PG&E Grid Expansion 2026: The $73 Billion Plan to Power AI Data Centers
Industry Risks: From Manageable Growth to Exponential Demand Overload
Pacific Gas and Electric’s strategic focus shifted from accommodating predictable load growth before 2025 to managing an unprecedented and volatile surge in data center power requests, forcing a fundamental overhaul of its infrastructure planning and risk management. The velocity of new demand requests exposed the limitations of the existing grid and interconnection processes, creating a critical bottleneck for the technology sector’s expansion.
- Prior to 2025, PG&E‘s forecasts handled data center growth as part of a broader 1-3% annual load increase, with plans for 3.5 GW of new capacity through 2029. This was considered a significant but manageable challenge within existing capital planning cycles.
- Beginning in February 2025, the demand pipeline exploded, jumping from 5.5 GW to a peak of 10 GW by July 2025. This represented a near-tripling of projected demand in less than six months, overwhelming previous infrastructure assumptions.
- The scale of individual requests also intensified, with the City of San José alone accounting for 2, 000 MW (2 GW) of new demand. This concentrated load, capable of tripling the city’s total energy use, introduced localized grid stability risks that were not a primary concern in the 2021-2024 period.
- This new demand profile proved volatile, with the pipeline contracting to 9.5 GW by November 2025 due to project attrition. This introduced a new risk: building costly infrastructure for speculative projects that may not materialize, a risk directly addressed by new CPUC rules requiring customer-funded upfront costs.
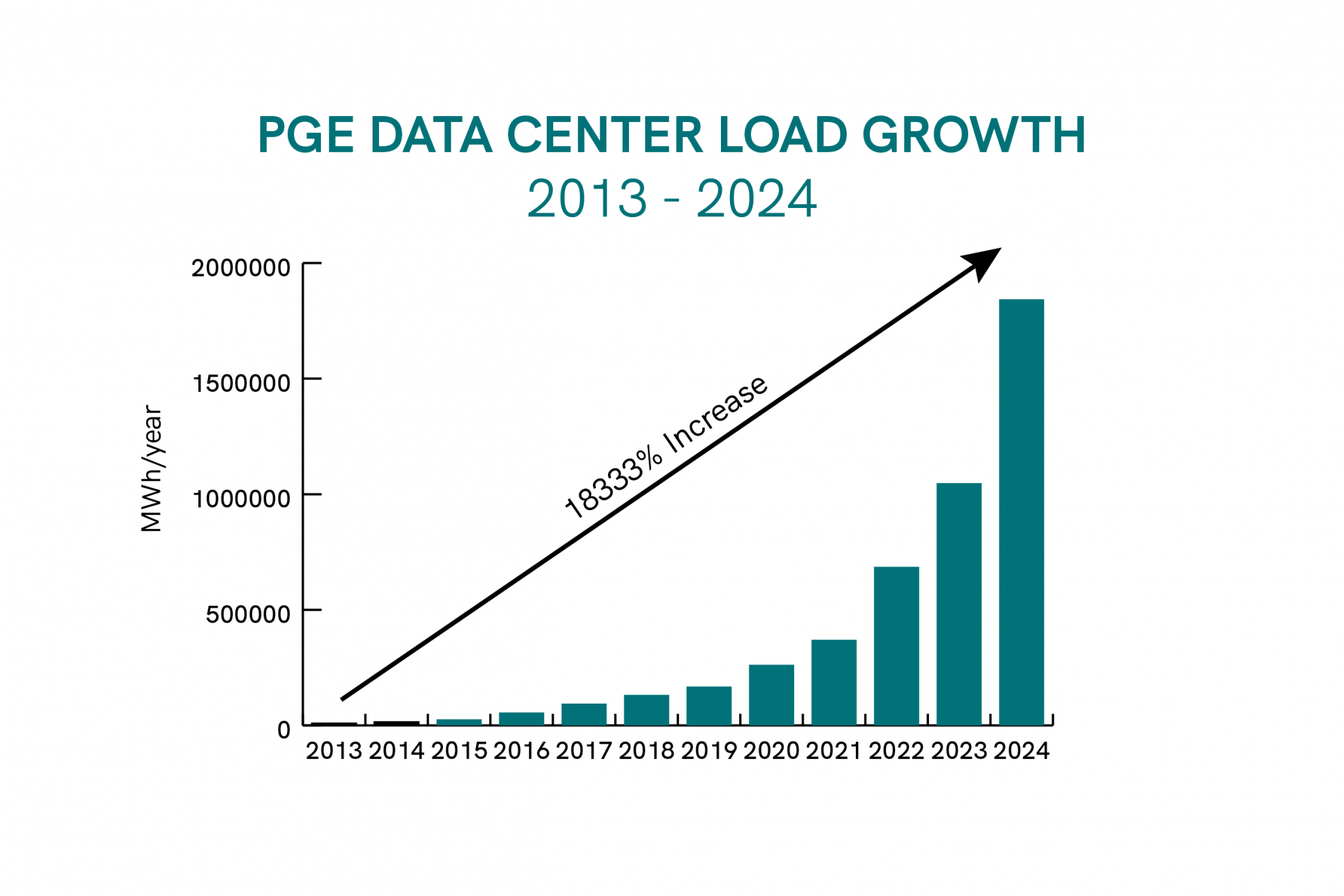
PG&E Data Center Demand Soars 18,333%
This chart perfectly illustrates the section’s theme of ‘exponential demand overload,’ showing the dramatic surge in PG&E’s specific data center load that created the crisis.
(Source: Oregon Citizens’ Utility Board)
Investment Analysis: A Pivot to a $73 Billion Data Center-Focused Capital Plan
PG&E‘s capital strategy transformed from a broad $62 billion grid modernization plan in 2024 to a highly targeted $73 billion investment framework announced in 2025, designed specifically to support the 10 GW data center demand pipeline. This shift reflects a strategic decision to use the AI boom as the primary driver and funding mechanism for a generational upgrade of its transmission and distribution systems.
- In the 2021-2024 period, capital allocation was driven by diverse needs including wildfire mitigation and general electrification. In November 2024, PG&E added $1 billion to its five-year plan in an early response to growing demand.
- The announcement of the $73 billion capital plan in September 2025 marked a definitive pivot. The investment is explicitly linked to building out transmission and infrastructure for data centers, estimated to cost between $500 million and $1.6 billion for every 1, 000 MW of new capacity.
- To fund this massive expenditure without overburdening ratepayers, PG&E secured a conditional $15 billion loan guarantee from the U.S. Department of Energy in December 2024 and pursued strategic asset monetization, including the sale of a minority stake in its generation portfolio to KKR.
Table: PG&E’s Capital Strategy to Support Data Center Growth
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid Infrastructure Upgrade Plan | September 2025 | Announced a $73 Billion capital plan by 2030 for transmission and grid upgrades, directly targeting the new 10 GW data center load. | Reuters |
| DOE Loan Guarantee | December 2024 | Secured a conditional commitment for a $15 Billion federal loan to finance hydropower, battery storage, and transmission upgrades essential for data center capacity. | Power Magazine |
| Capital Plan Increase | November 2024 | Increased the 2024-2028 capital plan by $1 Billion (to $62 Billion total) in an initial response to rising customer demand, including from data centers. | PG&E Corp. |
| KKR Strategic Partnership | April 2024 | Entered talks to sell a minority stake in its $3.5 Billion non-nuclear generation portfolio to KKR to raise capital for grid investments. | PG&E Corp. |
Partnership Dynamics: Alliances to Accelerate Grid Interconnection
Since 2025, PG&E has initiated a series of high-stakes partnerships with municipalities, technology providers, and developers to accelerate infrastructure deployment, a strategic shift from the more conventional utility-customer relationships of the past. These collaborations are designed to de-risk investments, streamline regulatory approvals, and pilot new technologies to expand grid capacity faster than traditional methods allow.
- The landmark agreement with the City of San José in July 2025 provides power delivery guarantees to attract data centers, a first-of-its-kind municipal partnership aimed at securing San José’s position as a primary data center hub. The first project under this deal, Equinix‘s SV 12 x data center, was energized in January 2026.
- A collaboration with developer Westbank, announced in November 2024 and advanced in 2025, integrates 200 MW of data centers with 4, 000 residential units. This project pioneers a district energy system to repurpose waste heat, transforming data centers into a community energy asset.
- To maximize existing infrastructure, PG&E partnered with Smart Wires in May 2025 to deploy advanced power flow controls. This technology enhances capacity on current lines, providing a faster, non-wires alternative to meet immediate demand in San José while larger projects are built.
- Collaboration extended to industry-wide initiatives like the DCFlex program with EPRI, Google, and NVIDIA in October 2024. This initiative seeks to standardize methods for data centers to provide grid flexibility, a concept that was largely theoretical before the recent demand surge.
Table: Key PG&E Partnerships for Data Center Expansion
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equinix | January 2026 | Energized the SV 12 x data center, the first project completed under the historic agreement with the City of San José to streamline new connections. | Silicon Valley |
| City of San José | July 2025 | Established an agreement to provide power delivery guarantees and streamline connections for nearly 2, 000 MW of new data center demand. | Silicon Valley Business Journal |
| Smart Wires | May 2025 | Partnered to deploy advanced power flow control technology to enhance grid capacity and reliability for data centers on existing infrastructure. | PG&E Corp. |
| Westbank | April 2025 | Began infrastructure upgrades for a net-zero community integrating 200 MW of data centers with residential units, pioneering waste heat reuse. | Peterson Group |
Geography: Hyper-Concentration of Demand in Silicon Valley
The geography of data center demand has become acutely concentrated within PG&E‘s service area, with San José emerging as the undisputed epicenter for new large-scale power requests since 2025. This hyper-localization transforms the challenge from a system-wide issue to a critical, sub-regional infrastructure bottleneck requiring targeted, surgical investment.

Power Costs in San Jose to Outpace Rivals
This chart quantifies the economic impact in the exact geography—San Jose—that the section identifies as the ‘undisputed epicenter’ of hyper-concentrated demand.
(Source: Prime Data Centers)
- Between 2021 and 2024, data center growth was present but more distributed across Northern California. The focus was on system-wide capacity planning and accommodating a mix of industrial and high-tech customers.
- From 2025 onward, activity consolidated dramatically around Silicon Valley. San José alone generated requests for 2 GW of new power, making it the focal point of PG&E‘s entire data center strategy.
- The utility’s landmark agreement with the City of San José and targeted technology deployments like with Smart Wires are direct responses to this geographic concentration, aiming to solve localized constraints.
- This contrasts with other major data center markets like Northern Virginia, where growth is spread across a larger regional transmission organization (PJM). PG&E‘s challenge is more acute due to the density of demand in a single utility’s territory with high electricity costs and complex regulations.
Technology Maturity: Grid Modernization Moves from Pilot to Commercial Imperative
The post-2025 demand surge accelerated the maturity of advanced grid technologies and innovative project models, moving them from pilot or niche applications to commercially essential tools for managing grid constraints. Before this period, solutions like advanced power flow control and waste heat recovery were largely in research or small-scale trials; they are now central to PG&E‘s strategy for connecting gigawatts of new load.
- During the 2021-2024 timeframe, PG&E‘s technology focus was on internal process automation with tools like Microsoft Power Apps and early explorations into AI for grid management.
- The partnership with Smart Wires in May 2025 marks a key inflection point, deploying advanced power flow controls as a commercial solution to unlock capacity on existing transmission lines for data centers, providing a faster alternative to new construction.
- The Westbank project, advanced in 2025, moves the concept of data center waste heat recovery from a theoretical benefit to a core component of a large-scale, net-zero urban development, proving its commercial viability.
- Similarly, the launch of the DCFlex initiative with EPRI in October 2024 shows a shift toward standardizing data center participation in grid services, a level of integration that was not a priority when load growth was more modest.
SWOT Analysis: PG&E Data Center Grid Expansion
PG&E‘s strategic position has evolved from leveraging its location in a tech hub to actively shaping the region’s energy future, a move that introduces substantial new opportunities but also magnifies execution and financial risks. The analysis below contrasts the utility’s position before and after the 2025 AI-driven demand shock.

Data Centers Drive Widening Grid Demand Gap
This chart visualizes the fundamental ‘demand shock’ that prompted the SWOT analysis, showing the growing gap between total load and load without data centers for PG&E.
(Source: Oregon Citizens’ Utility Board)
Table: SWOT Analysis for PG&E and Data Centers
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Incumbent utility in Silicon Valley with an established, albeit aging, transmission network. Experience managing large industrial loads. | Proactive engagement with data center operators, creating “anchor tenant” demand. First-mover advantage with innovative partnerships (City of San José, Westbank). | The AI boom validated the strategic value of PG&E‘s location, transforming it from a service provider into an indispensable infrastructure partner for the world’s largest tech companies. |
| Weaknesses | High electricity rates ($0.17/k Wh) compared to regional competitors. Aging infrastructure requiring significant capital for modernization and wildfire hardening. | Massive $73 billion capital requirement introduces immense execution risk. Long lead times for permitting and building new transmission remain a key constraint. | The weakness of an aging grid became an opportunity for a complete overhaul, but the scale of investment required now represents the single largest point of failure. |
| Opportunities | General load growth from transportation and building electrification. Pilot new grid technologies. | Leverage data center demand to subsidize grid-wide upgrades and potentially lower rates for all customers (projected 1-2% reduction per GW). Pioneer new utility business models. | The opportunity shifted from incremental modernization to a generational, AI-funded infrastructure build-out. The “anchor tenant” model was validated as a viable strategy. |
| Threats | Regulatory scrutiny from the CPUC. Wildfire liability. Competition from municipal utilities like Silicon Valley Power. | Significant project attrition from the 9.5 GW pipeline could leave ratepayers with stranded assets. Demand surge may conflict with state decarbonization goals. | The primary threat shifted from operational and liability issues to large-scale strategic risk: committing billions to a demand forecast that proves volatile. Regulatory mechanisms to mitigate this risk (upfront payments) were established. |
Scenario Modelling and 2026 Outlook
If PG&E successfully executes the first phase of its $73 billion plan and connects a significant portion of the 3.6 GW of projects in late-stage engineering, it will validate its “anchor tenant” model, likely attracting further investment and locking in its role as the primary energy partner for the AI industry. Watch for quarterly earnings reports and CPUC filings detailing capital deployment and interconnection progress. These could be happening: accelerated deployment of grid-enhancing technologies and new tariff proposals for large-load customers.

Demand Forecasts Show Multiple Growth Scenarios
Matching the ‘Scenario Modelling’ heading, this chart explicitly visualizes four different potential futures for demand growth, highlighting the uncertainty and range of possibilities discussed.
(Source: POWER Magazine)
- The most critical signal to watch in 2026 is the conversion rate of the 3.6 GW of data center projects currently in the final engineering phase. Successful and timely energization, following the Equinix SV 12 x project, will confirm execution capability.
- Monitor the stability of the overall 9.5 GW demand pipeline. Any further significant attrition (more than 5-10%) could signal a cooling of the AI build-out or a shift to other regions, challenging the economic basis of the investment plan.
- Track regulatory decisions from the CPUC regarding cost recovery for the $73 billion plan and the application of new rules requiring upfront payments from large customers. Favorable rulings are essential for maintaining financial stability.
- Observe the progress of innovative partnerships like the Westbank net-zero community. Milestones in this project will signal the market’s willingness to adopt integrated energy models beyond standard grid connections.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why did PG&E launch a $73 billion grid expansion plan?
The plan is a direct response to an unprecedented surge in power demand from AI data centers. The demand pipeline exploded from a manageable level to a peak of 10 GW by July 2025, overwhelming previous infrastructure forecasts and forcing a massive, targeted investment to upgrade the grid.
How is PG&E funding this massive investment without overburdening its regular customers?
PG&E is using a multi-pronged funding strategy. This includes securing a conditional $15 billion loan guarantee from the U.S. Department of Energy, raising capital by selling a minority stake in its generation portfolio to KKR, and implementing new CPUC rules that require data centers to make customer-funded upfront payments for the infrastructure they require.
What is the biggest risk associated with this plan?
The primary risk is project attrition. The demand pipeline has proven volatile, and there is a threat that PG&E could invest billions in building costly infrastructure for speculative data center projects that may not materialize. This could potentially leave ratepayers with the cost of unused or “stranded” assets, a risk the utility is trying to mitigate with upfront customer payments.
Where is this new data center power demand concentrated?
The demand is hyper-concentrated in Silicon Valley, with the City of San José emerging as the clear epicenter. San José alone accounts for 2,000 MW (2 GW) of new power requests, transforming the challenge from a system-wide issue to a critical, sub-regional infrastructure bottleneck that requires targeted investment.
How is PG&E accelerating the process of connecting new data centers to the grid?
Instead of relying only on building new lines, PG&E is using innovative partnerships and technology. This includes a landmark agreement with the City of San José to streamline connections, deploying advanced power flow control technology from Smart Wires to maximize capacity on existing lines, and collaborating on projects like the Westbank development to pioneer waste heat reuse.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Bloom Energy SOFC 2025: Analysis of AI & Partnerships
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

