Microsoft’s 2025 Energy Strategy: Securing Power for the AI Infrastructure Boom
Microsoft AI Data Center Projects Expose Critical Power Grid Limitations 2025
Microsoft’s aggressive expansion of AI-ready data centers has pivoted from a primary focus on acquiring computational hardware to a strategic imperative to secure power, revealing the global energy grid as the main bottleneck to its growth ambitions.
- Between 2021 and 2024, Microsoft’s strategy centered on amassing computing power, exemplified by its large-scale purchases of NVIDIA GPUs. From 2025 onward, the critical constraint has become the physical availability of electricity, with new reports indicating that a sufficient chip inventory is rendered idle by a lack of power to run it.
- Microsoft is a primary driver of the projected $320 billion in combined capital expenditures by major tech firms in 2025, a spending surge creating a demand shock for power grid components like high-voltage transformers, not just semiconductors.
- The operational risk is significant, as Gartner forecasts that by 2027, power shortages will directly restrict the operations of 40% of AI data centers globally, impacting companies like Microsoft that are at the forefront of this buildout.
- A fundamental shift in competition is now evident. In 2025, Microsoft and other hyperscalers are no longer just competing with each other for AI dominance but are also competing with the energy sector for the same constrained resources, including critical minerals required for both grid components and processors.
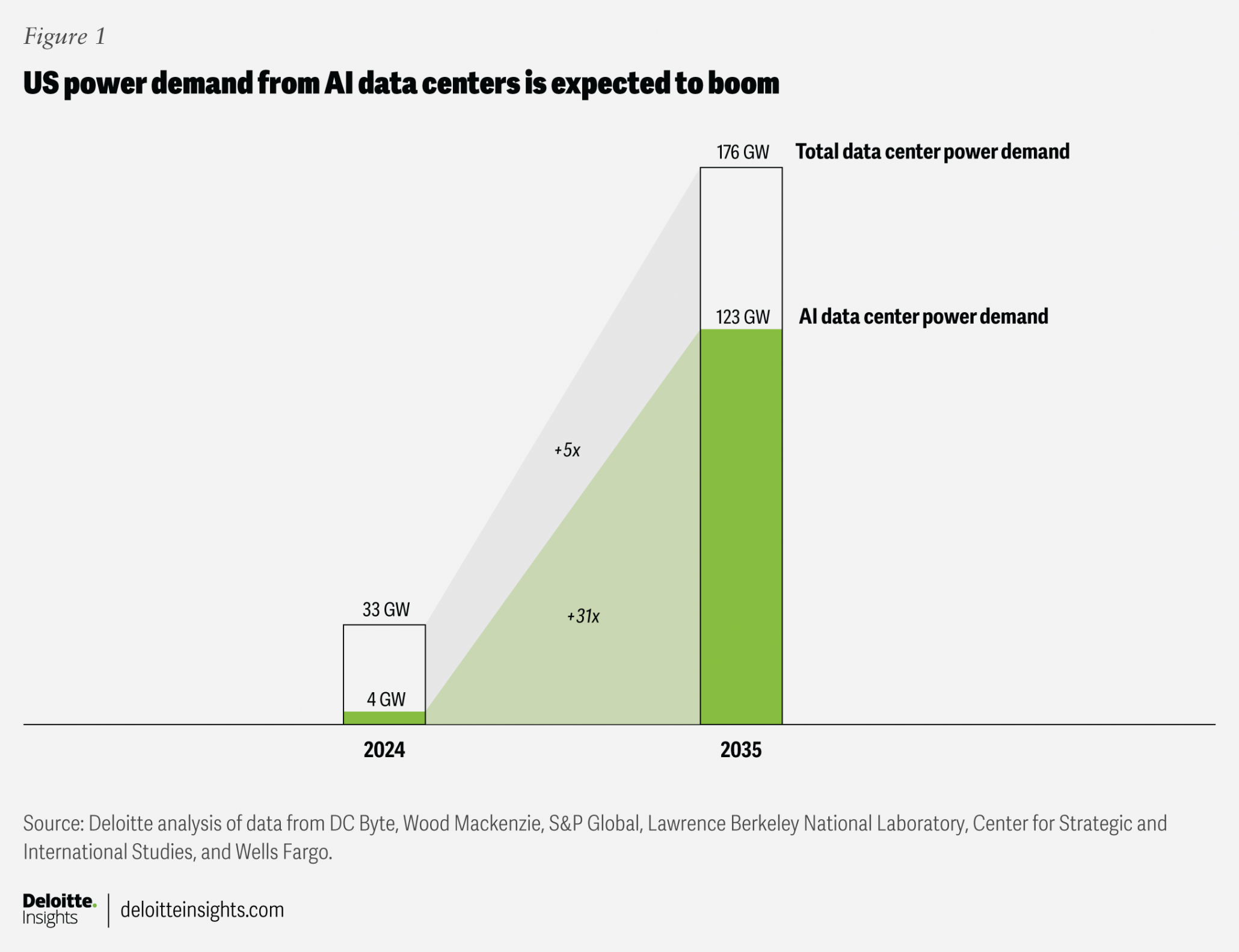
AI Power Demand to Skyrocket
This chart shows the projected 31-fold increase in power demand from AI data centers, directly illustrating the critical energy bottleneck Microsoft faces.
(Source: Deloitte)
Microsoft’s Capital Expenditure Signals Massive AI Infrastructure Investment 2025
Microsoft’s participation in the hundreds of billions of dollars of hyperscaler capital expenditure is creating an unprecedented demand shock for both the computational hardware and the vast amounts of electricity required to operate its AI factories.

AI Market Explodes Past $370B
The chart contextualizes Microsoft’s capital expenditure by showing the total AI market size in 2025, which aligns with the massive investment figures mentioned.
(Source: MarketsandMarkets)
- As one of the four key hyperscalers, Microsoft is contributing to a combined capital expenditure expected to reach as much as $320 billion in 2025 alone, dedicated to AI technologies and data center construction.
- This massive investment is a key factor in the total data center infrastructure market’s projected growth, which is forecast to approach $1 trillion in annual spending by the year 2030.
- The scale of this spending directly strains the physical supply chain for essential infrastructure components, with the demand surge affecting everything from advanced GPUs to the power transformers needed to connect data centers to the grid.
Microsoft’s Strategic Partnerships with NVIDIA and Open AI Reinforce AI Dominance 2025
Microsoft secures its market-leading position in the AI sector by executing critical, multi-billion dollar partnerships with foundational players like NVIDIA and Open AI, which guarantees it priority access to essential compute resources and allows it to co-develop the next generation of AI infrastructure.
- Microsoft’s multi-year, multi-billion dollar partnership with Open AI, including a reported $10 billion investment, provides the exclusive cloud computing infrastructure necessary to power Open AI’s research and commercial products on the Azure platform.
- In a crucial collaboration announced in late 2022, Microsoft and NVIDIA are building one of the world’s most powerful AI supercomputers, combining tens of thousands of NVIDIA’s A 100 and H 100 GPUs with Microsoft Azure’s advanced infrastructure.
- To mitigate supply chain risks and diversify its hardware portfolio, Microsoft is also developing its own custom silicon, including the Maia 100 AI Accelerator, reducing its sole dependency on third-party chip designers.
- Furthering its supply chain resilience strategy, Microsoft became a key customer for Intel Foundry Services in March 2024, planning to use Intel’s 18 A process technology for a future custom chip and securing an alternative, U.S.-based source for advanced semiconductor manufacturing.
Table: Microsoft Key AI Infrastructure Partnerships
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel | March 2024 | Microsoft plans to use Intel’s 1.8-nanometer process technology for a custom chip, establishing a U.S.-based supply of advanced chips and helping diversify its manufacturing base away from a single foundry. | Intel says Microsoft will be a customer for its foundry business |
| Open AI | January 2023 | A multi-year, multi-billion dollar investment (reported at $10 billion) to provide exclusive Azure cloud infrastructure for Open AI’s AI model development and deployment. | Microsoft and Open AI extend partnership |
| NVIDIA | November 2022 | A multi-year collaboration to build a powerful AI supercomputer using tens of thousands of NVIDIA GPUs on Azure, aimed at helping enterprises train and scale large foundation models. | Microsoft and NVIDIA Team Up to Build Massive Cloud AI Computer |
Microsoft’s Global Data Center Expansion Confronts Regional Energy Constraints 2025
While Microsoft continues its global data center expansion, its strategic site selection is increasingly dictated by regional power availability, with North America facing the most severe grid limitations despite being the current leader in AI infrastructure deployment.

North America Leads AI Infrastructure
This chart validates the section’s claim that North America is the leading region for AI infrastructure, providing a backdrop for its emerging energy constraints.
(Source: Data Bridge Market Research)
- Between 2021 and 2024, data center expansion was primarily driven by proximity to customers and fiber optic networks. Since the start of 2025, the primary factor has become access to stable and scalable power, with a lack of electricity now a direct impediment to deploying new AI capacity.
- North America, particularly the U.S., leads in AI infrastructure but is facing a severe power bottleneck. Data center power demand in the U.S. is projected to double to 409 terawatt-hours (TWh) by 2030, an amount that current grid infrastructure cannot support.
- The U.S. market is further constrained by massive utility interconnection queues and significant permitting delays for new transmission lines, which are long-term problems that cannot be solved with capital expenditure alone.
- The AI infrastructure market in the Asia-Pacific region is identified as having the highest growth potential. This suggests that future large-scale data center projects from companies like Microsoft may increasingly shift to regions with more favorable energy infrastructure and regulatory environments.
AI Power Consumption Reaches Commercial Scale, Outpacing Grid Infrastructure Maturity 2025
The power consumption required for commercial-scale AI has become a systemic operational reality, yet the supporting energy infrastructure, particularly the electricity grid, remains critically underdeveloped and unprepared for the escalating demand shock.
- In the 2021-2024 period, technology maturity was defined by the capabilities of AI models and the performance of GPU hardware. In 2025, the focus of maturity has shifted to the entire physical stack, where energy availability is now the least mature and most critical component.
- The demand is no longer a forecast but a present-day constraint, validated by projections that global data center power demand will see a 165% increase by 2030, driven almost entirely by AI workloads.
- AI data centers are orders of magnitude more power-intensive than their traditional counterparts. This mature, high-density power requirement is overwhelming grid capacity in key data center markets.
- The systemic risk was validated in 2025, with reports confirming that AI companies now possess sufficient chip inventories but are unable to deploy them due to a lack of available electricity, confirming that grid infrastructure has not matured in tandem with AI compute.
SWOT Analysis: Microsoft’s AI Ambitions vs. Physical Supply Chain Limits 2025
Microsoft’s primary strength lies in its immense capital and strategic partnerships, but this is directly threatened by its dependency on a fragile semiconductor supply chain and, most critically, the systemic weakness of global energy infrastructure.

AI Expansion Faces Key Risks
This diagram categorizes the exact risks mentioned in the SWOT analysis, such as supply chain dependency, which directly threatens Microsoft’s AI ambitions.
(Source: ScienceDirect.com)
- Strengths in capital and partnerships allow Microsoft to secure its supply chain, while Weaknesses in its dependence on the power grid present a hard limit to growth.
- Opportunities to diversify its hardware and energy sources are critical, as Threats from geopolitical events or a cascading grid failure could derail its entire AI strategy.
Table: SWOT Analysis for AI Infrastructure Growth
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2023 | 2024 – 2025 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Dominant cloud position (Azure) and software ecosystem. Strong balance sheet for investment. | Massive capital expenditure (part of a $320 B hyperscaler push) and deep partnerships with NVIDIA and Open AI to secure priority access to AI hardware and models. | Microsoft’s strategy shifted from leveraging its software dominance to using its capital to control the physical hardware layer of the AI stack, securing a competitive advantage. |
| Weakness | High dependency on NVIDIA for GPUs and TSMC for manufacturing. Known semiconductor shortages were the primary concern. | The primary bottleneck shifted from chip availability to the lack of available electrical power and grid capacity to run the hardware it has already procured. | The core weakness was validated as moving downstream in the supply chain. The problem is no longer just sourcing chips but sourcing the megawatts needed to power them. |
| Opportunity | Exploration of custom silicon to reduce reliance on NVIDIA. Standard cloud service expansion. | Actively diversifying the supply chain by developing custom chips (Maia 100) and signing on as a foundry customer with Intel. Opportunity to invest directly in energy generation. | Microsoft validated its strategy to mitigate single-supplier risk in semiconductors. The new, larger opportunity is to apply the same diversification strategy to its energy supply. |
| Threat | Geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China impacting chip exports and supply chain stability. | Direct operational threats from physical power shortages, cascading grid failures, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities in core hardware (e.g., NVIDIAScape CVE-2025-23266). | The primary threat evolved from a geopolitical policy risk to a direct physical and cybersecurity risk. A grid failure is now as significant a threat as a manufacturing disruption in Taiwan. |
Outlook 2025: Microsoft’s AI Future Hinges on Securing New Energy Sources
Microsoft’s most critical strategic action for the next 18-24 months will be to secure massive, long-term, and scalable power sources for its data centers, a challenge that will require direct investment in energy generation, innovative procurement models, and partnerships with utilities and grid operators.

AI Infrastructure Market to Soar
This forecast quantifies the massive growth potential of the AI infrastructure market, highlighting what is at stake for Microsoft if it cannot solve the energy challenge.
(Source: Fortune Business Insights)
- The most recent data from 2025 confirms that power availability, not chip supply, is the primary gating factor for AI growth. This forces energy strategy to the forefront of corporate planning at Microsoft.
- The emerging competition for critical minerals and supply chain components between the AI and energy sectors will compel Microsoft to move beyond traditional power purchase agreements toward more direct involvement in energy development to secure its supply.
- With Gartner predicting that power shortages will restrict 40% of AI data centers by 2027, Microsoft must address this as an urgent, present-day operational risk, not a distant forecast.
- Going forward, Microsoft’s growth trajectory in AI will be defined less by its partnerships with chipmakers and more by its ability to forge new, large-scale alliances with energy companies to ensure its AI factories have the power to run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main bottleneck for Microsoft’s AI expansion in 2025?
The main bottleneck has shifted from acquiring AI chips (like NVIDIA GPUs) to securing sufficient electrical power. Reports indicate that even with an adequate supply of chips, there is not enough available electricity or grid capacity to run the new AI data centers, making power the primary constraint on growth.
How is Microsoft addressing the risk of relying too heavily on NVIDIA for chips?
Microsoft is diversifying its hardware supply chain in two key ways. First, it is developing its own custom silicon, including the Maia 100 AI Accelerator. Second, it has formed a strategic partnership with Intel Foundry Services (as of March 2024) to use their 18A process for a future custom chip, securing an alternative, U.S.-based manufacturing source.
What is the significance of the projected $320 billion in capital expenditures for 2025?
This $320 billion, representing combined spending by major tech firms including Microsoft, signals an unprecedented investment in AI infrastructure. It creates a massive demand shock not just for semiconductors, but also for essential power grid components like high-voltage transformers, straining the entire physical supply chain required to build and operate AI ‘factories’.
According to the report, what is the most significant operational risk facing AI data centers by 2027?
The most significant risk is direct operational restriction due to power shortages. A Gartner forecast cited in the analysis predicts that by 2027, 40% of all AI data centers globally will be impacted by a lack of sufficient power, turning a future challenge into a present-day operational threat for companies at the forefront of the AI buildout, like Microsoft.
How has the nature of competition changed for Microsoft in the AI race?
The competition is no longer just between tech hyperscalers for AI dominance. In 2025, Microsoft and its peers are now also competing directly with the energy sector for the same constrained resources. This includes critical minerals and supply chain components like transformers, which are needed for both building the power grid and manufacturing AI hardware.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

