Mega Battery Technology in 2026: How LFP and Integrated Systems Are Dominating Grid-Scale Storage
BESS Project Evolution: From Custom Builds to Standardized Mega-Systems
The utility-scale Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) market has decisively shifted from customized project engineering to the deployment of standardized, factory-built “blocks, ” a change driven by the need for faster installation and improved system economics. This productization strategy, which accelerates project timelines and reduces costs, signals a mature industrial process replacing the bespoke solutions that characterized the market before 2024.
- In the 2021-2024 period, the primary technology shift was chemical, with companies like Tesla announcing in 2021 their move to Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) chemistry for stationary storage. This set the stage for cost reductions and improved safety but projects were still largely engineered on a site-by-site basis.
- The 2025-2026 period is defined by physical integration. Tesla launched its Megablock in September 2025, a pre-packaged 20 MWh system that combines multiple battery units and a transformer. This approach minimizes on-site construction and standardizes grid connection.
- Similarly, CATL announced in May 2025 its TENER Stack, a 9 MWh system, for mass production. In January 2026, a 400 MWh station using EVE Energy’s ultra-large 628 Ah cells went into operation in China, showing that high-density, containerized solutions are now commercially active at a massive scale.
- The emergence of alternative chemistries in standardized formats is also a key signal. In August 2025, Peak Energy launched and shipped the first grid-scale sodium-ion BESS in the U.S., showing that the productization trend extends beyond lithium-ion.
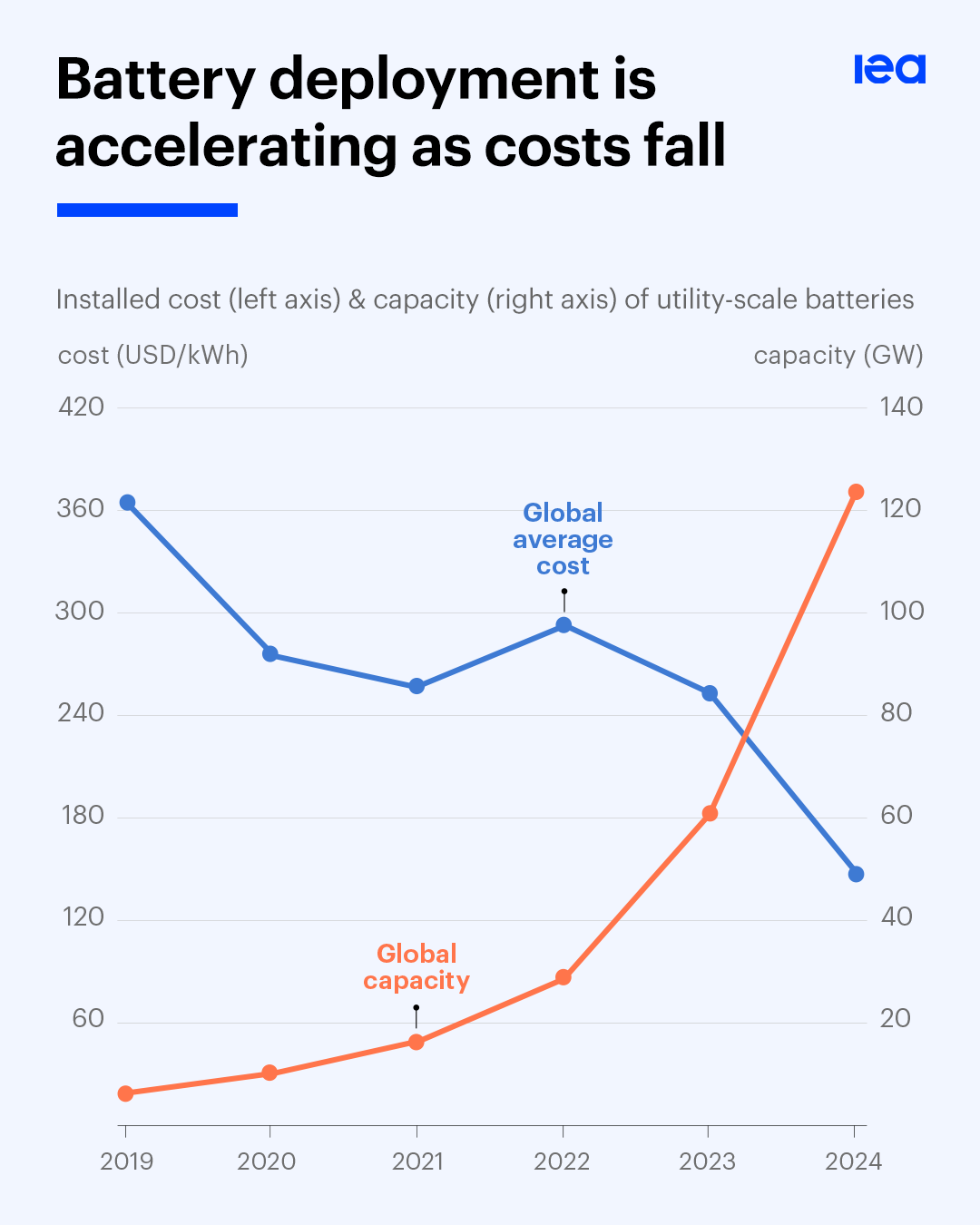
Falling Costs Fuel Exponential Battery Deployment
This chart visualizes the section’s key point, showing how falling costs, driven by standardization, directly correlated with soaring global deployment capacity between 2019 and 2024.
(Source: LinkedIn)
Investment Analysis: Capital Follows Technology Integration and AI Demand
Investment patterns in 2025 and 2026 confirm that capital is flowing toward integrated BESS technologies and the companies that supply them, driven by the new, power-hungry AI data center market. Unlike earlier funding rounds that focused on broad renewable projects, recent major investments specifically target battery technology manufacturers, recyclers, and large-scale deployments that leverage standardized systems like Tesla Megapacks.
- Norway’s sovereign wealth fund signaled its entry into the battery storage market in February 2026, targeting projects with a minimum investment of approximately $1.2 billion each. This indicates that BESS is now viewed as a stable, large-scale infrastructure asset class by the world’s most conservative investors.
- The link between AI and battery demand was validated in January 2026 when Google participated in a $425 million capital raise for Redwood Materials, a battery recycling and materials provider. This strategic investment is designed to secure the supply chain for the massive energy storage required to power AI compute infrastructure.
- Project financing now favors standardized technology. A $500 million financing package was secured in December 2025 for a large California battery project explicitly built with Tesla Megapacks, demonstrating funder confidence in the reliability and economic performance of productized solutions.
Table: Selected Major Investments in Battery Storage (2025-2026)
| Investor / Company | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Norway’s Sovereign Wealth Fund | 2026-02-16 | Signaled intent to make large-scale BESS investments, with a minimum of $1.2 Billion per project, treating it as a core infrastructure asset. | ess-news.com |
| 2026-01-28 | Participated in a $425 Million capital raise for Redwood Materials to secure the battery recycling supply chain, linking tech giant demand directly to energy storage infrastructure. | esgtoday.com | |
| Kyuden International Corp. | 2026-01-08 | Invested in Spearmint Energy to support the development of 400 MWh of BESS capacity in the Texas (ERCOT) market, a key growth region for grid services. | energyglobal.com |
| Various (Project Financing) | 2025-12-17 | $500 Million in financing was raised for a large California battery project powered by Tesla Megapacks, validating the bankability of standardized systems. | teslanorth.com |
| US Energy Industry Members | 2025-05-10 | A collective commitment to invest $100 Billion over five years to build and buy American-made batteries, driven by policy incentives like the IRA. | electrek.co |
Partnership Analysis: Building a Vertically Integrated Mega Battery Ecosystem
Strategic partnerships formed in 2025 and 2026 reveal a clear trend toward vertical integration, connecting automotive battery expertise, advanced materials recycling, and energy management software. These alliances are crucial for securing supply chains and developing the sophisticated control systems needed for next-generation BESS applications, moving beyond simple component supply deals that were common in prior years.
- The partnership between automaker GM and recycler Redwood Materials, announced in July 2025, aims to use EV-grade battery technology and recycled materials for stationary energy storage. This creates a circular economy and leverages automotive scale for the grid.
- Solid-state battery innovator Pro Logium partnered with electronics firm Delta in January 2026 to develop a new battery energy management system. This collaboration focuses on creating the software and controls for next-generation battery applications, moving beyond the cell itself.
- Leading battery maker CATL forged a strategic partnership with battery asset operator Mirattery in July 2025. This alliance combines manufacturing prowess with operational expertise to build out battery swapping and management ecosystems, showing a focus on the entire asset lifecycle.
Table: Key Strategic Partnerships in the Battery Ecosystem (2025-2026)
| Partners | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pro Logium & Delta | 2026-01-07 | Developing a new battery energy management system specifically for next-generation solid-state battery applications, creating the software needed to commercialize new hardware. | prnewswire.com |
| GM & Redwood Materials | 2025-07-16 | Collaborating on using U.S.-built batteries and recycled materials for energy storage applications, directly linking the EV and grid-scale storage supply chains. | news.gm.com |
| CATL & Mirattery | 2025-07-12 | A strategic partnership to combine CATL’s battery technology with Mirattery’s asset operation expertise, focused on building out the battery swapping and management ecosystem. | news.metal.com |
Geographic Focus: US and Australia Lead Deployment, China Leads Cell Innovation
The geographic distribution of BESS activity shows a clear division of leadership: the United States and Australia are the epicenters for large-scale project deployment and investment, while China is demonstrating a commanding lead in the manufacturing and operationalization of next-generation, high-density battery cell technology.

China’s Battery Pipeline Dwarfs Global Competition
As the section discusses geographic leadership, this chart directly illustrates China’s dominance by showing its in-development capacity dwarfs the rest of the world combined.
(Source: LinkedIn)
- The U.S. has become a primary market for large project financing and deployment, driven by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). Major projects backed by hundreds of millions in financing, such as the $500 million Tesla Megapack project in California and 400 MWh of new capacity in Texas, confirm its status as a top deployment region.
- Australia has emerged as a globally significant market, with investment in large-scale batteries hitting a record $2.4 billion in the first quarter of 2025 alone. This demonstrates an aggressive national push to use BESS to manage its transition to renewables.
- China’s leadership is in core technology manufacturing and rapid implementation. The world’s first 400 MWh energy storage station using ultra-large 628 Ah cells from EVE Energy came online there in January 2026, a milestone no other region has matched at commercial scale. This shows China’s ability to quickly move from cell innovation to grid-scale operation.
Technology Maturity: BESS Reaches Commercial Scale with LFP and Integrated Products
Grid-scale battery technology has unequivocally reached commercial maturity, a status defined by the widespread adoption of LFP chemistry and the market dominance of productized, multi-MWh integrated systems. The period from 2025 onward has been about scaling and standardizing the foundational LFP technology shift that began between 2021 and 2024, turning it into a mass-producible industrial good.
- The 2021-2024 timeframe was marked by strategic validation, most notably Tesla’s 2021 pivot to LFP for its Megapack. This move confirmed LFP’s superior cost, safety, and longevity for stationary storage, but the market still lacked fully integrated, off-the-shelf products.
- In 2025, the market saw the launch of highly integrated, standardized systems designed for mass deployment. Fluence’s modular 7.5 MWh platform (February 2025), CATL’s 9 MWh TENER Stack (May 2025), and Tesla’s 20 MWh Megablock (September 2025) all represent a decisive move toward “plug-and-play” utility-scale hardware.
- The operational launch of a 400 MWh station in January 2026 using EVE Energy’s record-setting 628 Ah cells confirms that the highest-density cell technologies are no longer in the lab but are being deployed at scale. This validates the entire high-density LFP technology roadmap.
- The successful U.S. pilot of Peak Energy’s grid-scale sodium-ion BESS in August 2025 provides the first commercial-scale validation for a viable alternative to lithium-ion, marking the next frontier of technology diversification.
SWOT Analysis: Market Dynamics of the Mega Battery Revolution
The BESS market’s primary strength lies in its rapidly maturing and cost-competitive LFP technology, creating massive opportunities in new sectors like AI, but its growth is constrained by supply chain concentration and the slow pace of grid modernization.
- Strengths: The demonstrated economic viability of BESS, with Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS) falling to $65/MWh, makes it directly competitive with traditional power sources.
- Weaknesses: Despite diversification into LFP, the battery supply chain remains heavily concentrated in China, creating geopolitical risk for Western deployments.
- Opportunities: The voracious energy demand from the AI industry has created a new, high-value, and urgent customer base for BESS, with manufacturers already pivoting production from EV batteries to meet storage demand.
- Threats: Grid interconnection queues and regulatory delays remain a primary bottleneck, potentially stranding billions in BESS investment and slowing the pace of deployment regardless of technological readiness.
Table: SWOT Analysis for the Mega Battery Energy Revolution
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – 2026 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | LFP chemistry adopted for its theoretical cost and safety benefits (e.g., Tesla’s 2021 shift). | LCOS confirmed at $65/MWh. Productization (Megablock, TENER Stack) dramatically lowers deployment costs and complexity. | The economic and operational benefits of LFP chemistry have been fully validated at commercial scale, making it the dominant technology for stationary storage. |
| Weaknesses | Reliance on nickel and cobalt for high-density batteries created significant supply chain and cost risks. | Shift to LFP reduces reliance on cobalt/nickel, but cell manufacturing and processing remain highly concentrated in China (e.g., EVE Energy, CATL). | The market swapped one supply chain dependency (cobalt) for another (concentrated LFP manufacturing and processing capacity in Asia). |
| Opportunities | Primary use case was renewable energy firming and ancillary grid services. | A new, massive demand center emerged from AI data centers, leading manufacturers like CATL to pivot production from EVs to storage cells. | The AI boom created an urgent, high-value revenue stream for BESS that is less sensitive to electricity market price volatility, fundamentally de-risking the business model. |
| Threats | High upfront capital costs and uncertain revenue streams from grid services were major barriers. | Falling costs have improved economics, but physical grid constraints and long interconnection queues are now the primary threat to deployment speed. | The main threat has shifted from financial viability to physical and regulatory bottlenecks in grid infrastructure. Technology is ready, but the grid is not. |
2026 Forward Look: AI Demand Will Force BESS as Standard Data Center Infrastructure
If the extreme energy demand from AI data centers continues to grow at its current rate, co-located battery energy storage will shift from a niche grid solution to a standard, required component of all new data center builds. This will force an acceleration in the deployment of integrated, multi-MWh block systems, as they are the only solution capable of providing the necessary power reliability and speed of interconnection that AI operations require.
- If this happens: Expect data center operators and tech giants like Google and Microsoft to sign multi-billion-dollar, long-term procurement deals directly with BESS manufacturers like Tesla and CATL, bypassing traditional utility procurement cycles.
- Watch this: The market performance and price point of the first commercial sodium-ion BESS deployments, like Peak Energy’s pilot. A successful, low-cost deployment could trigger a rapid diversification away from lithium-ion for stationary storage, especially in regions concerned about lithium supply chain concentration.
- This could be happening: A bifurcation in battery technology, with high-density LFP systems serving performance-critical applications like data centers, while lower-cost sodium-ion systems capture the bulk energy shifting and renewables firming market. The signal is the simultaneous mass production of high-density LFP and the first commercial pilots of sodium-ion.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are LFP batteries dominating the grid-scale storage market in 2026?
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries are dominating because they offer a superior combination of safety, longer lifespan, and lower cost compared to older chemistries. The technology has matured to the point where the Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS) has fallen to a competitive $65/MWh. Furthermore, LFP chemistry does not require nickel or cobalt, which reduces dependence on volatile and concentrated supply chains.
What is the biggest change in how large battery projects are built now compared to a few years ago?
The biggest change is the shift from custom, site-by-site project engineering to the deployment of standardized, factory-built integrated systems. Before 2024, projects were bespoke. Now, in 2025-2026, companies like Tesla (Megablock) and CATL (TENER Stack) offer pre-packaged, multi-MWh “blocks” that include batteries and transformers, which significantly accelerates installation, reduces costs, and improves reliability.
How is the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) impacting the battery industry?
The massive energy demand from AI data centers has created a new, urgent, and high-value customer for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS). To ensure the power reliability needed for AI compute, companies are now viewing BESS as essential infrastructure. This is driving major investments, such as Google’s participation in a capital raise for a battery recycler, and is forcing BESS to become a standard component of new data center designs.
Which countries are leading the battery storage revolution?
There is a clear division of leadership. The United States and Australia are leading in large-scale project deployment and investment, driven by favorable policies and the need to support renewable energy grids. In contrast, China is demonstrating a commanding lead in core manufacturing and cell technology innovation, evidenced by its rapid, commercial-scale deployment of next-generation, high-density cells like EVE Energy’s 628 Ah cells.
Are there any viable alternatives to lithium-ion batteries for grid storage?
Yes, sodium-ion battery technology is emerging as a commercially viable alternative. In August 2025, Peak Energy launched the first grid-scale sodium-ion BESS in the U.S. This marks a key step toward technology diversification, offering a potential lower-cost solution that could reduce reliance on the lithium supply chain, especially for applications like bulk energy shifting.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

