France’s Nuclear Build-Out: 2026 Execution Risks & Infrastructure Constraints
France’s Nuclear Renaissance: From Fleet Reliability to New-Build Execution Risk
France’s nuclear strategy has pivoted from managing the operational reliability of its aging fleet to confronting the immense industrial execution risks of its new-build program. The period between 2021 and 2024 was defined by stabilizing the existing 56 reactors after a severe corrosion crisis, whereas the post-2025 era is characterized by a massive, state-backed push to construct new capacity, testing the limits of the nation’s industrial and financial resources.
- Between 2021 and 2024, the primary challenge was operational. A 2022 crisis saw a record 26 of 56 reactors offline for maintenance and corrosion repairs, forcing France, a traditional power exporter, into the position of a net electricity importer and exposing the vulnerabilities of its aging infrastructure.
- From January 2025, the focus shifted decisively to future capacity under the third Multiannual Energy Programme (PPE 3). This plan mandates the construction of six new EPR 2 reactors and allocates €70 billion, a significant escalation from the initial €51.7 billion estimate, placing immense pressure on project execution and cost control.
- The primary constraint on this new-build program is the need to rebuild France’s “eroded” nuclear industrial ecosystem. The completion of the Flamanville 3 reactor in December 2024, over a decade late and with costs ballooning from €3.3 billion to over €13.2 billion, serves as a critical precedent for the execution risks facing the new EPR 2 fleet.
- A persistent, non-financial risk is the increasing climate vulnerability of the nuclear fleet. Nearly all of France’s 18 nuclear sites have reported capacity reductions due to heat waves and droughts, a physical constraint that threatens reactor availability and adds a layer of operational complexity to the strategic build-out.
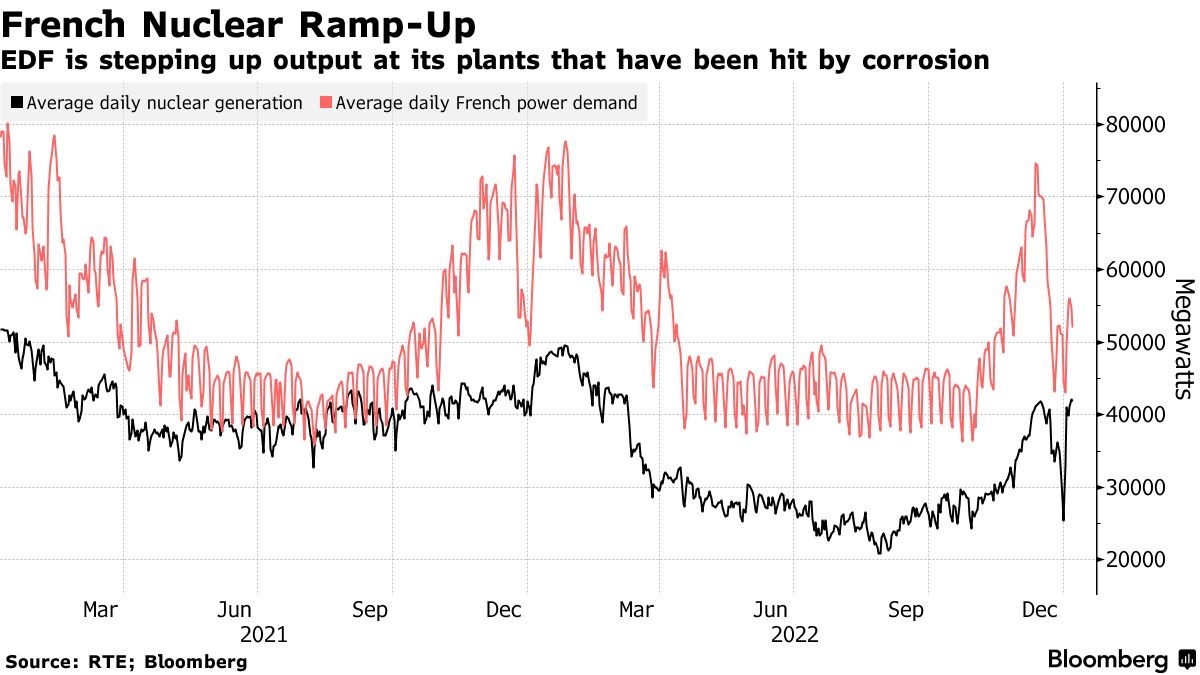
French Nuclear Output Rebounds Post-2022 Crisis
This chart shows the significant dip in nuclear generation during the 2022 corrosion crisis and the subsequent recovery, directly illustrating the fleet reliability challenges discussed.
(Source: Bloomberg.com)
Investment Analysis: Escalating Capital Commitments for France’s Nuclear Program
Financial commitments for France’s nuclear program have significantly increased since 2024, with the government deploying new financing mechanisms to de-risk the massive capital outlay required for both new construction and fleet modernization. The investment strategy has moved from ad-hoc financing for maintenance to a structured, long-term capital plan designed to ensure the viability of its ambitious targets.
- The total capital requirement for the new EPR 2 program has escalated significantly, rising from an initial estimate of €51.7 billion in 2022 to €70 billion by 2025, signaling the immense financial scope of the industrial undertaking.
- To support this, the French government is now considering a large-scale, zero-interest loan for EDF to finance the new reactors, a clear move to subsidize the high upfront costs and shield the project from market financing pressures.
- Beyond large reactors, the “France 2030” plan has formalized a €1 billion fund dedicated to accelerating Small Modular Reactor (SMR) development, diversifying the nation’s technology portfolio and investment risk.
- Fleet modernization remains a parallel priority, evidenced by EDF securing €5.8 billion in green bank loans in May 2024 and a €400 million EIB loan for Orano‘s uranium enrichment facility in March 2025 to strengthen the domestic fuel supply chain.
Table: Key Investments in France’s Nuclear Sector (2024-2026)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDF / New EPR 2 Reactors | Nov 2024 | The French government began weighing a zero-interest loan to finance a significant portion of the €67.4 billion program to build six new EPR 2 reactors, de-risking the massive capital expenditure for EDF. | Reuters |
| EDF / Fleet Life Extension | May 2024 | EDF secured €5.8 billion ($6.3 billion) in green bank loans to finance the life extension of its existing 56-reactor fleet beyond 40 years, ensuring continued baseload power generation. | World Nuclear News |
| EDF / New EPR 2 Program | Mar 2024 | EDF revised the cost estimate for the six new EPR 2 reactors to €67.4 billion, a significant increase from the 2022 estimate of ~€50 billion, highlighting early cost pressures. | |
| Orano / Georges Besse 2 Facility | Mar 2025 | Orano secured a €400 million loan from the European Investment Bank (EIB) to expand its uranium enrichment facility, strengthening Europe’s domestic nuclear fuel supply chain and energy security. | Orano Group |
| French Government / SMR Development | Jan 2024 | Under the “France 2030” plan, the government allocated €1 billion to support startups and projects developing SMRs and advanced reactors, fostering innovation beyond traditional large-scale plants. | Sifted |
Partnership Dynamics: Alliances to Rebuild France’s Nuclear Industrial Base
France is strategically forming international and domestic partnerships to rebuild its nuclear industrial capacity, accelerate next-generation reactor development, and construct a supportive political coalition within the EU. These alliances are critical for de-risking its national strategy and creating a broader market for French nuclear technology and expertise.
- France has moved to solidify its leadership of the pro-nuclear bloc in Europe, formalizing a “Nuclear Alliance” with nations including Poland, Sweden, and the Czech Republic to advocate for technology neutrality in EU energy policy.
- To support industrial development, France has signed bilateral cooperation agreements with key European partners. A 2024 agreement with the Netherlands focuses on joint development, while agreements with Slovenia (2024) and the UK (2023) center on R&D, training, and SMRs.
- In the advanced reactor segment, French entities are pursuing technology partnerships to accelerate innovation. The collaboration between French SMR developer NAAREA and UK-based Newcleo (January 2024) aims to fast-track Generation IV reactor designs.
- The French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) also partnered with Newcleo in April 2024 to advance lead-cooled fast reactor technology, demonstrating a commitment to securing a leadership position in next-generation nuclear systems.
Table: Key Strategic Nuclear Partnerships Involving France (2023-2025)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pro-Nuclear EU States / “Nuclear Alliance” | Mar 2025 | France leads a coalition of member states to ensure nuclear energy remains a key part of the EU’s decarbonization toolkit, creating a political bloc to counter anti-nuclear sentiment and secure favorable policy. | Government of Sweden |
| Netherlands | Oct 2024 | France and the Netherlands announced a long-term cooperation agreement for joint development of new nuclear technologies, expanding the potential market and industrial base for French reactor designs. | Nuc Net |
| NAAREA / Newcleo (UK) | Jan 2024 | A strategic and industrial partnership was formed to accelerate the development of their respective fourth-generation nuclear technologies, pooling expertise to advance beyond conventional reactor designs. | World Nuclear News |
| Slovenia | Sep 2024 | Bilateral agreements were signed to strengthen cooperation in R&D and training, supporting the human capital and skills pipeline needed for both countries’ nuclear programs. | Nuc Net |
Geographic Analysis: France’s Nuclear Strategy Fractures EU Energy Policy
France has solidified its position as the leader of a pro-nuclear bloc in Europe, creating a significant policy fracture with historically anti-nuclear nations like Germany and fundamentally reshaping the EU’s path to decarbonization. This diplomatic and political maneuvering has created a more favorable environment for nuclear investment across the continent.

France’s Low CO2 Path Diverges From Germany
This chart visualizes the policy fracture with Germany by showing how France’s nuclear-powered grid has maintained significantly lower per capita CO2 emissions since 1980.
(Source: Reddit)
- Between 2021 and 2024, the primary geographic dynamic was the Franco-German standoff over nuclear’s role in the EU’s green transition. France focused on building its “Nuclear Alliance” to counter German-led opposition.
- A landmark shift occurred in May 2025 when Germany’s new government signaled it would no longer oppose treating nuclear power on par with renewables in EU legislation. This diplomatic victory for France was critical in unlocking access to green financing mechanisms for nuclear projects.
- France is leveraging its nuclear status for broader geopolitical influence. President Macron initiated talks in February 2026 with Germany’s Chancellor to explore creating a joint European nuclear deterrent, extending France’s strategic influence beyond energy policy.
- The inclusion of nuclear power in the EU’s Complementary Climate Delegated Act, a direct result of French lobbying, has paved the way for an estimated €240 billion in nuclear investments across Europe by 2050, with France positioned to capture a significant share.
Technology Maturity: Balancing Proven EPR 2 Deployment with Next-Gen SMR Innovation
France’s technology strategy is a two-pronged approach: deploying the commercially-ready but execution-plagued EPR 2 technology at scale while simultaneously investing in earlier-stage SMRs and Generation IV reactors to secure future technological leadership and diversify risk.

France’s Nuclear Fleet Built in 1980s Boom
The chart provides historical context on technology maturity, showing the rapid construction of France’s current reactor fleet which contrasts with today’s new-build execution challenges.
(Source: CarbonCredits.com)
- The EPR/EPR 2 technology is considered commercially mature, but its deployment is fraught with execution challenges. The Flamanville 3 project, which came online in 2024 after a 12-year delay, demonstrates that even proven designs face significant construction risks. The EPR 2 is an evolution optimized for series construction, but its ability to reduce costs and timelines remains unproven.
- SMRs and advanced reactors are in the R&D and pre-commercial phase. The “France 2030” plan’s €1 billion investment and the selection of six innovative reactor projects for support in November 2023 confirm a national strategy to nurture these technologies from pilot to commercial scale.
- The period from 2021-2024 saw a focus on resolving issues with the existing fleet and the delayed EPR. The period from 2025 to today marks a formal commitment to a dual-technology track, with firm government mandates and funding for both large-scale deployment and next-generation innovation.
- Partnerships like those between NAAREA, Newcleo, and the CEA on Generation IV reactors indicate that while France is building EPR 2s for its immediate needs, it is actively developing the technologies that will define the post-2040 nuclear landscape.
SWOT Analysis: France’s Nuclear Execution Challenge
France’s nuclear strategy is underpinned by strong state support and industrial history but faces severe execution risks, financial pressures, and physical climate threats. A major shift occurred post-2024 as a favorable EU policy environment, secured by French diplomacy, coincided with the crystallization of the immense domestic challenge of delivering a new reactor fleet on time and on budget.

France Decoupled Economic Growth From CO2 Emissions
Illustrating a key strength in the SWOT analysis, this chart shows how France’s nuclear strategy successfully enabled GDP growth while its per capita CO2 emissions declined.
(Source: Reddit)
Table: SWOT Analysis for France’s Nuclear Energy Strategy
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – Today | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | An existing fleet of 56 reactors providing low-carbon baseload power. State-controlled utility (EDF) and an integrated industrial base (Orano, Framatome). | Established leadership of the EU “Nuclear Alliance.” A clear government mandate and financial backing via the PPE 3 plan. Geopolitical leverage from its nuclear deterrent status. | France successfully translated its nuclear expertise into political leadership in the EU, creating a more favorable policy landscape for its national strategy. |
| Weaknesses | Severe operational reliability issues, highlighted by the 2022 corrosion crisis. An eroded industrial skills base and supply chain. Extreme cost overruns and delays on the Flamanville 3 EPR project. | High LCOE for new nuclear builds compared to renewables. The immense financial burden of the €70 billion EPR 2 program and €50 billion modernization plan. A workforce not yet scaled for a massive new-build program. | The completion of Flamanville 3 validated the weakness in project execution, making on-time, on-budget delivery the central challenge for the new EPR 2 fleet. |
| Opportunities | Growing demand for energy security post-Ukraine invasion. Lobbying for nuclear inclusion in the EU Taxonomy for sustainable finance. Building a coalition of pro-nuclear EU states. | Germany’s May 2025 policy reversal on opposing nuclear power. Access to green financing via the EU Taxonomy. An emerging European market for SMRs. Growing demand for stable, non-intermittent clean energy. | Germany’s policy shift resolved a major political obstacle, validating France’s long-term diplomatic strategy and opening the door to greater EU-level support for nuclear power. |
| Threats | Political opposition from anti-nuclear EU states, led by Germany. Public and political concern over project costs and timelines. Technical challenges of extending the life of an aging fleet. | Physical risks from climate change (heatwaves, droughts) forcing reactor curtailments. The risk of major cost overruns on the EPR 2 program. Supply chain bottlenecks for specialized components and skilled labor. | Climate-related curtailments have become a recurring, validated threat to reactor availability, adding a physical risk layer on top of the financial and industrial execution risks. |
2026 Scenario Model: Execution and Cost Control are the Critical Signals to Watch
The success of France’s nuclear strategy in 2026 hinges on EDF‘s ability to demonstrate tangible progress in controlling costs and schedules for the first EPR 2 projects, with any early delays serving as a critical negative signal for the entire program’s viability.

Nuclear Power Has Long Dominated French Energy
This chart illustrates a primary strength noted in the SWOT table, showing how nuclear power became and remained the dominant source of French energy since the 1980s.
(Source: WTS Energy)
- If pre-construction activities and supply chain procurement for the first EPR 2 site at Penly face delays or cost revisions in 2026, then watch for a potential scaling back of the 14-reactor ambition or a renewed policy push toward SMRs as a less capital-intensive alternative.
- If the summer of 2026 brings another severe heatwave that forces significant nuclear power curtailments, then watch for accelerated investment in reactor cooling upgrades and a re-evaluation of siting criteria for future plants to mitigate climate-related operational risks.
- If France successfully leverages its “Nuclear Alliance” to establish joint financing mechanisms or common industrial standards, then watch for the emergence of a pan-European nuclear supply chain, which would de-risk France’s national program and solidify its industrial leadership.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary shift in France’s nuclear strategy after 2024?
After 2024, France’s nuclear strategy pivoted from managing the operational reliability of its existing 56 reactors to confronting the industrial execution risks of a massive new-build program. The focus moved from maintenance and repairs (2021-2024) to the construction of six new EPR 2 reactors under the PPE 3 plan.
How much is the new EPR 2 reactor program expected to cost, and how has that changed?
The estimated cost for the six new EPR 2 reactors has significantly escalated. Initially estimated at €51.7 billion in 2022, the cost was revised to €67.4 billion by March 2024 and is cited as part of a €70 billion program by 2025, highlighting major cost pressures before construction even begins.
How is climate change affecting France’s nuclear fleet?
Climate change poses a direct operational threat. Nearly all of France’s 18 nuclear sites have had to reduce capacity or shut down temporarily due to heat waves and droughts, which limit the availability of cooling water. This has become a validated, recurring physical risk to the fleet’s reliability.
Why is the Flamanville 3 reactor significant for France’s future plans?
The Flamanville 3 project, which was completed over a decade late with costs ballooning from €3.3 billion to over €13.2 billion, serves as a critical precedent. It validates the immense execution risks, cost overruns, and delays that the French nuclear industry faces, making it a cautionary tale for the new EPR 2 build-out.
What is the ‘Nuclear Alliance’ and what was its major diplomatic success?
The ‘Nuclear Alliance’ is a coalition of pro-nuclear EU countries, led by France, formed to advocate for nuclear energy’s role in European policy. Its most significant success occurred in May 2025, when Germany’s government signaled it would no longer oppose treating nuclear power on par with renewables, a major diplomatic victory that helps unlock green financing for nuclear projects.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

