Shell’s Top 10 AI Projects for 2025-2026: A Strategic Analysis
In 2025 and 2026, Royal Dutch Shell has decisively shifted its artificial intelligence strategy from internal optimization to a dual-pronged approach that also positions it as a critical enabler of the AI-driven economy. The company’s AI initiatives now span its entire value chain, leveraging a data lake containing trillions of data rows to enhance legacy asset profitability while creating new revenue streams tied directly to the digital sector’s growth. This analysis breaks down Shell’s top AI projects, investments, and partnerships, providing a clear view of its competitive positioning.
Shell’s Commercial Scale AI Projects Show Deep Industry Adoption 2026
Shell has moved its artificial intelligence applications from isolated pilot programs to deeply integrated, commercially scaled deployments that are core to its operational strategy and new business development.
- Between 2021 and 2024, Shell focused on scaling its predictive maintenance program with C 3 AI, reaching over 10, 000 pieces of equipment globally and establishing foundational data platforms with partners like Databricks. This period centered on proving AI’s value for optimizing existing oil and gas assets, achieving up to a 20% reduction in unplanned downtime.
- Starting in 2025, Shell‘s AI adoption has evolved significantly toward co-development and commercialization. The collaboration with SLB announced in December 2025 aims to create “agentic AI” for upstream experts, a leap beyond simple predictive models. This move shows a shift from being a consumer of AI to a co-creator of advanced industry solutions.
- The launch of the Shell DLC Fluid S 3 in June 2025, an immersion cooling liquid for data centers certified by Intel, marks Shell‘s entry into the AI infrastructure market. This contrasts with its earlier internal focus by creating an external, high-growth revenue stream directly serving the AI industry’s energy needs.
- Partnerships in 2025 with Yokogawa to integrate machine vision for robotic plant maintenance and with Google to supply renewable power for UK AI data centers further illustrate this dual strategy. Shell is simultaneously using AI to cut emissions and costs in its core operations while selling enabling technologies and energy to the AI sector itself.
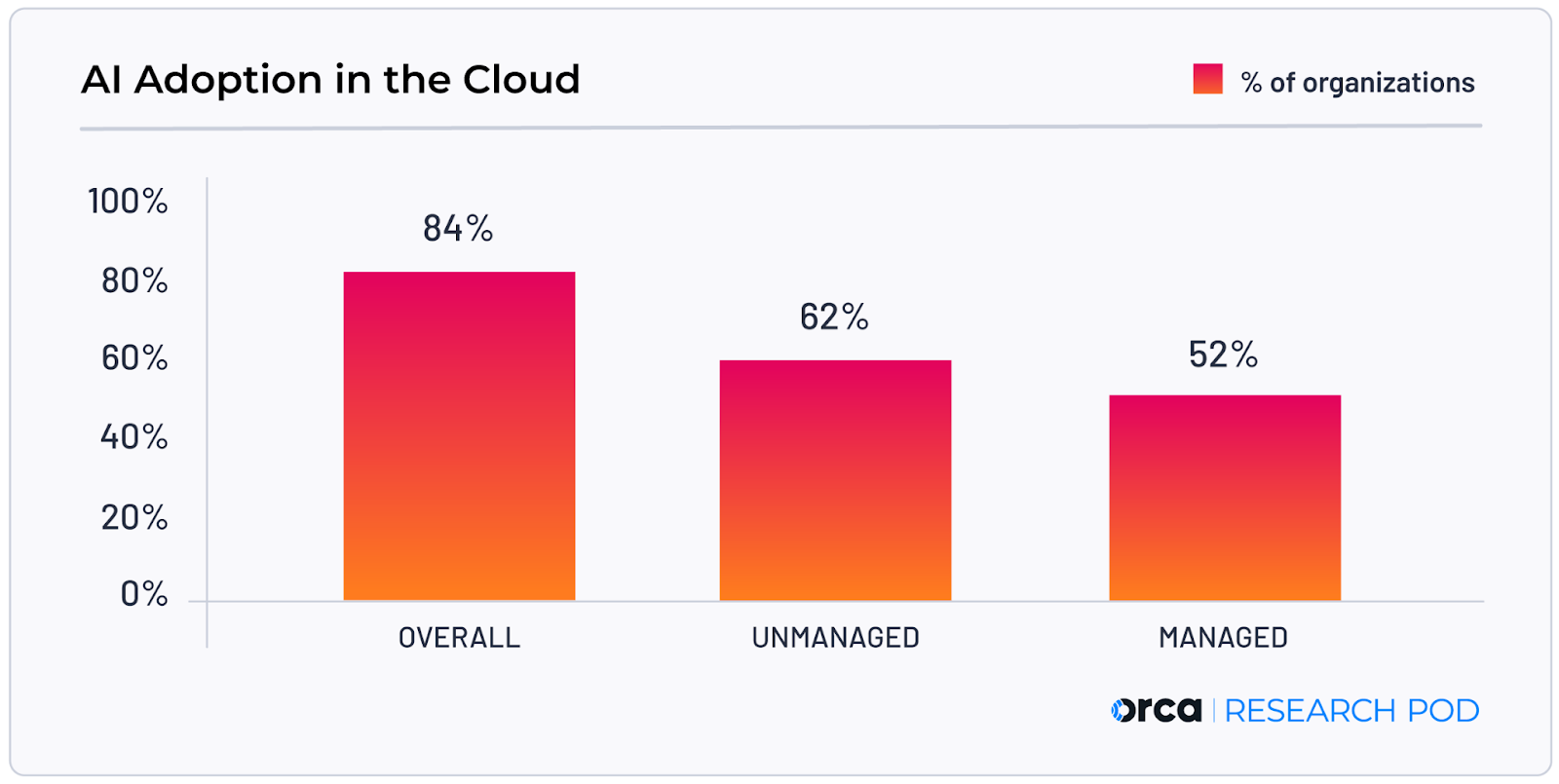
Widespread AI Adoption in the Cloud
This chart illustrates the widespread cloud AI adoption that forms the backdrop for Shell’s move from pilot programs to deeply integrated, scaled deployments.
(Source: Orca Security)
Investment Analysis: Shell’s Capital Allocation Powers Dual AI Strategy
Shell’s investment strategy in 2025 and 2026 underpins its dual-pronged approach, allocating significant capital to both optimize its core business through AI and fund new, AI-related low-carbon and digital ventures.
- Shell has committed to a substantial annualized capital expenditure of approximately $21 billion as of December 2025, providing the financial power to pursue large-scale digital transformation across its entire asset base. This sustained investment ensures that AI initiatives are not just experiments but are resourced for enterprise-wide impact.
- A dedicated investment of $10-15 billion in low-carbon solutions, announced in July 2025, explicitly includes funding for AI-powered grid optimization. This demonstrates a clear financial commitment to using artificial intelligence to build out its energy transition businesses.
- The company’s focus on shareholder returns, highlighted by a $3.5 billion share buyback in Q 4 2025, is supported by the efficiency gains realized from its AI deployments. AI-driven predictive maintenance, for example, has directly contributed to cost savings and operational reliability, bolstering the cash flow that funds these returns.
Table: Shell’s Key AI-Related Investments (2022-2026)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q 4 2025 Share Buyback | 2026-02-05 | Announced a $3.5 billion share buyback, partly enabled by operational efficiencies and cost savings derived from large-scale AI deployments. | Stock Titan |
| Annualized Capex Plan | 2025-12-08 | Maintained a planned annualized capex of ~$21 billion to fund investments across its asset stack, including digital and AI transformation projects. | Seeking Alpha |
| Low-Carbon Solutions Investment | 2025-07-27 | Allocated $10-15 billion for low-carbon solutions, with a specific focus on areas like AI-powered grid optimization and hydrogen. | Enki AI |
| Investment in Ai Dash | 2022-09-18 | Shell Ventures invested in Ai Dash, an AI and satellite analytics company, signaling early interest in using AI for asset integrity and risk management. | Ai Dash |
Partnership Analysis: Shell’s Alliances Build an AI-Powered Ecosystem
Shell executes its AI strategy through a carefully constructed ecosystem of partnerships, collaborating with technology leaders to co-develop solutions, accelerate deployment, and enter new digital markets.
- The 2025 strategic shift is most evident in its collaborations with SLB and Yokogawa. The SLB partnership moves beyond using off-the-shelf AI to co-developing “agentic AI” for upstream operations, while the Yokogawa deal integrates Shell‘s proprietary machine vision tool into a commercial robotics platform, turning internal innovation into a marketable product.
- In contrast, partnerships from the 2021-2024 period, such as the expanded agreement with C 3 AI and the implementation of Databricks, were focused on creating the internal scaled platforms necessary for enterprise-wide AI. These laid the foundation for the more advanced, externally-focused collaborations seen today.
- Shell‘s 2025 partnerships with technology giants like NVIDIA and Google demonstrate its dual role. It collaborates with NVIDIA to train its own custom LLMs, achieving a 30% accuracy increase, while simultaneously acting as a supplier to Google by providing renewable energy for its UK AI infrastructure.
Table: Shell’s Top Strategic AI Partnerships (2021-2026)
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLB | 2025-12-18 | Co-development of agentic AI solutions to augment technical experts in upstream operations, leveraging SLB‘s Lumi platform. | JPT |
| 2025-09-16 | Agreement for Shell Energy Europe to supply renewable energy to power Google‘s AI data center operations in the UK. | Energy Voice | |
| Yokogawa | 2025-06-18 | Integration of Shell‘s “Operator Round by Exception” (ORE) machine vision tool into Yokogawa‘s robotics platform to commercialize and scale automated plant maintenance. | Yokogawa |
| NVIDIA | 2025-06-11 | Used NVIDIA‘s Ne Mo framework to train a custom LLM that achieved a 30% increase in accuracy, demonstrating advanced in-house AI development capabilities. | NVIDIA |
| Spark Cognition | 2023-05-17 | Collaborated to use generative AI for processing seismic data to accelerate deep-sea oil exploration, an early move into advanced AI applications. | Reuters |
| C 3 AI | 2022-03-08 | Scaled AI predictive maintenance to over 10, 000 pieces of equipment globally, proving the commercial value of AI for asset management. | C 3 AI |
Shell’s Global AI Footprint Matures with Regional Specialization
Shell’s AI activities have expanded from broad, platform-based global deployments to include specialized, high-impact projects concentrated in key operational regions like the Americas, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
- From 2021 to 2024, Shell‘s AI strategy was characterized by the global rollout of enterprise platforms, such as the C 3 AI Suite and Microsoft Azure, creating a standardized digital backbone across its worldwide operations without a specific geographic focus.
- In 2025, a pattern of regional specialization emerged. In the United States, particularly the Gulf of Mexico, Shell is focusing AI on upstream growth, evidenced by its collaboration with SLB on agentic AI and a potential $3 billion acquisition of LLOG Exploration.
- Europe has become a hub for Shell‘s AI-as-an-enabler strategy, highlighted by the September 2025 agreement to supply renewable energy to Google‘s AI infrastructure in the UK. This positions Shell‘s European energy business to directly capitalize on the continent’s growing AI sector.
- In Southeast Asia, Shell is leveraging AI for complex operational challenges and partnerships. The November 2025 collaboration with Petronas in Malaysia focuses on using AI for seismic imaging, while a project in Brazil with MODEC uses AI to improve safety on FPSO vessels.

Global Developer Population Growth Forecast to 2025
This chart’s forecast of developer growth in key regions provides context for Shell’s maturing global footprint and its strategy of regional specialization.
(Source: The GitHub Blog)
Shell’s AI Technology Maturity Advances to Generative and Agentic Systems
Shell’s AI technology stack has matured from foundational predictive analytics to the deployment and co-development of sophisticated generative and agentic AI systems, signifying a major leap in capability.
- During the 2021-2024 period, Shell‘s primary technological achievement was the successful scaling of predictive AI. The deployment of its predictive maintenance system with C 3 AI across 10, 000 assets, processing billions of data rows, validated the commercial viability of AI for industrial asset management.
- The year 2025 marks a clear inflection point with the adoption of generative and agentic AI. The collaboration with SLB to build “agentic AI” solutions, announced in December 2025, aims to create systems that can reason and support complex human decisions, moving far beyond pattern recognition.
- Similarly, Shell‘s use of NVIDIA‘s Ne Mo framework to build a custom LLM in June 2025 demonstrates a move from being a buyer of AI to a sophisticated in-house developer. Achieving a 30% accuracy gain over the base model shows a high level of technical maturity.
- The development and commercialization of the Shell DLC Fluid S 3 in 2025, an enabling technology for AI hardware, further validates Shell‘s maturity. It indicates the company is not only using advanced AI but is also creating physical products essential for the AI ecosystem’s operation.

Architecture for Production-Grade Agentic AI Systems
This diagram provides a technical blueprint for the sophisticated, production-grade agentic AI systems that the section describes Shell as developing and deploying.
(Source: Level Up Coding – Gitconnected)
SWOT Analysis: Shell’s AI Strategy in 2025-2026
Shell’s AI strategy has transitioned from internal optimization to a dual role as both a user and a supplier to the AI economy, capitalizing on its operational scale while creating new market opportunities.
- Strengths have evolved from successful pilot programs to proven, scaled AI deployments that deliver quantifiable financial benefits, such as a 40% reduction in equipment failures.
- Opportunities have expanded from operational cost-cutting to generating new revenue streams, such as selling specialized cooling fluids and renewable energy to the data center market.
- Weaknesses remain centered on balancing investment between its profitable legacy business and its energy transition goals, a tension reflected in its AI project portfolio.
- Threats are increasingly external, stemming from the rapid pace of AI innovation and the massive energy demands of the AI sector itself, which Shell now aims to supply.
Table: SWOT Analysis for Shell’s AI Initiatives
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – 2026 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Established key partnerships with AI leaders like C 3 AI and Microsoft. Built foundational data platforms (e.g., Databricks). | Scaled AI predictive maintenance to over 10, 000 assets, achieving 20-40% fewer failures. Developed advanced in-house capabilities (e.g., custom LLM with NVIDIA). | The value of AI was validated at a commercial scale, moving from partnership potential to proven ROI and deep technical expertise. |
| Weakness | AI applications were heavily focused on optimizing existing fossil fuel assets, with fewer scaled deployments in renewables. | The strategic pivot to “more value, less emissions” and scrapping of the 2035 emissions target risks skewing AI investment further towards oil and gas. | The strategic conflict between maximizing legacy profits and funding the energy transition became more pronounced, shaping where AI capital is directed. |
| Opportunity | Primary opportunity was operational efficiency: reducing downtime, cutting costs, and improving safety in core operations. | Expanded to creating new revenue streams by enabling the AI economy via cooling fluids (Shell DLC Fluid S 3), renewable power (Google deal), and co-developed software (SLB deal). | The opportunity set grew from internal cost savings to external revenue generation, positioning Shell as a technology supplier to the AI industry. |
| Threat | Pace of digitalization among competitors (e.g., other energy majors). Risk of failed pilot projects and inability to scale. | The exponential growth of AI is creating immense energy demand, which Shell forecasts will delay peak oil. This presents both a market opportunity and a reputational/regulatory risk. | The primary threat shifted from internal execution risk to managing the systemic impacts and opportunities of the global AI boom itself. |
Future Outlook: Shell to Solidify Role as Technology Enabler for AI Economy
Looking ahead, Shell’s most critical strategic action will be to solidify and scale its new role as a foundational technology and infrastructure provider for the artificial intelligence industry.
- The market performance of the Shell DLC Fluid S 3 and other immersion cooling solutions will be a key indicator. Success in the data center market, projected to grow at a 14% CAGR, would establish a significant new revenue stream completely independent of traditional energy sales.
- Progression of the “agentic AI” collaboration with SLB will be crucial. If the co-developed solutions become an industry standard for upstream operations, Shell will have successfully transitioned from an AI consumer to a high-value AI product developer, capturing value across the sector.
- The expansion of energy supply agreements, like the one with Google, will determine Shell‘s ability to capitalize on AI’s massive power consumption. Watch for new Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) that link Shell‘s renewable and low-carbon energy portfolio directly to data center operators.
- Shell‘s own energy security scenarios predict that AI will be a major driver of future energy demand. Its ability to balance shareholder returns with the heavy capital investments needed for both its legacy and AI-enabling businesses will define its long-term success in this new landscape.

Training Costs for Top AI Models Soar
This chart highlights the massive training costs for advanced AI, explaining the market need for the infrastructure solutions Shell aims to provide in its future role.
(Source: Stanford HAI – Stanford University)
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the biggest change in Shell’s AI strategy for 2025-2026?
The biggest change is a shift from using AI primarily for internal optimization to a dual-pronged strategy. In addition to improving its own legacy operations, Shell is now positioning itself as a critical enabler of the AI-driven economy by selling products and energy directly to the AI sector, such as immersion cooling fluids and renewable power for data centers.
How is Shell using AI to improve its traditional oil and gas operations?
Shell uses AI extensively to enhance efficiency in its core business. Its most prominent project is a predictive maintenance program, scaled with C3 AI to over 10,000 pieces of equipment globally, which has reduced unplanned downtime by up to 20%. The company is also co-developing advanced “agentic AI” with SLB to assist upstream technical experts in complex decision-making.
In what new ways is Shell generating revenue directly from the AI industry?
Shell is creating new revenue streams by directly serving the AI sector’s needs in three main ways: 1) Selling enabling hardware technologies like the Shell DLC Fluid S3, an immersion cooling liquid for data centers. 2) Supplying renewable energy to power AI infrastructure, as seen in its agreement with Google. 3) Co-developing and commercializing software, such as its machine vision tool integrated with Yokogawa’s robotics platform.
Who are Shell’s most important AI partners and what are they doing?
The analysis highlights several key partners. For 2025-2026, the most strategic are: SLB (co-developing agentic AI for upstream experts), Google (supplying renewable energy for its AI data centers), Yokogawa (commercializing Shell’s machine vision tool for robotic maintenance), and NVIDIA (providing the framework for Shell to build its own custom LLMs).
How is Shell funding its large-scale AI projects?
Shell’s AI initiatives are supported by a substantial annualized capital expenditure of approximately $21 billion, which funds digital transformation across its assets. Additionally, a dedicated investment of $10-15 billion is allocated for low-carbon solutions, which explicitly includes funding for AI-powered projects like grid optimization.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks- From Breakout Growth to Operational Crossroads
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

