EV Manufacturing Under Pressure: Why Automakers Are Reversing Billions in Investment for 2026
EV Adoption Risk: Automakers Face a Market Correction as Growth Stalls in 2026
The electric vehicle industry has transitioned from a period of hyper-growth and aggressive investment to a significant market recalibration, forcing automakers to confront stalling demand and reverse ambitious production plans. What was a race to announce multi-billion dollar EV factories between 2021 and 2024 has become a strategic retreat characterized by massive financial writedowns and production delays from 2025 to today. This shift exposes the financial risk of misjudging the pace of mainstream consumer adoption.
- From 2021 to 2024, automakers announced over $330 billion in EV and battery investments, driven by strong policy support like the Inflation Reduction Act, which spurred $52 billion in North American supply chain commitments. In contrast, by early 2026, the industry absorbed at least $65 billion in losses and writedowns as companies scaled back those same plans.
- The earlier period saw a focus on securing future capacity, with companies like Ford and GM committing to an all-electric future. However, by late 2025, consumer demand failed to meet these forecasts, evidenced by the U.S. retail EV market share collapsing to 6.6% in December 2025 from 11.2% a year prior.
- The initial strategy was predicated on rapid, continuous growth, with global EV sales expanding quickly post-pandemic. The current reality reflects a sharp deceleration, with global EV registrations falling 3% year-over-year in January 2026 and the U.S. market forecast to contract by 15% in 2026.
- This downturn forced a strategic pivot across the industry, resulting in over 50, 000 job cuts in the U.S. auto sector since mid-2025 and causing market leader Tesla to report its first annual revenue drop as it shifts focus to AI and robotics.
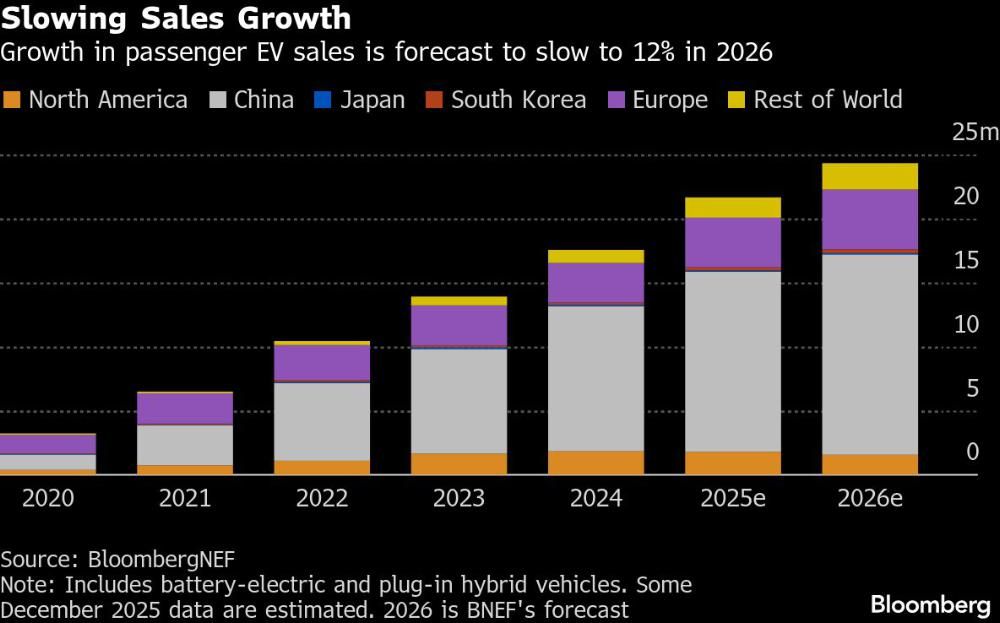
Global EV Sales Growth Forecast to Slow
This chart supports the section’s core thesis by showing that while total sales volume rises, the rate of growth is projected to slow to 12% in 2026. This visualizes the market recalibration and stalling growth described in the text.
(Source: Financial Post)
Investment Cancellations: Carmakers Book Over $65 Billion in Writedowns Amid EV Slowdown
Massive financial writedowns and investment pullbacks are now the defining features of legacy automakers’ EV strategies, as the cost of the transition proves far greater and the timeline to profitability far longer than initially projected. The bullish announcements of the early 2020 s have given way to stark financial realities in 2025 and 2026, with companies publicly acknowledging billions in losses tied directly to their EV divisions and scaling back future capital expenditure.
- Ford‘s pivot illustrates the severe financial strain, with its “Model e” EV unit now projected to incur costs of $20.9 billion through 2027. After announcing major investments in prior years, the company took a $19.5 billion charge in late 2025 to scale back its EV plans.
- General Motors executed a significant reversal, announcing a $6 billion writedown in January 2026 as part of a total $7.6 billion hit to its EV business. This followed an earlier $1.6 billion charge in late 2025, signaling a rapid deterioration in its EV outlook.
- Stellantis recorded the largest single financial impact, booking €22.2 billion ($27 billion) in writedowns in the second half of 2025. This move reflects a deep strategic realignment away from its previous, more aggressive EV targets.
- Japanese automakers are also impacted, with Honda forced into a strategic overhaul after its EV-related losses and expenses mounted to ¥267.1 billion ($1.71 billion) in the nine months leading up to December 31, 2025.
Table: Automaker Financial Writedowns and Strategic Pullbacks (2025-2026)
| Company / Group | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Carmakers | Feb 2026 | The industry collectively absorbed at least $65 billion in financial hits from reversing previous EV ambitions and scaling back production plans. | City AM |
| Stellantis | Feb 2026 | Booked $27 billion (€22.2 billion) in writedowns in the second half of 2025, signaling a major pullback from its prior EV investment strategy. | Reuters |
| Ford | Dec 2025 – Feb 2026 | Took a $19.5 billion charge to scale back EV plans and now projects its EV pivot will cost $20.9 billion through 2027. | Automotive News |
| General Motors | Oct 2025 – Jan 2026 | Sustained a total $7.6 billion hit to its EV business, including a $6 billion writedown on its EV pullback announced in January 2026. | American Bazaar Online |
| Honda | Feb 2026 | Accumulated $1.71 billion in EV-related losses and expenses in the nine months to Dec 31, 2025, forcing a major strategic review. | Automotive News |
Geographic Analysis: US and China Lead EV Market Slowdown in 2026
The electric vehicle market slowdown is a global phenomenon, with the two largest markets, the United States and China, exhibiting the most significant signs of cooling demand in 2026. Between 2021 and 2024, both regions were epicenters of rapid growth, fueled by subsidies and policy mandates. However, by late 2025, the expiration of incentives and persistent affordability issues triggered a sharp reversal, fundamentally altering the global growth trajectory.

Analysts Slash US EV Market Growth Projections
This chart directly supports the geographic analysis of a US market slowdown by showing that 2025 sales projections have been cut significantly. The specific data on declining California sales and Tesla deliveries reinforces the section’s claims.
(Source: S&P Global)
- The U.S. market is experiencing a contraction, with a forecast 15% decline in EV sales for 2026. This is a direct consequence of the expiration of up to $7, 500 in consumer tax credits in late 2025, which had previously propped up demand.
- China, the world’s largest EV market, is also facing headwinds. After years of explosive growth, sales are expected to slow to just 1% growth in 2026 due to the introduction of a new purchase tax and a reduction in government subsidies.
- In January 2026, the impact of these slowdowns became clear as global EV registrations fell by 3% year-over-year. This marked a significant departure from the double-digit growth rates that characterized the 2021-2024 period.
- While some regions show resilience, such as Canada maintaining its long-term targets, the cooling in the U.S. and China is the primary driver of the global “EV winter” and the resulting financial distress for automakers dependent on these key markets.
Technology Maturity: Carmakers Pivot to Hybrids as Full-EV Strategy Falters
The 2026 market correction is forcing a pragmatic technological pivot away from a singular focus on battery electric vehicles (BEVs) toward a renewed emphasis on hybrid technology. Between 2021 and 2024, the dominant strategy for legacy automakers was to declare an “all-in” commitment to BEVs to compete with Tesla. The current market reality has validated that a multi-powertrain approach, leveraging profitable hybrids as a bridging technology, is essential for financial stability during the transition.
- The prior era was defined by automakers like GM and Ford setting aggressive timelines to phase out internal combustion engines entirely. By 2026, these same companies are delaying EV models and reintroducing or expanding hybrid options to meet consumer demand for affordable, practical vehicles without range anxiety.
- The financial losses associated with BEV-only divisions, such as Ford‘s “Model e” unit losing billions, have made the profitability of hybrids strategically critical. Hybrid sales are now expected to account for 34% of all passenger vehicles sold by 2034, a significant upward revision.
- This shift is not an abandonment of electrification but a recalibration of the timeline. Automakers are now focusing on developing cheaper, next-generation EV platforms, like BMW‘s “Neue Klasse, ” while using hybrid sales to fund the long-term R&D and bridge the gap until BEVs reach price parity with ICE vehicles.
- The market is rewarding this pragmatism. Companies that can effectively scale hybrid production are better positioned to navigate the 2026-2028 period, while those who remain over-leveraged to a stalled BEV market face continued financial pressure.
SWOT Analysis: Navigating the EV Market Correction in 2026
The electric vehicle market has moved from a supply-constrained, high-growth phase to a demand-constrained correction, fundamentally altering the strategic calculus for automakers. The strengths and opportunities of the 2021-2023 period, centered on policy-driven growth, have been replaced by a focus on managing financial weaknesses and mitigating new market threats in 2024-2025 and beyond.
- Strengths have shifted from investment capacity to operational resilience, with profitability from legacy ICE and hybrid vehicles now a critical advantage to fund the costly EV transition.
- Weaknesses are no longer about the high cost of R&D but the direct, multi-billion-dollar operational losses from unprofitable EV divisions.
- Opportunities have moved from capturing premium early adopters to developing affordable mass-market EVs and capturing share in the resurgent hybrid market.
- Threats have evolved from supply chain shortages to a combination of weakening consumer demand, high interest rates, and intense price competition from vertically integrated players like BYD.
Table: SWOT Analysis for the EV Market Transition (2021-2026)
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2023 | 2024 – 2025 | What Changed / Validated by 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Strong policy support (U.S. Inflation Reduction Act); High investor appetite for EV growth stories; Automakers announced $330 B+ in EV investments. | Established manufacturing scale and brand loyalty; Profitable legacy ICE and hybrid vehicle portfolios generating cash flow. | The ability to generate profits from non-EV segments was validated as a critical strength for surviving the cash burn of unprofitable EV divisions. |
| Weaknesses | High battery costs preventing price parity with ICE; Lack of profitable, high-volume EV platforms; Reliance on government subsidies to drive sales. | EV divisions posting massive losses (Ford‘s “Model e” losing $5.5 B); High inventory of unsold, expensive EVs; Inability to match the cost structure of EV-native companies. | The core weakness shifted from a future profitability challenge to a present-day financial crisis, forcing writedowns and strategic reversals. |
| Opportunities | Capturing the early adopter market with premium EVs; Securing government grants and incentives for new battery and assembly plants. | Developing and launching affordable, mass-market EVs (sub-$35, 000); Expanding market share in the resurgent hybrid segment. | The primary opportunity shifted from high-margin premium sales to achieving scale and profitability in the mainstream market, including hybrids. |
| Threats | Battery raw material shortages and supply chain disruptions; Slow build-out of public charging infrastructure. | Sustained high interest rates suppressing consumer demand; The expiration of key government subsidies; Intense price competition from Chinese automakers like BYD. | The dominant threat moved from supply-side constraints to demand-side destruction and heightened competition, leading to an “EV winter.” |
Scenario Modelling: 2026 Recovery Hinges on Affordable Models and Economic Stability
If automakers can successfully launch a new generation of affordable EVs by late 2026 and the macroeconomic environment improves, the market could begin a sustainable recovery in 2027. Watch for automakers to aggressively market hybrid models as a primary profit driver to fund this next phase of the transition. These could be the early signals of a market finding its equilibrium after the current correction.

Long-Term EV Growth Projected Despite Current Slowdown
This chart perfectly illustrates the recovery scenario by showing a long-term adoption S-curve. It acknowledges the current slow growth but projects significant acceleration later, matching the section’s theme of a future rebound.
(Source: Inside Climate News)
- A key signal to watch is the market reception of cheaper EVs planned for late 2026 and 2027. The sales volumes for these models will confirm whether affordability was the primary barrier to mass adoption.
- Monitor central bank interest rate decisions. A reduction in rates would immediately improve vehicle affordability and act as a significant tailwind for the entire auto industry, including EVs.
- Track the sales velocity of hybrid vehicles. Continued strong growth in hybrid sales, projected to reach 34% of the market, would confirm that a multi-powertrain strategy is the most viable path to profitability for legacy automakers in the near term.
- The pace of public charging infrastructure deployment remains a critical enabler. Government programs aiming to expand networks, like Canada’s plan to double investment to $1.5 billion, are essential for alleviating consumer range anxiety and supporting the next growth wave.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are major automakers pulling back on their multi-billion dollar EV investments?
Automakers are reversing their investments because the growth in consumer demand for EVs has stalled significantly, failing to meet earlier aggressive forecasts. This slowdown is driven by persistent high vehicle prices, high interest rates, the expiration of key government subsidies (like the $7,500 U.S. tax credit), and consumer concerns like range anxiety. This has led to a “market correction” after a period of hyper-growth.
What is the financial impact of this EV slowdown on car companies?
The financial impact has been massive. By early 2026, the industry collectively absorbed at least $65 billion in financial writedowns and losses from scaling back EV plans. Specific examples from late 2025 and early 2026 include Stellantis booking a $27 billion writedown, Ford taking a $19.5 billion charge, and General Motors sustaining a $7.6 billion hit to its EV business.
With the all-electric strategy faltering, what technology are carmakers focusing on now?
Carmakers are making a strategic pivot toward hybrid vehicles. They are reintroducing and expanding their hybrid lineups to meet consumer demand for affordable and practical options without range anxiety. Hybrids are now seen as a critical “bridging technology” that generates profits to fund the long-term development of cheaper, next-generation battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
Is the decline in EV sales a global problem?
Yes, the slowdown is a global phenomenon, but it is most pronounced in the world’s two largest EV markets: the United States and China. The U.S. market is forecast to contract by 15% in 2026 following the expiration of consumer tax credits. Similarly, China’s market growth is expected to slow to just 1% due to subsidy reductions and new taxes. This cooling in the two biggest markets is the primary driver of the global “EV winter.”
What could lead to a recovery in the EV market?
According to the analysis, a market recovery hinges on several factors. The most critical are the successful launch of more affordable mass-market EVs, an improvement in the macroeconomic environment such as lower interest rates to make financing cheaper, and the continued build-out of public charging infrastructure to alleviate range anxiety. Strong hybrid sales are also a key indicator of automakers’ ability to fund this transition.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

