2021 to 2024 was defined by a race for model superiority, where high training costs, such as the $192 million for Google‘s Gemini Ultra, represented the primary barrier to entry. In 2025, the bottleneck has decisively shifted to infrastructure, as the commoditization of foundational models makes deployment and energy consumption the new frontiers of competition.

AI Model Training Costs Exceed $190M
This chart quantifies the high cost of the ‘model scarcity’ era, specifically validating the section’s reference to Gemini Ultra’s training cost of nearly $200 million.
(Source: Visual Capitalist)
- The technological challenge has moved from model R&D to infrastructure engineering. The rise of open-source AI, now used by 72% of technology leaders, and the development of smaller, more efficient models have made advanced AI accessible, shifting the competitive focus to scalable deployment.
- The new measure of technological maturity is the ability to secure and manage power. The industry’s vocabulary has evolved to include “AI gigafactories” and large-scale power agreements, signaling that the core technical problem is now one of energy and systems engineering, not just computer science.
- This shift is validated by the deflationary pressure on software, where the marginal cost of cognitive tasks is approaching zero, while the costs associated with the underlying data centers and energy are rising, making infrastructure the primary strategic asset.
SWOT Analysis: AI Infrastructure and Energy Demand in 2025
While massive investment and the plummeting unit cost of AI create unprecedented opportunities for value creation, the entire ecosystem is threatened by emerging physical constraints in energy supply and data center capacity. This dynamic creates a complex strategic environment where efficiency gains are pitted against escalating infrastructure demands, with the potential to concentrate market power among firms that control the physical assets.

AI Costs Plummet as Performance Soars
This chart illustrates the “plummeting unit cost” opportunity mentioned in the SWOT analysis, showing a 99.7% cost decrease for models alongside rising performance.
(Source: LinkedIn)
Table: SWOT Analysis for AI-Driven Business Model Transformation
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Rapid improvement in AI model capabilities (e.g., GPT-3 to GPT-4). High capital investment as a barrier to entry for model developers. | Plummeting inference costs and the rise of smaller, efficient models. Commoditization of foundational models (72% open-source adoption). | The source of competitive strength shifted from owning the best proprietary model to applying commoditized intelligence most effectively and at the lowest operational cost. |
| Weaknesses | Extremely high and escalating model training costs (e.g., $79 M for GPT-4) limited participation to a few large firms. | Massive energy consumption of data centers at scale. Long lead times and geographic constraints for building new data center capacity and securing grid connections. | The primary weakness is no longer the cost of R&D but the physical and logistical challenge of deploying and powering infrastructure, a direct concern for the energy sector. |
| Opportunities | Productivity gains within existing business structures. Automation of specific, narrow tasks. | Creation of new outcome-based revenue models. Rise of autonomous “agentic workflows” reducing operational costs by 20-30%. A $7 trillion market for new data center infrastructure by 2030. | The opportunity expanded from incremental efficiency to fundamental business model transformation, creating a massive new market for the energy and infrastructure sectors that support it. |
| Threats | Market concentration among a few AI labs (e.g., Open AI, Google) that could afford to train large models. | Energy availability becoming the primary bottleneck, constraining growth. Grid instability from concentrated data center loads. Market consolidation around infrastructure owners (cloud providers, energy firms). | The central threat shifted from a monopoly on algorithms to a monopoly on physical compute and power, making grid capacity and energy partnerships a critical strategic issue. |
Forward Outlook: Will Energy Availability Constrain AI’s Growth Trajectory?
The single most critical variable determining the pace of AI adoption over the next 12-24 months is the ability of the energy and infrastructure sectors to meet exponential demand; failure to do so will fragment the market, slow innovation, and force a radical rethinking of AI deployment strategies. Executives and investors should monitor the success and velocity of new energy-focused partnerships as the leading indicator of whether AI’s growth can be sustained.

Data Center Energy Demand Forecast to Surge
This projection visualizes the core question of the forward outlook, illustrating the “exponential demand” for energy from data centers that will constrain AI’s growth trajectory.
(Source: National Center for Energy Analytics)
- If the strategic partnerships between AI firms and energy providers, such as the New Era Energy deal, accelerate and are replicated in other regions, watch for a wave of new data center campus announcements exceeding 250 MW. This would signal that the industry is successfully de-risking the energy constraint, allowing the projected $7 trillion infrastructure build-out to proceed on schedule.
- Conversely, if these energy-focused partnerships stall or grid connection queues continue to lengthen, watch for AI companies to pivot their strategies. Key signals would include major investments in proprietary, off-grid power generation or a strategic shift away from massive centralized data centers toward smaller, distributed compute nodes that are easier to power.
- Such a pivot would indicate that the energy bottleneck is binding, which could slow the overall growth trajectory of large-scale AI. This would in turn create new opportunities for distributed energy solutions, microgrids, and technologies that improve the power usage effectiveness (PUE) of data centers, reshaping the investment landscape for energy infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary business risk for AI deployment starting in 2025?
Starting in 2025, the primary business risk has shifted from the high cost of AI software to the physical constraint of energy availability and data center capacity. The main challenge is no longer managing software expenses but securing the massive-scale power and infrastructure required for large-scale AI deployment.
How much is the demand for AI data center capacity projected to grow?
According to the report, the demand for AI-ready data center capacity is projected to grow at an average rate of 33% per year through 2030. This rapid growth outpaces traditional energy infrastructure planning cycles and creates significant risks for grid stability.
Why are strategic partnerships becoming critical in the AI industry in 2025?
Strategic partnerships are now the dominant strategy for mitigating the risks of compute and energy scarcity. As the bottleneck shifts to physical infrastructure, AI leaders are forming alliances with specialized cloud providers and energy firms to secure long-term access to the power and data center capacity needed for growth, as demonstrated by deals involving OpenAI, Oracle, and CoreWeave.
Which country is leading the global AI infrastructure build-out and why?
The United States has become the global epicenter for the AI infrastructure build-out. This is driven by the heavy concentration of its domestic technology giants (Google, Meta, Microsoft, Amazon), massive capital inflows for data centers, and the initiation of new, large-scale energy projects specifically tied to powering AI workloads, such as the 250 MW campus in Texas.
What is the most critical factor that will determine the pace of AI adoption over the next two years?
The single most critical variable is the ability of the energy and infrastructure sectors to meet the exponential demand from AI. The success and velocity of new energy-focused partnerships will be the leading indicator of whether AI’s growth can be sustained. Failure to meet this demand could slow innovation and force a shift in AI deployment strategies.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Google Clean Energy: 24/7 Carbon-Free Strategy 2025
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

