The New Utility Playbook 2026: How Alliances are Accelerating Solar-Led Grid Expansion
From Silos to Ecosystems: The 2026 Shift in Utility Grid Expansion Projects
The utility industry has pivoted from incremental, project-by-project procurement to a new model of integrated, programmatic co-development to meet unprecedented electricity demand. This strategic shift is driven by the need to build entire energy ecosystems at a scale and speed that matches the exponential load growth from data centers and artificial intelligence.
- Between 2021 and 2024, the market was defined by utilities executing individual Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) and pursuing discrete transmission projects, such as Xcel Energy’s Colorado’s Power Pathway, often in response to state mandates. This approach proved too slow and fragmented to address the gigawatt-scale demand emerging from single customer segments.
- The market changed in early 2026 with the formation of strategic alliances designed for systemic co-development. The Memorandums of Understanding between Xcel Energy, Next Era Energy, and GE Vernova in February 2026 exemplify this new model, aligning a utility, a developer, and a technology supplier to jointly build out generation, storage, and transmission for a planned 6 GW data center load.
- This trend extends beyond the main players, indicating a broader industry adoption of the ecosystem model. The February 2026 partnership between Hanwha Renewables and Chrysalis Renewables targets 3.5 GW of solar and storage, while the January 2025 joint development between Chevron, GE Vernova, and Engine No. 1 aims for 4 GW of power projects, validating the strategy across different market participants.
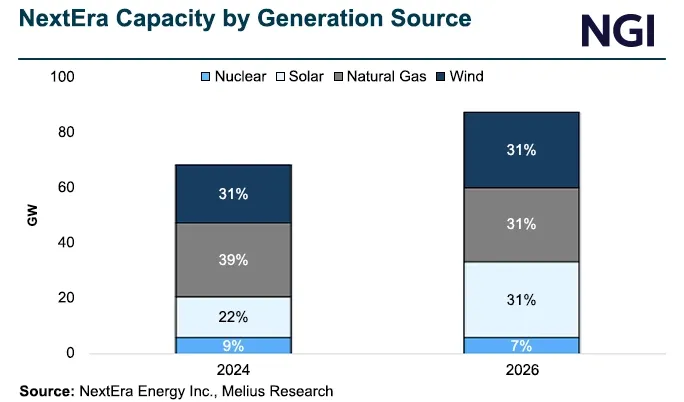
NextEra Shifts Generation Mix Towards Solar
This chart illustrates the strategic shift to renewables discussed in the section by showing solar’s increasing share in NextEra’s generation mix by 2026.
(Source: Natural Gas Intelligence)
Capital Unleashed: Analyzing the Trillion-Dollar Investment in Grid Modernization
Massive, multi-year capital expenditure plans are the financial foundation enabling this new co-development model, with utilities committing hundreds of billions to modernize and expand the grid backbone required for a solar-led energy system. These investments are no longer just for maintenance but are a fundamental re-architecting of the network to support a high-volume, decentralized future.

Utilities Project $1.1 Trillion Grid Investment
This chart directly visualizes the massive capital commitment to grid modernization, forecasting the $1.1 trillion in aggregate spending mentioned in the article.
(Source: POWER Magazine)
- Xcel Energy has committed to a five-year capital plan of over $60 billion between 2025 and 2029. This funding is allocated to build 1, 500 miles of new high-voltage transmission lines, deploy 7.5 GW of renewables and 1.9 GW of storage, and secure 3 GW of firming gas generation.
- Next Era Energy is deploying even larger-scale capital, with a plan to invest nearly $74.6 billion over the same 2025-2029 period. This investment is aimed at strengthening its grid infrastructure and massively expanding its clean energy asset base to meet both decarbonization goals and new customer demand.
- These individual plans are part of a sector-wide trend, with U.S. Investor-Owned Utilities projected to spend a collective $1.1 trillion on grid modernization by 2029. This aggressive capital deployment is a direct response to spiraling power demand from data centers and electrification.
- Technology providers are scaling their own manufacturing capacity to meet this surge. GE Vernova is making direct investments, including $16 million in India, C$22.2 million in Quebec, and adding 250 jobs in Pennsylvania, to expand its production of critical grid components.
Table: Utility Capital Commitments for Grid Expansion (2025-2029)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Next Era Energy | 2025 – 2029 | $74.6 billion capital plan to strengthen infrastructure and add clean electricity generation assets. | The Globe and Mail |
| Xcel Energy | 2025 – 2029 | Over $60 billion capital plan for grid modernization, including 1, 500 miles of new transmission, 7.5 GW of renewables, and 1.9 GW of storage. | Utility Dive |
| Investor-Owned Utilities (Aggregate) | By 2029 | Projected $1.1 trillion in aggregate capital spending to modernize infrastructure in response to spiraling power demand. | Power Magazine |
| GE Vernova | 2025 | Multiple investments to expand manufacturing capacity for grid technologies, including in Pennsylvania (250 jobs), Quebec (C$22.2 M), and India ($16 M). | GE Vernova |
Strategic Alliances: How Xcel, Next Era, and GE Vernova Redefine Solar-Led Expansion
Utilities are forging deep, multi-faceted alliances that integrate development, supply chain security, and technology collaboration, moving decisively beyond the transactional nature of traditional PPAs. This new model of programmatic co-development allows partners to de-risk investments and accelerate execution by aligning the capabilities of the utility, developer, and technology provider.

Xcel Energy Faces 26 GW Data Center Demand
This chart quantifies the immense data center load growth driving the strategic alliances discussed, showing the massive demand pipeline Xcel Energy must serve.
(Source: POWER Magazine)
- The February 2026 Memorandum of Understanding between Xcel Energy and Next Era Energy establishes a framework to co-develop generation, storage, and transmission through the 2030 s. The objective is to align two of the industry’s top development teams to streamline project execution and match grid capacity with large customer demand.
- Simultaneously in February 2026, Xcel Energy formed a strategic alliance with GE Vernova to secure the supply chain for critical equipment like gas turbines and grid hardware. This agreement also establishes a framework for collaboration on grid modernization and AI applications, creating a direct feedback loop between the operator and technology provider.
- Underscoring the pragmatic need for firm power, Next Era Energy separately secured 4 GW of gas turbine slots from GE Vernova. This move demonstrates that the co-development model is designed to deliver reliable power by securing both renewable and firming generation capacity in parallel.
- This alliance model builds on earlier, simpler partnership structures. For example, in June 2024, Next Era and Entergy formed a joint development agreement to build up to 4.5 GW of solar and storage, showing the evolution towards more integrated, large-scale collaborations.
Table: Key Strategic Alliances for Systemic Grid Development
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xcel Energy / Next Era Energy | Feb 2026 | Mo U to co-develop generation, storage, and transmission infrastructure to serve large loads, including a 6 GW data center pipeline. | Xcel Energy |
| Xcel Energy / GE Vernova | Feb 2026 | Strategic alliance to secure the supply of generation and grid equipment and collaborate on AI, grid modernization, and R&D. | Business Wire |
| Hanwha Renewables / Chrysalis Renewables | Feb 2026 | Strategic partnership to deploy over 3.5 GW of solar and battery storage projects globally, demonstrating a similar co-development model. | Business Wire |
| Chevron / GE Vernova / Engine No. 1 | Jan 2025 | Joint development to build up to 4 GW of power projects, leveraging natural gas with carbon capture potential for data centers. | Chevron |
| Next Era Energy / Entergy | Jun 2024 | Joint agreement to develop up to 4.5 GW of new solar generation and storage projects, an earlier example of large-scale utility-developer collaboration. | Utility Dive |
North America Leads Grid Expansion: Mapping the Epicenters of Solar and Data Center Growth
North America, and the United States in particular, has emerged as the clear geographical center for this new integrated utility expansion model, driven by the hyper-concentration of data center development and a mature regulatory environment that allows for large-scale capital deployment.

Xcel Sees Strong Regional C&I Growth
This chart pinpoints the geographic epicenters of demand by breaking down rising Commercial and Industrial (C&I) electricity use across Xcel’s specific service territories.
(Source: NewsData)
- In the 2021-2024 period, renewable energy development was geographically widespread, driven by state-level policies and favorable economics, with key transmission projects like Xcel Energy’s Colorado’s Power Pathway initiated to unlock wind and solar resources.
- From 2025 onwards, growth has become highly concentrated within specific utility service territories experiencing massive data center load requests. Xcel Energy’s identification of a potential 6 GW data center load in its service territories (Midwest and Southwest) and Next Era’s discussions for 9 GW of nuclear capacity for data centers highlight this focused demand.
- Specific regions are becoming hubs for this integrated model. Xcel’s plan for the Sherco Energy Hub in Minnesota, combining a 600 MW battery with 460 MW of solar at a retiring coal plant site, is a direct outcome of this strategy, concentrating investment to serve regional demand.
- The supply chain is reorganizing to support this regional focus. GE Vernova’s investments in its Pennsylvania, Quebec, and New York manufacturing facilities are strategic decisions to place production capacity closer to the epicenters of North American grid and generation buildout.
Commercial Scale Now: Solar, Storage, and Grid Tech Converge for Rapid Deployment
The technologies central to this accelerated expansion—utility-scale solar, lithium-ion battery storage, and advanced grid orchestration software—are commercially mature and being deployed as integrated systems at an unprecedented scale, removing technology risk as a primary barrier to rapid grid modernization.

Renewables Proven as Least-Cost Power Solution
Supporting the section’s theme of commercial maturity, this chart shows new solar and wind are the cheapest generation options, reinforcing their readiness for rapid deployment.
(Source: POWER Magazine)
- Between 2021 and 2024, the market focused on proving these technologies individually at scale and piloting next-generation solutions. This included early large-scale solar-plus-storage projects and partnerships like Xcel Energy’s agreement with Form Energy in January 2023 to pilot 100-hour iron-air batteries.
- Starting in 2025, the focus shifted from piloting to mass deployment of integrated solutions. Solar and battery storage are now the primary tools for rapid expansion due to their modularity and speed, as seen in Xcel’s plan to add 7.5 GW of renewables and 1.9 GW of storage.
- Grid orchestration software, once a future concept, is now a critical, commercially available enabler. GE Vernova’s Grid OS® software, adopted by 75% of Fortune 500 utilities, is essential for managing the complexity of grids with high renewable penetration and is being enhanced through acquisitions like Greenbird.
- The strategy is pragmatic, integrating mature, dispatchable technologies for reliability. The explicit inclusion of GE Vernova’s F-class gas turbines in the Xcel and Next Era alliances confirms that proven firming capacity is a required component of the solar-led expansion model.
SWOT Analysis: Risks and Opportunities in the Utility Co-Development Model
The integrated alliance model provides significant advantages in execution speed, risk mitigation, and scale, but it also concentrates risks in the supply chain and creates dependencies on the continued growth of large-load customers.
Table: SWOT Analysis for Xcel Energy, Next Era Energy, and GE Vernova partner on new generation, storage, and transmission: How are utilities accelerating solar-led grid expansion?
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2023 | 2024 – 2025 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Individual company capabilities, such as Next Era’s vast development pipeline or GE’s technology portfolio. | Integrated ecosystem strength combining utility regulatory expertise (Xcel), developer scale (Next Era), and technology supply (GE Vernova). | The model shifted from leveraging siloed strengths to creating force multiplication through deep, programmatic alliances, enabling faster and larger project execution. |
| Weakness | Long interconnection queues (2, 600 GW backlog at end of 2023) and fragmented, multi-year planning cycles for individual projects. | High dependency on a few large-load customers (e.g., data centers) and concentration of risk in a few key technology supply chains (e.g., transformers, turbines). | While alliances address planning bottlenecks, they introduce new systemic risks. A slowdown in data center growth could jeopardize the economics of multi-gigawatt buildouts. |
| Opportunity | Falling costs of solar and storage, supported by incentives like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), enabled project-level profitability. | Proactively capture a generational boom in electricity demand from AI and data centers, justifying multi-billion-dollar, system-wide investments. | The opportunity evolved from incremental renewable additions to building entire energy ecosystems to power the next industrial revolution, attracting massive capital. |
| Threat | Project-specific regulatory delays and local opposition (NIMBYism) were the primary threats to individual renewable developments. | Macroeconomic risks, including high interest rates on massive capital plans ($60 B+), and physical supply chain disruptions for critical grid components. | Risks have shifted from the project level to the systemic level. Supply chain constraints and the cost of capital now pose a greater threat than individual project hurdles. |
Forward Outlook: Key Signals for the AI-Powered Grid Expansion
The single most critical factor for success in 2026 and beyond is whether the industrial supply chain for critical grid components like transformers, switchgear, and turbines can scale as rapidly as utilities are deploying capital and signing development agreements.

GE Vernova Backlog Highlights Supply Chain Demand
This chart provides a key signal for the supply chain outlook, showing a major manufacturer’s backlog surging, which directly relates to the section’s focus on equipment availability.
(Source: Natural Gas Intelligence)
- If this happens: If equipment manufacturers like GE Vernova continue to announce and execute on factory expansions, and if lead times for essential grid hardware begin to stabilize or decrease, it will validate that the supply side can support the unprecedented demand.
- Watch this: Monitor the quarterly backlogs and revenue of the “Electrification” segments of major suppliers like GE Vernova. A rapidly growing backlog without a corresponding increase in production output is a leading indicator of a supply chain bottleneck that could slow physical deployment.
- These could be happening: Expect more utilities to announce similar tripartite alliances to secure their positions in supply and development queues. The Xcel/Next Era/GE Vernova model is likely to be replicated by other large investor-owned utilities facing similar data center-driven load growth, signaling a permanent shift in how grid expansion is executed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ‘new utility playbook’ and how is it different from the old model?
The new playbook is a shift from utilities pursuing individual, project-by-project power agreements to forming large-scale strategic alliances with developers and technology suppliers. Unlike the older, slower model, this new approach focuses on programmatic co-development of entire energy ecosystems (generation, storage, and transmission) to meet unprecedented, gigawatt-scale demand from sectors like data centers and AI.
Why is this massive grid expansion happening now?
The primary driver is the exponential growth in electricity demand from data centers, artificial intelligence (AI), and broader electrification. The article highlights that the old, fragmented approach was too slow to address gigawatt-scale requests from single customer segments, forcing the industry to adopt a faster, more integrated model for building out the grid.
What is the significance of the alliance between Xcel Energy, Next Era Energy, and GE Vernova?
This alliance, formed in February 2026, exemplifies the new co-development model. It strategically combines a utility (Xcel Energy), a major developer (Next Era Energy), and a key technology/equipment supplier (GE Vernova). Their goal is to jointly build the infrastructure needed to serve a massive 6 GW data center load, aligning development, supply chain, and technology to accelerate execution and de-risk the investment.
How much money is being invested in this grid modernization?
The capital commitments are massive. For the 2025-2029 period, Xcel Energy has a plan for over $60 billion, and Next Era Energy plans to invest nearly $74.6 billion. Collectively, U.S. Investor-Owned Utilities are projected to spend an aggregate of $1.1 trillion on grid modernization by 2029 to meet the spiraling power demand.
What is the biggest risk or challenge facing this new model of accelerated grid expansion?
According to the analysis, the most critical risk is whether the industrial supply chain for essential components like transformers, switchgear, and turbines can scale fast enough to meet the unprecedented demand. A failure to ramp up manufacturing could create severe bottlenecks, slowing down the physical deployment of these multi-billion-dollar projects despite the available capital and signed agreements.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Google Clean Energy: 24/7 Carbon-Free Strategy 2025
- Bloom Energy SOFC 2025: Analysis of AI & Partnerships
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

