Microsoft’s 2025 Power Strategy: How Data Center Energy Demand Reshapes Markets
Microsoft Commercial Scale Projects Redefine Energy Procurement for AI Data Centers in 2025
Microsoft has fundamentally shifted its infrastructure strategy from procuring data center space to securing massive-scale power generation, making energy availability the primary constraint and driver of its global AI expansion. This pivot from a real estate-centric model to an energy-centric one reflects the extreme power demands of AI and positions the company as a major new force in global energy markets.
- Between 2021 and 2024, Microsoft’s data center growth was driven by general cloud services adoption, with power procurement handled through conventional utility agreements and power purchase agreements. The focus was on securing capacity in established data center hubs.
- Starting in 2025, the explosive growth of AI workloads, requiring specialized, power-intensive hardware, has forced Microsoft to address energy as a systemic bottleneck. The company is now part of a collective hyperscaler investment expected to reach $225 billion over 12 months, with a significant portion dedicated to securing the power needed for this infrastructure.
- The company’s commitment to more than double its datacenter footprint in the UK, announced in November 2023, exemplifies this new strategy, requiring a multi-gigawatt power procurement and infrastructure development plan that goes far beyond traditional data center operations.
- This shift is validated by the company’s development of custom, energy-efficient silicon like the Azure Maia 100 AI accelerator, a strategic move to control and optimize power consumption at the hardware level, thereby managing its escalating energy footprint.
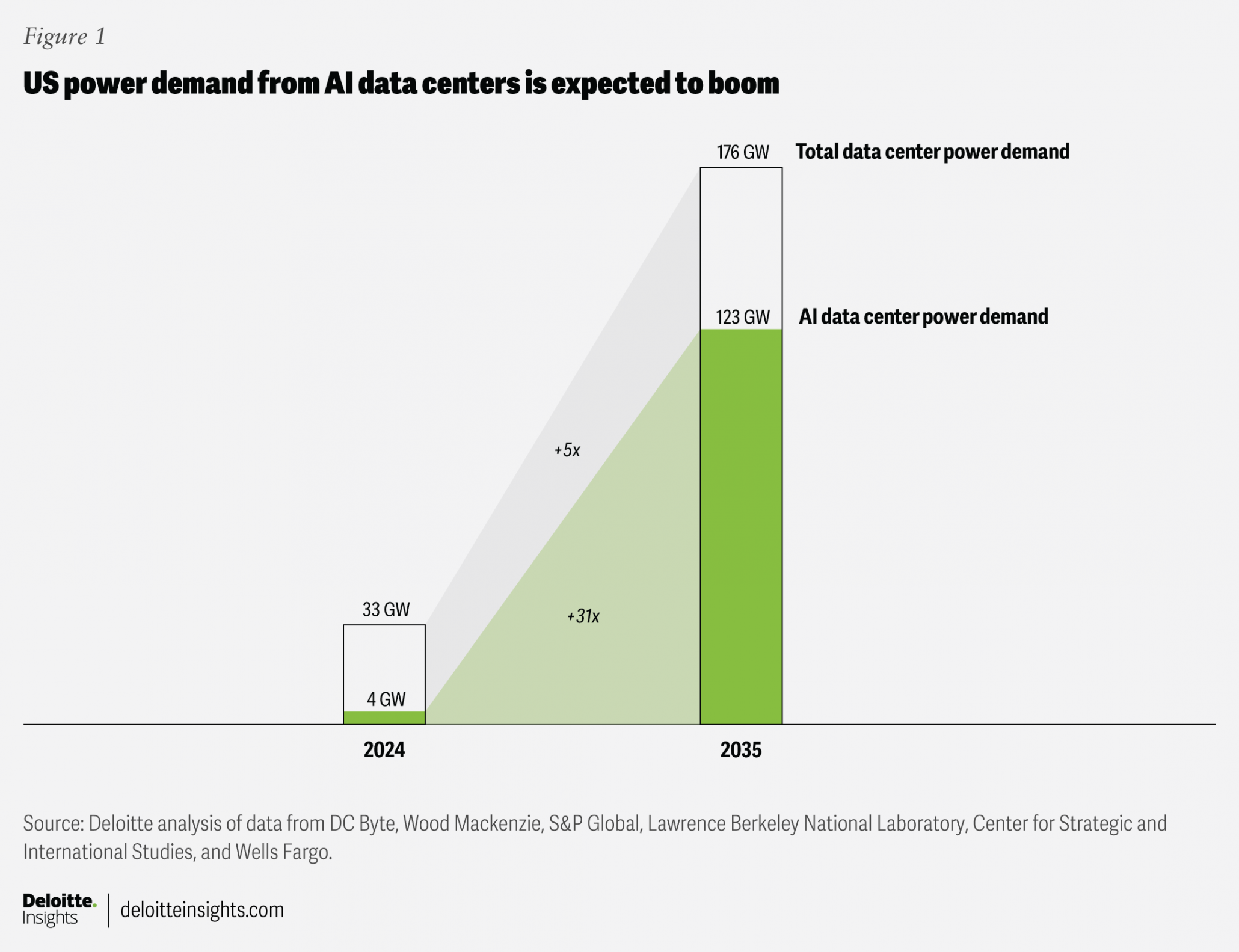
AI Power Demand to Increase 31-Fold
This chart quantifies the extreme surge in power demand from AI data centers, which is the primary driver behind Microsoft’s strategic shift toward securing energy infrastructure as described in the section.
(Source: Deloitte)
Microsoft’s Multi-Billion Dollar Investments Target AI Energy Infrastructure Bottlenecks
Microsoft’s investment strategy has evolved to directly finance the energy and data center infrastructure required to overcome physical supply chain limitations. The scale of these financial commitments demonstrates that securing power is now as critical as securing semiconductors for the company’s AI ambitions.
- The most significant financial signal is the September 2024 partnership with Global Infrastructure Partners, Black Rock, and MGX, which has a potential investment scale of $100 billion dedicated to building data centers and the supporting power infrastructure. This moves Microsoft from a consumer of power to a direct financier of energy generation and transmission.
- This initiative is part of a broader trend where hyperscalers like Microsoft are projected to invest a combined $225 billion in cloud and AI infrastructure. This level of capital expenditure is necessary to support the 33% average annual growth in data center capacity required for AI workloads through 2030.
- In November 2023, Microsoft announced a major investment to more than double its UK datacenter presence. This financial commitment necessitates a parallel investment in the region’s energy grid and generation capacity to support the new facilities.
Table: Microsoft’s Strategic Investments in AI and Energy Infrastructure
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Investment Partnership | September 2024 | A partnership with Global Infrastructure Partners, Black Rock, and MGX to invest in data centers and power infrastructure with a potential size of $100 billion. This initiative directly addresses the energy bottleneck for AI growth. | Global Infrastructure Partners, Black Rock, Microsoft, and … |
| UK Datacenter Expansion | November 2023 | A commitment to more than double its datacenter footprint in the United Kingdom. This investment is intrinsically tied to securing sufficient long-term power to operate the expanded infrastructure. | Our investment in AI infrastructure, skills and security to boost … |
Microsoft’s Strategic Alliances with Energy and Tech Firms Drive AI Infrastructure Growth
Microsoft is building a diverse ecosystem of partners across finance, energy, and technology sectors to de-risk its supply chain and secure the foundational inputs for its AI infrastructure. These alliances are crucial for navigating the complex bottlenecks in power availability and semiconductor supply.

Framework Outlines Critical AI Infrastructure Risks
This diagram identifies key supply chain risks like ‘Limited capacity bottlenecks’ and ‘Dependency on key supplier’. It directly contextualizes Microsoft’s strategy of forming diverse alliances to mitigate these exact threats.
(Source: ScienceDirect.com)
- The September 2024 partnership with infrastructure investment giants Global Infrastructure Partners and Black Rock is a clear strategic move. It allows Microsoft to leverage external capital and expertise to build out the energy generation and transmission assets required for its future data centers, a task outside its traditional core competency.
- To address the power consumption of its hardware, Microsoft is collaborating closely with its partner Open AI. The custom Azure Maia 100 AI accelerator was developed in collaboration with and tested by Open AI to optimize performance and energy efficiency for large language models.
- In a move to diversify its hardware supply and provide customers with alternatives, Microsoft announced in November 2023 that it would offer cloud instances based on AMD’s Instinct MI 300 X AI accelerators. This reduces its reliance on a single GPU supplier and introduces competitive pressure on performance and power efficiency.
- In February 2024, Microsoft partnered with Intel Foundry to use its 18 A process for a future chip. This alliance helps foster a competitive foundry market, creating a viable alternative to TSMC and securing a more resilient long-term semiconductor supply chain.
Table: Microsoft’s Key AI Infrastructure Partnerships
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Infrastructure Partners, Black Rock, MGX | September 2024 | Launched a partnership to invest in data centers and supporting power infrastructure, with a potential scale of $100 billion. This directly targets the energy bottleneck constraining AI growth. | Global Infrastructure Partners, Black Rock, Microsoft, and … |
| Intel Foundry | February 2024 | Microsoft will use Intel’s 18 A process for a custom chip design, strengthening Intel’s foundry business and diversifying the advanced semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem. | Intel Lays Out Process Roadmap to 2027, Announces New Foundry Customer |
| AMD | November 2023 | Announced plans to offer cloud instances powered by AMD’s Instinct MI 300 X accelerators. This diversifies hardware options for customers and reduces dependency on a single GPU provider. | Microsoft to offer AMD AI chips to cloud computing customers |
| Open AI | November 2023 | Unveiled the custom Maia 100 AI accelerator, developed and tested with Open AI to optimize hardware for large language models and improve power efficiency. | Microsoft ignites new era of AI with custom silicon and integrated systems |
Microsoft’s Geographic Expansion Strategy for AI Infrastructure Hinges on Power Availability
Microsoft’s global data center expansion, a core component of the AI Infrastructure Growth, is now geographically constrained by the availability of reliable and scalable power. The company’s site selection has shifted from a focus on low latency and land cost to a primary emphasis on regions with available grid capacity and pathways to new energy generation.

US AI Infrastructure Market Shows Rapid Growth
This chart highlights the rapid expansion of the U.S. AI infrastructure market. This growth underscores why North America, a region mentioned in the section, is a critical focus for Microsoft’s geographic expansion.
(Source: Grand View Research)
- Between 2021 and 2024, Microsoft’s geographic footprint expanded primarily in established data center markets in North America and Europe where connectivity and a customer base were already present.
- From 2025 onward, this strategy has been upended by the physical limitations of energy infrastructure. The commitment in November 2023 to more than double its data center footprint in the UK is a prime example of a large-scale regional investment now fundamentally tied to the ability to secure hundreds of megawatts, or even gigawatts, of new power.
- North America remains a critical region for expansion due to Microsoft’s corporate presence and customer base. However, data from Grid Strategies shows that surging data center demand is straining local grids, forcing Microsoft and its peers to seek new locations where utilities can accommodate their growth.
- The AI Infrastructure Growth is thus creating a new geographic calculus where future AI hubs will be determined not by proximity to users alone, but by proximity to massive power sources. This forces companies like Microsoft to engage directly with energy providers and governments in regions with development potential.
Microsoft’s Power Procurement Technology Matures from Commodity Buying to Strategic Infrastructure Investment
The technology of powering AI data centers has rapidly matured from a standard operational expenditure to a strategic, capital-intensive function involving direct investment in energy infrastructure and hardware innovation. This progression is a direct response to the AI Infrastructure Growth, where power has become the most significant physical constraint on scalability.

AI Infrastructure Market to Grow Explosively
The chart’s projection of explosive growth in the AI infrastructure market explains the strategic urgency behind Microsoft’s moves. This scale justifies shifting from commodity buying to direct infrastructure investment.
(Source: Research Nester)
- In the 2021-2024 period, the primary “technology” was the power purchase agreement (PPA), a financial instrument to procure renewable energy from existing or planned projects. The focus was on offsetting carbon footprint rather than securing raw gigawatts.
- From 2025 to today, the approach has become far more technologically and financially complex. The partnership with Global Infrastructure Partners and Black Rock represents a shift to investing in the physical construction of power generation and transmission assets, a far more direct and capital-intensive strategy.
- Technological maturity is also evident at the silicon level. The development of the custom Azure Maia 100 AI accelerator is a hardware-level intervention designed to manage and optimize power consumption, demonstrating a vertically integrated approach to addressing the energy challenge.
- The problem has matured from a procurement issue to a systems engineering challenge. It now involves balancing GPU deployments, custom silicon development, and direct investment in grid-scale energy projects to ensure that the pace of digital innovation is not stranded by the slower pace of physical infrastructure development.
Microsoft SWOT Analysis: Navigating the AI Infrastructure Growth Power Demands
Microsoft’s strategic position within the AI Infrastructure Growth is defined by its immense financial strength and market leadership, which it is leveraging to address the critical threat of energy and power bottlenecks. The company’s success depends on converting its opportunities in energy partnerships into a durable competitive advantage.
- Strengths: Microsoft possesses massive capital for investment and deep partnerships with technology leaders like Open AI and infrastructure investors like Black Rock.
- Weaknesses: The company has an extreme dependency on a public energy grid that was not designed for the concentrated, massive power demands of AI data centers.
- Opportunities: Microsoft has a unique opportunity to shape future energy markets by underwriting new generation projects and driving innovation in energy-efficient computing.
- Threats: The primary threat is the mismatch in timelines between rapid AI hardware deployment and the decade-long cycles required for new energy infrastructure development, creating risks of stranded assets.
Table: SWOT Analysis for Microsoft’s Role in the AI Infrastructure Growth
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2023 | 2024 – 2025 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Strong cloud market position (Azure) and substantial cash flow for general Cap Ex. | Leveraging a $225 B combined hyperscaler investment pool and strategic partnerships (Black Rock, GIP) to directly finance infrastructure. Development of custom silicon (Maia 100) for efficiency. | Changed from a passive cloud provider to an active builder of the underlying energy and hardware ecosystem. Validated that capital and partnerships are its key tools to overcome physical limits. |
| Weaknesses | Growing, but manageable, data center power consumption. Reliance on traditional utility contracts. | Exponential growth in power demand from AI (forecast to be 123 GW in the US by 2035 from 4 GW in 2025). Direct exposure to grid constraints and transformer shortages. | The scale of AI has turned a standard operational dependency (power) into a critical strategic vulnerability. The weakness is now a central focus of corporate strategy. |
| Opportunities | Opportunity to grow cloud market share and expand data center footprint in existing markets. | Opportunity to become a primary financier of new energy projects through its $100 B potential investment partnership. Ability to drive standards for energy-efficient AI hardware. | The energy bottleneck has created a new opportunity for Microsoft to enter and influence the energy infrastructure market, moving beyond its core software and cloud business. |
| Threats | Competition from other cloud providers (AWS, Google). Standard supply chain disruptions. | A fundamental mismatch between the rapid pace of AI development and the slow, multi-year process of building power plants and transmission lines. Risk of overbuilding and stranded assets if AI monetization lags Cap Ex. | The primary threat shifted from market competition to physical world constraints. Validated that the biggest risk to AI growth is the lack of power infrastructure, not a lack of chips. |
Future Outlook: Microsoft’s AI Success Hinges on Securing Energy Infrastructure
Microsoft’s ability to execute its AI strategy in 2025 and beyond will be determined by its success in securing and building out dedicated power infrastructure, a challenge that now outweighs the procurement of semiconductors. The company’s long-term competitive advantage in the AI race will be directly correlated to its ability to solve the energy equation through strategic, capital-intensive partnerships.

AI Infrastructure Market to Exceed $422B
This forecast shows the immense future value of the AI infrastructure market. It frames the high-stakes environment discussed in the outlook, where securing energy is key to capturing this future value.
(Source: Data Bridge Market Research)
- The most critical forward-looking indicator is the execution of the partnership with Global Infrastructure Partners and Black Rock. The deployment of capital from this $100 billion initiative into tangible power generation and transmission projects will be the ultimate validation of Microsoft’s energy strategy.
- Continued investment in custom silicon, such as successors to the Maia 100 chip, will be essential for managing operational costs and mitigating the impact of rising electricity demand. Progress in performance-per-watt will be a key metric of success.
- The company’s ability to navigate regulatory and permitting hurdles for new energy and data center projects will dictate the pace of its expansion. Success in regions like the UK will provide a template for future developments globally.
- Ultimately, Microsoft’s actions show that the frontier of AI innovation is no longer just in software, but in the steel, copper, and concrete of the global energy system. Tracking these infrastructure plays is essential to understanding the true trajectory of the AI economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Microsoft now focusing so heavily on securing power instead of just building data centers?
Microsoft is focusing on power because the explosive growth of AI has created extreme energy demands that traditional power grids cannot meet. AI workloads require specialized, power-intensive hardware, making energy availability the primary bottleneck for expansion. This has forced Microsoft to shift from a real estate-centric strategy to an energy-centric one, where securing multi-gigawatt power sources is more critical than just acquiring land and space.
What is Microsoft’s single largest initiative to address this energy bottleneck?
The most significant initiative is the September 2024 partnership with Global Infrastructure Partners, Black Rock, and MGX. This partnership has a potential investment scale of $100 billion and is aimed at directly financing and building the necessary data centers and, crucially, the supporting power generation and transmission infrastructure required for Microsoft’s AI ambitions.
How is Microsoft trying to control energy consumption at the hardware level?
Microsoft is developing its own custom, energy-efficient silicon to manage power consumption directly. The company unveiled its Azure Maia 100 AI accelerator, which was designed in collaboration with OpenAI to optimize performance and power efficiency specifically for large language models, giving Microsoft more control over its escalating energy footprint.
What is the biggest risk or threat to Microsoft’s AI infrastructure growth?
The primary threat is the mismatch in timelines between the rapid deployment of AI technology and the much slower, multi-year process of developing and building new energy infrastructure like power plants and transmission lines. This gap creates a risk that Microsoft could build data centers that lack sufficient power, leading to stranded assets and a bottleneck for its AI growth.
Besides investing in power, what other partnerships is Microsoft making to support its AI infrastructure?
Microsoft is diversifying its technology supply chain through key partnerships. It announced it will offer cloud services using AMD’s Instinct MI300X AI accelerators to reduce dependency on a single GPU provider. Additionally, it is partnering with Intel Foundry to manufacture a future custom chip, helping to foster a more competitive and resilient semiconductor manufacturing ecosystem.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

