Toshiba’s Green Hydrogen Strategy for 2025-2026: Key Partnerships Driving Commercial Scale
In the competitive clean energy market, understanding a company’s strategic direction is crucial for investors and executives. Enki, a leading research platform, has analyzed millions of data points to reveal how major players are positioning themselves. This report focuses on Toshiba’s targeted strategy in the green hydrogen sector, leveraging deep analysis of its commercial activities from 2021 to today.
Toshiba Green Hydrogen Projects Signal Shift from R&D to Commercial Application
Toshiba is systematically advancing its green hydrogen business from internal research and development toward commercial-scale production and application through targeted industry partnerships.
- Between 2021-2024, Toshiba’s focus was on foundational technology, highlighted by the 2022 development of a production method for electrolysis electrodes that slashed iridium use by 90%, directly addressing a critical cost and supply chain barrier for PEM electrolyzers.
- A significant strategic shift occurred from 2024 onwards, moving from component innovation to full-stack collaboration, as shown by the November 2024 strategic cooperation agreement with Bekaert to jointly produce and sell Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEAs) on a global scale.
- The company is now targeting high-value, future-facing applications, demonstrated by its October 2024 partnership with Airbus to co-develop a two-megawatt superconducting motor for hydrogen-powered aircraft, moving beyond terrestrial energy into clean aviation.
- Further evidence of commercial application is the November 2024 joint development with Nimbus to create a next-generation pure hydrogen fuel cell stack, combining Toshiba’s commercialization experience with specialized technology to target specific market segments.
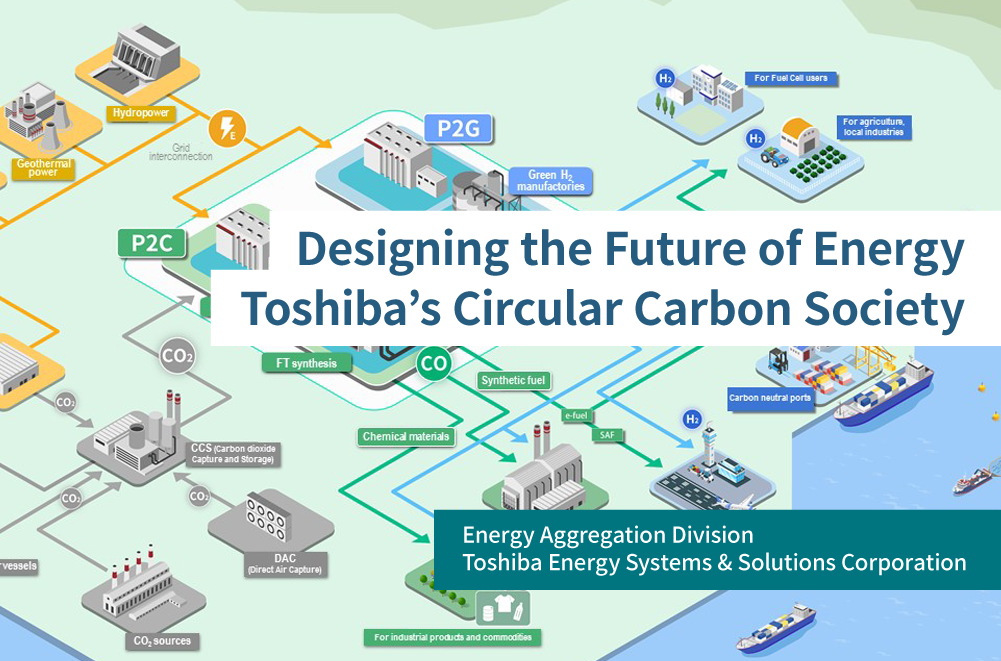
Toshiba Visualizes Its Hydrogen Ecosystem
The diagram illustrates the commercial application of green hydrogen across industries, directly matching the section’s focus on Toshiba’s shift from R&D to commercial-scale use.
(Source: Toshiba Clip)
Toshiba’s Strategic Capital Fuels Energy Infrastructure and Semiconductor Dominance
Toshiba is directing substantial capital into its foundational energy infrastructure and power semiconductor businesses, creating the enabling ecosystem required to support and scale its green hydrogen ambitions.
- The company’s revitalization plan, backed by a $13.5 billion take-private buyout by Japan Industrial Partners (JIP) in 2023, set the stage for focused, long-term investments in core growth areas like clean energy.
- A critical investment is the JPY 125 billion (approx. $850 million) commitment announced in December 2023 to more than double its power semiconductor production, which is essential for managing power flows in both hydrogen electrolyzers and the electric grids they connect to.
- To support the grid infrastructure needed for integrating large-scale renewables that power green hydrogen production, Toshiba announced a JPY 10 billion investment in July 2024 to expand its power transmission and distribution (T&D) equipment capacity in India.
- This is part of a broader $640 million investment strategy revealed in June 2024 to achieve a target of doubling the operating profit of its energy and infrastructure business by March 2027, with semiconductors and grid solutions as primary drivers.

Toshiba’s Tech Revenue Shows Growth
This chart’s depiction of growing tech revenue aligns with the section’s theme of strategic capital investment driving growth in areas like power semiconductors.
(Source: ElectroIQ)
Table: Toshiba’s Key Strategic Investments Post-2023
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Semiconductor Expansion | December 2023 | Announced a JPY 125 billion investment to more than double power chip production capacity. These components are critical for EVs, grid modernization, and efficient operation of hydrogen electrolyzers. | Reuters |
| Energy & Infrastructure Business Growth | June 2024 | Committed $640 million to grow its energy and infrastructure business, with a goal to double operating profit by March 2027. This capital underpins the expansion of hydrogen-enabling technologies. | Nikkei Asia |
| India T&D Capacity Expansion | July 2024 | Invested JPY 10 billion to increase production capacity for power transmission and distribution (T&D) equipment in India, strengthening the grid infrastructure needed for large-scale renewable energy integration. | Toshiba India |
| Japan Industrial Partners (JIP) Buyout | December 2023 | A $13.5 billion take-private buyout was completed, providing Toshiba with a stable ownership structure to pursue long-term strategic initiatives in core areas, including clean energy and hydrogen. | Leaders League |
Toshiba’s Hydrogen Partnerships Create a Path to Global Market Leadership
Toshiba is constructing a global green hydrogen ecosystem through a network of strategic partnerships that combine its core technology with the market access, scale, and application expertise of industry leaders.
- The November 2024 global cooperation agreement with Belgian technology group Bekaert is a cornerstone of its commercialization strategy, designed to scale up the production and sale of Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEAs) for the growing PEM electrolyzer market.
- In a move to enter the future clean aviation market, Toshiba partnered with Airbus in October 2024 to apply its advanced superconductivity research to the development of powerful, lightweight motors for hydrogen-fueled aircraft.
- The partnership with Nimbus announced in November 2024 demonstrates a focus on specific applications, targeting the development of a next-generation pure hydrogen fuel cell stack by integrating specialized partner technology with Toshiba’s mass-production capabilities.
- While not directly hydrogen, the July 2023 agreement with General Electric (GE) to establish a supply chain for offshore wind turbines in Japan is critical, as large-scale renewable power generation is the prerequisite for producing green hydrogen.

Toshiba’s Integrated Hydrogen Value Chain
This diagram of an integrated energy value chain visually represents the end-to-end ecosystem that Toshiba is building through the strategic partnerships discussed in the text.
(Source: Toshiba Asia Pacific | Press Release)
Table: Toshiba’s Strategic Green Hydrogen Partnerships
| Partner / Project | Time Frame | Details and Strategic Purpose | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bekaert | November 2024 | Finalized a global partnership to produce and sell Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEAs) for PEM electrolyzers, signaling a move from R&D to commercial-scale manufacturing of critical hydrogen components. | Toshiba Global |
| Nimbus | November 2024 | Entered a joint development agreement to create a next-generation pure hydrogen fuel cell stack, combining Toshiba’s manufacturing expertise with Nimbus’s specialized technology for targeted applications. | Toshiba Newsroom |
| Airbus | October 2024 | Formed a technology collaboration to co-develop a two-megawatt superconducting motor for hydrogen-powered aircraft, aiming to enter the high-value clean aviation market. | Airbus |
| General Electric (GE) | July 2023 | Announced plans to establish a domestic supply chain in Japan for offshore wind equipment, securing the renewable energy source necessary for large-scale green hydrogen production. | Reuters |
Toshiba Energy’s Global Hydrogen Footprint Expands from Japan to Europe
Toshiba Energy is executing a geographically focused hydrogen strategy, using Japan as its core R&D and manufacturing hub while forging key partnerships in Europe to access major industrial markets and co-develop next-generation applications.
- During the 2021-2024 period, Toshiba’s hydrogen activities were heavily centered in Japan, focusing on in-house R&D for foundational technologies like low-iridium electrodes and power semiconductors at its Japanese facilities.
- Since 2024, Toshiba’s geographic focus has expanded significantly into Europe, evidenced by its strategic agreements with Bekaert (Belgium) for electrolyzer components and Airbus (France/Europe) for hydrogen aviation technology.
- This “Hub and Spoke” model allows Toshiba to leverage its deep domestic engineering and manufacturing strengths in Japan while using European partners to tap into the continent’s aggressive decarbonization targets and established industrial ecosystems.
- The United States remains a key market for Toshiba’s broader energy business, particularly in grid infrastructure, but the primary nexus for its advanced hydrogen technology development and commercialization partnerships is currently the Japan-Europe axis.
Toshiba Energy Hydrogen Technology Reaches Commercial Readiness
Toshiba Energy’s green hydrogen technology has matured from the component-level research phase into a state of commercial readiness, validated by recent partnerships aimed at mass production and integration into real-world, high-value applications.
- The period between 2021-2024 was defined by R&D breakthroughs, most notably the October 2022 announcement of a technology to produce MEAs with a 90% reduction in iridium, solving a critical materials challenge at the lab and pilot scale.
- The technology’s maturity is validated by the shift in partnership focus from 2024 onwards; the agreement with Bekaert is not for research but for the global production and sale of MEAs, signaling a transition to commercial-scale manufacturing.
- Further proof of maturity is the move into application-specific engineering with the Airbus collaboration, which aims to develop a functional two-megawatt motor, moving beyond component efficiency to system integration for the demanding aerospace sector.
- The acquisition of the Eta PRO AI platform in 2021 provides a mature digital layer that can be applied to optimize the operation of green hydrogen production facilities, complementing the hardware advancements with proven operational intelligence.

Hydrogen Is Key to Net-Zero Goal
This chart positions hydrogen as a core pillar of Toshiba’s long-term strategy, providing the high-level context for why the technology’s ‘commercial readiness’ is a critical milestone.
(Source: Toshiba Clip)
SWOT Analysis: Assessing Toshiba Energy’s Position in the Hydrogen Market 2026
Toshiba Energy has leveraged its deep engineering strengths and strategic partnerships to build a formidable position in the green hydrogen market, though its success depends on executing these collaborations and navigating a competitive global landscape.
- Strengths are rooted in proprietary technology like its low-iridium MEAs and decades of experience in power electronics and large-scale manufacturing.
- Weaknesses include a potential reliance on partners for market access in key regions like Europe and the historical context of corporate restructuring which required significant internal focus.
- Opportunities are immense, driven by global decarbonization mandates and the potential to supply critical technology to nascent but high-growth sectors like clean aviation.
- Threats arise from intense global competition and the economic viability of green hydrogen, which is dependent on renewable energy costs and policy support.

Renewables Growth Fuels Hydrogen Market
This chart illustrates the growth in renewable energy, which is the foundational driver for the green hydrogen market, providing essential context for the ‘Opportunities’ in the section’s SWOT analysis.
(Source: POWER Magazine)
Table: SWOT Analysis for Toshiba Energy
| SWOT Category | 2021 – 2024 | 2025 – 2026 | What Changed / Resolved / Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Core competency in power electronics and R&D (e.g., low-iridium MEA development in 2022). Strong legacy in heavy industry and engineering. | Strategic partnerships with global leaders (Bekaert, Airbus). Commercial-ready technology validated by production agreements. Stabilized corporate structure post-JIP buyout. | The company validated its R&D by securing partnerships to commercialize it, transforming a theoretical strength into a market-facing one. |
| Weaknesses | Internal focus due to prolonged corporate turmoil and buyout discussions leading up to the 2023 deal. Technology was primarily in the R&D phase with limited commercial partnerships. | Reliance on partners for market access in key growth regions like Europe and in new application areas like aviation. Execution risk on new large-scale partnerships. | The corporate instability was resolved by the JIP buyout, but this created a new weakness: a dependency on executing partner-led growth strategies. |
| Opportunities | Growing global interest in green hydrogen. Initial partnerships with firms like GE for renewable energy infrastructure. | Entry into high-value, nascent markets like clean aviation (Airbus). Surging energy demand from AI data centers creates a massive market for clean, stable power. | The opportunity has evolved from general “green energy” to specific, high-margin applications like powering AI and aviation, which Toshiba is now directly targeting. |
| Threats | High cost and material constraints (e.g., iridium) for PEM electrolyzers. Global competition from other industrial giants. | Intensifying competition from specialized hydrogen startups and established energy players. Economic viability is still dependent on external factors like renewable energy prices. | Toshiba directly addressed the iridium threat with its technology, but the broader competitive and economic threats remain and have likely intensified as more players enter the market. |
2026 Outlook: Toshiba’s Hydrogen Strategy Hinges on Commercial Execution
The critical factor for Toshiba’s green hydrogen business in 2026 will be its ability to transition its strategic partnerships, particularly with Bekaert and Airbus, from agreements into tangible commercial production and technology demonstrators.
- The primary indicator to watch is the operational progress of the Bekaert collaboration. Moving from an Mo U to a functioning, large-scale MEA production line will be the ultimate validation of Toshiba’s commercial strategy and technological readiness.
- Milestones from the Airbus partnership, such as the successful testing of a prototype superconducting motor, will be crucial in demonstrating the viability of Toshiba’s technology for high-value, next-generation markets and securing a long-term competitive advantage.
- The successful deployment of its JPY 125 billion investment in power semiconductor capacity will directly impact its ability to supply the critical components needed for the entire hydrogen value chain, from electrolyzers to grid integration.
- Tracking these complex commercial activities, investments, and partnerships across different regions and technology stacks is essential for any professional navigating the energy transition. Platforms designed for deep competitive intelligence provide the necessary tools to monitor these signals and inform strategic decisions in real-time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the core of Toshiba’s new green hydrogen strategy?
Toshiba’s strategy has shifted from internal research and development (R&D) to commercial-scale production and application. This is being achieved through targeted global partnerships, such as with Bekaert to mass-produce key components and with Airbus to develop high-value applications like hydrogen-powered aircraft.
Who are Toshiba’s key partners for commercializing its hydrogen technology?
Toshiba has several key partners, including Bekaert for the global production and sale of Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEAs), Airbus to co-develop a superconducting motor for hydrogen aircraft, Nimbus for creating a next-generation pure hydrogen fuel cell stack, and General Electric (GE) to help secure the renewable energy supply from offshore wind.
What specific technological breakthrough gives Toshiba an edge in the hydrogen market?
Toshiba’s key technological advantage is a production method developed in 2022 that reduces the use of iridium, a rare and expensive metal, by 90% in its electrolysis electrodes. This innovation directly addresses a critical cost and supply chain barrier for PEM electrolyzers, a core technology for producing green hydrogen.
How are Toshiba’s investments in semiconductors and grid infrastructure related to its hydrogen goals?
These investments create the enabling ecosystem for green hydrogen. The JPY 125 billion investment in power semiconductors provides essential components for managing power efficiently in hydrogen electrolyzers. Investments in grid infrastructure, like the expansion in India, are crucial for integrating the large-scale renewable energy sources required to produce green hydrogen.
What is the main challenge Toshiba faces in its hydrogen business leading into 2026?
According to the analysis, the critical challenge for Toshiba is execution. Its success hinges on its ability to transition its strategic partnerships, particularly with Bekaert and Airbus, from agreements into tangible commercial production and successful technology demonstrators. The company is also reliant on these partners for market access in key regions like Europe.
Experience In-Depth, Real-Time Analysis
For just $200/year (not $200/hour). Stop wasting time with alternatives:
- Consultancies take weeks and cost thousands.
- ChatGPT and Perplexity lack depth.
- Googling wastes hours with scattered results.
Enki delivers fresh, evidence-based insights covering your market, your customers, and your competitors.
Trusted by Fortune 500 teams. Market-specific intelligence.
Explore Your Market →One-week free trial. Cancel anytime.
Related Articles
If you found this article helpful, you might also enjoy these related articles that dive deeper into similar topics and provide further insights.
- E-Methanol Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Battery Storage Market Analysis: Growth, Confidence, and Market Reality(2023-2025)
- Carbon Engineering & DAC Market Trends 2025: Analysis
- Climeworks 2025: DAC Market Analysis & Future Outlook
- Bloom Energy SOFC 2025: Analysis of AI & Partnerships
Erhan Eren
Ready to uncover market signals like these in your own clean tech niche?
Let Enki Research Assistant do the heavy lifting.
Whether you’re tracking hydrogen, fuel cells, CCUS, or next-gen batteries—Enki delivers tailored insights from global project data, fast.
Email erhan@enkiai.com for your one-week trial.

